


7.1. The parameters
The initial goal of structure formation studies is to accurately
determine the fundamental parameters describing our Universe. So far
I've stressed the three inflationary parameters,
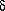 H, n
and r, which describe the initial perturbations which inflation
generates. However, except on very large scales where they remain
untouched by causal processes, we do not see the original perturbations
but rather than perturbations after they have been processed by a
variety of physical mechanisms. This processing depends on many
quantities, all of which must be either fixed by assumption or determined
from observations. A basic list features four categories; the global
dynamics, the way in which the matter content is divided amongst the
different particle species, astrophysics effects such as reionization
which would affect the microwave background photons, and the initial
perturbation spectrum that we are here assuming comes from inflation. A
possible list might look like this
H, n
and r, which describe the initial perturbations which inflation
generates. However, except on very large scales where they remain
untouched by causal processes, we do not see the original perturbations
but rather than perturbations after they have been processed by a
variety of physical mechanisms. This processing depends on many
quantities, all of which must be either fixed by assumption or determined
from observations. A basic list features four categories; the global
dynamics, the way in which the matter content is divided amongst the
different particle species, astrophysics effects such as reionization
which would affect the microwave background photons, and the initial
perturbation spectrum that we are here assuming comes from inflation. A
possible list might look like this
 B *
B *
 HDM
HDM
 (*)
(*)
 *
*
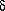 H(k =
a0H0) *
H(k =
a0H0) *
A cold dark matter contribution is not mentioned under matter content as it is assumed to take the value required to make the sums add up (i.e. to give the right spatial curvature k given the other matter densities).
In this list, I've starred those parameters which need to be included in even the most minimal model, while the rest can be set to some particular value by assumption. I've partially starred the cosmological constant because although most people would like to set it to zero, the observational case for a non-zero value is near to overwhelming.