

Adelman and Snijders (1974)
published a bibliography of atomic line identification lists which
supplemented
the material contained in the Ultraviolet and Revised Multiplet
Tables
(Moore 1945,
1950,
1952,
1962)
and in
Kelly and Palumbo (1973)
for the wavelength region
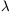
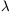 911-8250 and the first four
spectra of all elements.
Table I contains additional references
published for the most part after the first supplement
(Adelman 1978)
was completed. Some references are provided to higher spectra of
astrophysical interest. Each reference lists the
wavelength region covered and the type of paper: A = analysis, CL =
classified lines, EA = extension of analysis,
NMT = new multiplet table, RA = revised analysis, TC = temperature
classification, and W = line list. The
user is advised to examine the references to ascertain their qualities.
911-8250 and the first four
spectra of all elements.
Table I contains additional references
published for the most part after the first supplement
(Adelman 1978)
was completed. Some references are provided to higher spectra of
astrophysical interest. Each reference lists the
wavelength region covered and the type of paper: A = analysis, CL =
classified lines, EA = extension of analysis,
NMT = new multiplet table, RA = revised analysis, TC = temperature
classification, and W = line list. The
user is advised to examine the references to ascertain their qualities.
Since 1978 several publications of related interest have appeared, in particular Tables of Spectral Lines of Atoms and Ions (Striganov and Odintsova 1982), which contains all the spectra of hydrogen through neon, the first through sixth spectra of sodium through chlorine, and the first ten spectra of argon, and Atomic Emission Lines in the Near Ultraviolet: Hydrogen through Krypton (Kelly 1979), which complements Kelly and Palumbo (1973). The wavelength tables in Wavelengths and Transition Probabilities for Atoms and Atomic Ions (Reader et al. 1980) contain the strongest lines of the first five spectra of all elements. The first table of this publication, which is lines arranged by spectra, is included in the most recent editions of the CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (see e.g., Reader and Corliss 1982) and contains some lines which are in no other sources. Multiplet tables and atomic energy level compilations of O IV - O VIII are given by Moore (1979, 1980, 1983). Additional information on recent and current laboratory work in atomic spectroscopy is contained in Martin (1983).
This work was supported in part by a grant from The Citadel Development Foundation.