


5.4.2. Background Cosmological Surface ( ~ 8000 Gpc)
Another method to detect an intergalactic magnetic field is
based on the delay in arrival of secondary
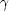 rays with
respect to primary
rays with
respect to primary
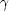 rays
from QSO and galaxies undergoing
outburts. The delay would be caused by the action of an
intergalactic magnetic field on the
electron cascades caused by the scattering of some
rays
from QSO and galaxies undergoing
outburts. The delay would be caused by the action of an
intergalactic magnetic field on the
electron cascades caused by the scattering of some
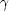 rays
(photon-photon collisions in the
cosmic background radiation, enabling particle pair productions).
The time delay is
proportional to B2. The question of whether such a
proposed model is practical deserves
further study. As an example, an intergalactic magnetic field of
10-16 Gauss might have been detected
(Plaga, 1995),
althought confirmation is needed (see
Kronberg, 1995).
rays
(photon-photon collisions in the
cosmic background radiation, enabling particle pair productions).
The time delay is
proportional to B2. The question of whether such a
proposed model is practical deserves
further study. As an example, an intergalactic magnetic field of
10-16 Gauss might have been detected
(Plaga, 1995),
althought confirmation is needed (see
Kronberg, 1995).
Is there a cosmological background screen ? A predicted
value of RM = 280 rad/m2 has come out of a recent model of
Kosowsky and Loeb (1996),
for a magnetic field of 10-9 Gauss,
for emission totally generated within the redshift range
900 < z < 1400, near the surface of
last scattering for the 2.7° K Cosmic Microwave Background
Radiation. Observations of the
CMB Radiation at 30 GHz with a 30' beamwidth is proposed. For
H0 = 50 km/s/Mpc, q0 = 1, then such
a z 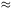 1400
corresponds to a distance of about 8 400 Gpc (= 8.4 Teraparsecs).
1400
corresponds to a distance of about 8 400 Gpc (= 8.4 Teraparsecs).