Copyright © 1990 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved
| Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1990. 28:
37-70 Copyright © 1990 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved |
2.1.3
Most NIR photometry is at the Johnson filters J (1.25
µm), H (1.65 µm),
and K (2.2 µm). Whittet
(166)
tabulates E (J - H) / E (H - K) as
determined by several studies, in diffuse dust and outer-cloud dust alike,
and finds them to be consistent with the value E (J - H) / E (H - K)
= 1.61 ± 0.04. Koornneef
(87)
considered a large body of data and suggests
an extinction law which has a value of 1.70 for this ratio. Jones and
Hyland
(79)
also concluded that NIR extinction is the same for
both diffuse dust and outer-cloud dust, although they found E (J - H)
/ E(H - K) = 2.09 ± 0.10. The constancy of their ratio between
lines of sight
through diffuse dust and outer-cloud dust is more significant than the
difference in the numerical value itself, which depends upon reduction
to a standard photometric system.
The NIR extinction law is well fitted by the form A(
The constancy of the NIR extinction law implies that the size
distributions of the largest particles are almost the same in all
directions. This conclusion was also reached
(111)
on the basis of the interstellar polarization law, which involves only the
largest particles.
2.1.4.
2.1.5.
In the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), there are almost no
suitably
reddened stars. In general there seems to be a low value of
RV, almost no bump, and a very steep far-UV rise
(11,
121),
as might be expected from a small RV. One star, though,
shows an extinction law similar to the Galaxy
(96).
The N(H) / E (B - V) is 4.5 x 1022 atoms
mag-1, about 10 times galactic and
consistent with the gaseous C abundance in the SMC
(104).
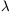 ) / A(J) = (
) / A(J) = (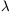 /1.25 µm)-
/1.25 µm)- . Recent values of
. Recent values of  are 1.70 ± 0.08
(166);
1.61
(136);
1.75
(37),
and ~ 1.8
(108).
The value 1.70 seems a reasonable compromise for both diffuse dust and
outer-cloud dust and implies that E (J - H) / E (H - K) ~ 1.6.
are 1.70 ± 0.08
(166);
1.61
(136);
1.75
(37),
and ~ 1.8
(108).
The value 1.70 seems a reasonable compromise for both diffuse dust and
outer-cloud dust and implies that E (J - H) / E (H - K) ~ 1.6.
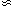 3.2 ±
0.2, virtually Galactic
(24,
86,
119).
For the UV, the stars near the giant H II
region 30 Doradus have weak bumps and extinctions rising steeply at the
shortest IUE wavelengths, a behavior unfortunately known as ``the
LMC
extinction law''. However, the stars well away from
30 Doradus (> 500 pc
projected distance), spread throughout the galaxy, have approximately
galactic extinction laws
(24,
53).
The N(H) / E (B - V) is 2 x 1022 atoms
mag-1
(86,
53),
about four times the Galactic value
(9)
and about proportional to the gaseous carbon abundance in the
LMC.
3.2 ±
0.2, virtually Galactic
(24,
86,
119).
For the UV, the stars near the giant H II
region 30 Doradus have weak bumps and extinctions rising steeply at the
shortest IUE wavelengths, a behavior unfortunately known as ``the
LMC
extinction law''. However, the stars well away from
30 Doradus (> 500 pc
projected distance), spread throughout the galaxy, have approximately
galactic extinction laws
(24,
53).
The N(H) / E (B - V) is 2 x 1022 atoms
mag-1
(86,
53),
about four times the Galactic value
(9)
and about proportional to the gaseous carbon abundance in the
LMC.