


4.2.4. Cosmic Ray Detection
If low-energy cosmic ray events were left unidentified in WFPC2 data,
we would unintentionally include the signal from those events in the
inferred background level. Figure 6 shows the
total number of cosmic ray events as a function of total flux, peak
flux, and affected pixels per event. In each histogram, the number of
cosmic ray events falls off sharply well before cosmic rays would
become difficult to detect: both peak and total fluxes for cosmic ray
events are significantly higher than the mean level of the background
(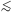 10 DN), and the
total number of pixels affected by a single
cosmic ray event rarely drops below three. We therefore conclude that
the cosmic ray removal process detects virtually all cosmic rays which
hit the chips.
10 DN), and the
total number of pixels affected by a single
cosmic ray event rarely drops below three. We therefore conclude that
the cosmic ray removal process detects virtually all cosmic rays which
hit the chips.