


4.7. Summary
In Table 5 we summarize the surface densities
measured (estimated) from the various search techniques described
above. We see that the nonoptical search techniques have very low
surface densities, most spectacularly for GRBs whose surface density is
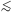 10 per year per
Hubble volume. The optical/near-IR techniques which are sensitive to
normal, star-forming galaxies typically have surface densities of a few
per square arcminute per unit redshift. In
Section 6 we
consider the biases in the different techniques and discuss how
independent the methods may be.
10 per year per
Hubble volume. The optical/near-IR techniques which are sensitive to
normal, star-forming galaxies typically have surface densities of a few
per square arcminute per unit redshift. In
Section 6 we
consider the biases in the different techniques and discuss how
independent the methods may be.
| Technique | z Range | Sources arcmin-2 | Limiting Flux Density | Reference |
| Radio sources... | All | 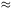 0.03 0.03 |
S1.4 GHz > 1 mJy | 1 |
| Submillimeter galaxies... | All | 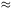 0.09 0.09 |
S850 µm > 2 mJy | 2 |
| X-ray sources... | All | 0.27 ± 0.04 | 10-15 ergs cm-2 s-1 | 3 |
| GRBs... | All | 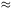 10-7 yr-1 10-7 yr-1 |
... | |
| Lyman-break galaxies... | ~ 3 | 0.68 ± 0.02 | RAB
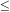 25.0 25.0 |
4 |
| Lyman-break galaxies... | ~ 4 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | IAB
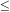 25.0 25.0 |
4 |
| Photometric candidates... | 4.5-5.5 | 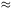 1.0 (unit-z)-1 1.0 (unit-z)-1 |
I814AB
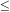 26.5 26.5 |
5 |
| Narrowband surveys, CADIS... | ~ 5.75 | 0.2 (unit-z)-1 | 5.0 × 10-17 ergs
cm-2 s-1
(5  ) ) |
6 |
| Narrowband surveys, Hawaii... | ~ 4.6 | 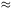 3 (unit-z)-1 3 (unit-z)-1 |
1.5 × 10-17 ergs
cm-2 s-1
(5  ) ) |
7 |
| Grism survey, NICMOS... | 0.7-1.9 | 0.5 | 2.0 × 10-17 ergs cm-2 s-1 | 8 |
| Serendip survey, Berkeley... | 4.5-5.5 | 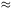 2 ± 1 (unit-z)-1 2 ± 1 (unit-z)-1 |
1.0 × 10-17 ergs
cm-2 s-1
(5  ) ) |
9 |
REFERENCES. - (1) Becker et al. 1995; (2) Hughes et al. 1998; (3) Hasinger et al. 1998; (4) Steidel et al. 1999; (5) Fernàndez-Soto et al. 1999; (6) Thommes et al. 1998; (7) Cowie & Hu 1998; (8) McCarthy et al. 1999; (9) Stern et al. 1999a. |
||||