


2.4 The 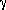 -ray
Continuum
-ray
Continuum
Until recently, the only QSO which had been detected in
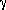 -rays was
3C 273.
76
However, the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory has detected
about 14 AGN so far, most of which are highly polarized compact radio
sources. 77 For
instance, the OVV 3C 279 has shown a luminosity
78 ~
1048 (
-rays was
3C 273.
76
However, the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory has detected
about 14 AGN so far, most of which are highly polarized compact radio
sources. 77 For
instance, the OVV 3C 279 has shown a luminosity
78 ~
1048 ( / 4
/ 4 ) erg s-1 between 100 MeV and
10 GeV, where
) erg s-1 between 100 MeV and
10 GeV, where  is the solid
angle. The apparent superluminal motion in this source should mean
that beaming is important. Thus,
is the solid
angle. The apparent superluminal motion in this source should mean
that beaming is important. Thus,  ~ 1 sr yields a
~ 1 sr yields a 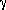 -ray luminosity ~
9 x 1046 erg s-1, which is still about one order
of magnitude higher
than the total emission in all other spectral bands. If this also
applies to other sources, the dominant radiation from jets may be
-ray luminosity ~
9 x 1046 erg s-1, which is still about one order
of magnitude higher
than the total emission in all other spectral bands. If this also
applies to other sources, the dominant radiation from jets may be
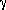 -rays.
-rays.
It is unclear at present how this radiation is produced. Pelletier
79
has argued that the jet should be composed of electron-positron pairs,
whose outflow rate would be ~ 10-3 M yr-1. The
Doppler-boost of the
luminosity then indicates a Lorentz factor
yr-1. The
Doppler-boost of the
luminosity then indicates a Lorentz factor 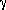 ~ 20. Maraschi et al.
80, 81
suggested that the entire IR to
~ 20. Maraschi et al.
80, 81
suggested that the entire IR to 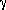 -ray spectrum of 3C 279 may be
explained in terms of an extended version of the inhomogeneous
relativistic jet model proposed by Ghisellini et al.,
82 and found a
Lorentz factor in the range 5-14. They also argued that
multiwavelength variability studies may yield information about jets
closer to the central engine than feasible with VLBI observations.
-ray spectrum of 3C 279 may be
explained in terms of an extended version of the inhomogeneous
relativistic jet model proposed by Ghisellini et al.,
82 and found a
Lorentz factor in the range 5-14. They also argued that
multiwavelength variability studies may yield information about jets
closer to the central engine than feasible with VLBI observations.
Sources with high-energy cutoffs in their 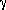 -ray spectra may be
used to constrain pair models. Fabian 33 concluded
that the evidence of
significant pair production in AGN seems weak at present.
-ray spectra may be
used to constrain pair models. Fabian 33 concluded
that the evidence of
significant pair production in AGN seems weak at present.