


2.4. Sizes
Little is known about the detailed structure of the clusters. Even with
the superior optics of the refurbished
HST, the two
SSCs in the
relatively nearby galaxy NGC 1569 (d
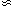 2.5 Mpc) still remain unresolved
(Leitherer, these proceedings). Given these limitations, it is impossible to
characterize the size of the clusters by conventional parameters such as the
core or tidal
radius. Instead, the observationally most straightforward parameter is the
half-light radius (Rh), sometimes also referred to as
the effective radius. Rh also has the advantage of
being relatively insensitive to evolutionary or environmental effects
(van den Bergh, Morbey,
& Pazder 1991).
Unfortunately, even such a simple parameter is difficult to determine with
accuracy. As discussed by
Meurer et al. (1995),
the measurement of cluster
radii from HST
images is complicated by severe crowding and background
confusion in many cases, rendering the sizes highly uncertain for galaxies
more distant than a few Mpc. Meurer et al. note a tendency to systematically
overestimate the sizes of distant clusters located on high-surface
brightness backgrounds. In view of these caveats, the half-light radii of
well-resolved SSCs seem to fall comfortably within the range of Galactic
globular clusters, whose median Rh
2.5 Mpc) still remain unresolved
(Leitherer, these proceedings). Given these limitations, it is impossible to
characterize the size of the clusters by conventional parameters such as the
core or tidal
radius. Instead, the observationally most straightforward parameter is the
half-light radius (Rh), sometimes also referred to as
the effective radius. Rh also has the advantage of
being relatively insensitive to evolutionary or environmental effects
(van den Bergh, Morbey,
& Pazder 1991).
Unfortunately, even such a simple parameter is difficult to determine with
accuracy. As discussed by
Meurer et al. (1995),
the measurement of cluster
radii from HST
images is complicated by severe crowding and background
confusion in many cases, rendering the sizes highly uncertain for galaxies
more distant than a few Mpc. Meurer et al. note a tendency to systematically
overestimate the sizes of distant clusters located on high-surface
brightness backgrounds. In view of these caveats, the half-light radii of
well-resolved SSCs seem to fall comfortably within the range of Galactic
globular clusters, whose median Rh 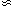 3 pc
(van den Bergh et
al. 1991).
The apparent tendency for the Rh distribution of SSCs
to be skewed toward somewhat larger sizes is probably not significant for the
reasons mentioned above
(Meurer et al. 1995).
In particular,
Meurer (1995)
has shown that the large radii reported by
Whitmore et
al. (1993) for the
clusters in the Antennae have probably been overestimated, thus obviating
van den Bergh's (1995)
other major objection to the young globular cluster
hypothesis for the SSCs in this system.
3 pc
(van den Bergh et
al. 1991).
The apparent tendency for the Rh distribution of SSCs
to be skewed toward somewhat larger sizes is probably not significant for the
reasons mentioned above
(Meurer et al. 1995).
In particular,
Meurer (1995)
has shown that the large radii reported by
Whitmore et
al. (1993) for the
clusters in the Antennae have probably been overestimated, thus obviating
van den Bergh's (1995)
other major objection to the young globular cluster
hypothesis for the SSCs in this system.
The compact sizes of SSCs can be used as supporting evidence that the clusters are most likely gravitationally bound. Any conceivable form of perturbation that may lead to the dispersal of the stars will traverse the clusters on a timescale shorter than 1 Myr, whereas the estimated ages are in some cases up to two orders of magnitude larger.