


Based on the agreement between the z 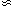 3 and z
3 and z
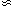 4 luminosity
functions at the bright end, it has been recently argued
[58] that
the decline in the luminosity density of faint HDF Lyman-break galaxies
observed in the same redshift interval
[38]
may not be real, but simply
due to sample variance in the HDF. When extinction corrections are applied,
the emissivity per unit comoving volume due to star formation may then
remain essentially flat for all redshift z
4 luminosity
functions at the bright end, it has been recently argued
[58] that
the decline in the luminosity density of faint HDF Lyman-break galaxies
observed in the same redshift interval
[38]
may not be real, but simply
due to sample variance in the HDF. When extinction corrections are applied,
the emissivity per unit comoving volume due to star formation may then
remain essentially flat for all redshift z 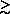 1 (see
Fig. 2). While this
has obvious implications for hierarchical models of structure formation,
the epoch of first light, and the reionization of the intergalactic medium
(IGM), it is also interesting to speculate on the possibility of a constant
star-formation density at all epochs 0
1 (see
Fig. 2). While this
has obvious implications for hierarchical models of structure formation,
the epoch of first light, and the reionization of the intergalactic medium
(IGM), it is also interesting to speculate on the possibility of a constant
star-formation density at all epochs 0 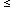 z
z 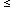 5, as recently
advocated by
[47].
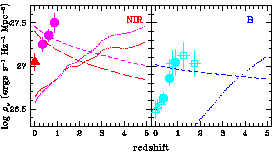
Figure 3 shows the time
evolution of the blue and near-IR
rest-frame luminosity density of a stellar population characterized by a
Salpeter IMF, solar metallicity, and a (constant) star-formation rate of
5, as recently
advocated by
[47].
Figure 3 shows the time
evolution of the blue and near-IR
rest-frame luminosity density of a stellar population characterized by a
Salpeter IMF, solar metallicity, and a (constant) star-formation rate of
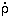 * = 0.054 M
* = 0.054 M yr-1 Mpc-3 (needed to produce
the observed EBL). The predicted evolution
appears to be a poor match to the observations: it overpredicts the
local B and K-band luminosity densities, and underpredicts the 1
µm
emissivity at z
yr-1 Mpc-3 (needed to produce
the observed EBL). The predicted evolution
appears to be a poor match to the observations: it overpredicts the
local B and K-band luminosity densities, and underpredicts the 1
µm
emissivity at z 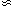 1
from the CFRS survey. (2)
1
from the CFRS survey. (2)
|
Figure 3. Left: Synthetic evolution
of the near-IR luminosity density at rest-frame wavelengths of 1.0
(long-dashed line) and 2.2
µm (short-dashed line). The model assumes a constant
star-formation rate of
|
At the other extreme, we know from stellar population studies that about half
of the present-day stars are contained in spheroidal systems, i.e. elliptical
galaxies and spiral galaxy bulges, and that these stars formed early and
rapidly
[4].
The expected rest-frame blue and near-IR emissivity
of a simple stellar population with formation redshift
zon = 5 and
total mass density equal to the mass in spheroids observed today (see below)
is shown in Figure 3. HST-NICMOS deep
observations may be
able to test similar scenarios for the formation of elliptical galaxies at
early times.
2 The near-IR light is dominated by
near-solar mass evolved stars,
the progenitors of which make up the bulk of a galaxy's stellar mass, and is
more sensitive to the past star-formation history than the blue light.
Back.