Copyright © 1998 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved
| Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1998. 36:
17-55 Copyright © 1998 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved |
 stars.
Ap. J. 348:647-67
Bowers EJC, Meikle WPS, Geballe TR, Walton NA, and
Pinto PA, et al.1997. Infrared and optical spectroscopy of Type Ia
supernovae in the nebular phase.
MNRAS 290:663-79
Branch D. 1992. The Hubble constant from nickel
radioactivity in Type Ia supernovae.
Ap J. 392:35-40
Branch D. 1998. Early-time spectra of Type Ia
supernovae and the nature of the peculiar SN 1991T. In
Supernovae and Cosmology, ed. L Labhardt, B Bingelli, R
Buser. Schaub Druck: Sissach. In press
Branch D, Doggett JB, Nomoto K, and Thielemann
F-K. 1985. Accreting white dwarf models for Type I supernovae. IV. The
optical spectra of carbon deflagration supernovae.
Ap. J. 294:619-25
Branch D, Drucker W, and Jeffery
DJ. 1988. Differences among expansion velocities of Type Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 330:L117-18
Branch D, Fisher A, Baron E, and Nugent
P. 1996a. On van den Bergh's method for measuring the Hubble constant
from Type Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 470:L7-L9
Branch D, Fisher A, Herczeg TH, Miller DL, and
Nugent P. 1994. The distance to the Type Ia supernova 1972E and its
parent galaxy NGC 5253: a prediction.
Ap. J. Lett. 421:L87-L90
Branch D, Fisher A, and Nugent P. 1993. On the
relative frequencies of spectroscopically normal and peculiar Type Ia
supernovae.
Astron. J. 106:2383-91
Branch D, Livio M, Yungelson LR, Boffi FR, and
Baron E. 1995. In search of the progenitors of Type Ia supernovae.
Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 107:1019-29
Branch D, Nugent P, and Fisher A. 1997. Type Ia
supernovae as extragalactic distance indicators. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al 1997b, pp. 715-34
Branch D, Romanishin W, and Baron
E. 1996b. Statistical connections between the properties of Type Ia
supernovae and the B - V colors of their parent galaxies,
and the value of H0.
Ap. J. 465:73-78
Branch D, and Tammann GA. 1992. Type Ia supernovae
as standard candles.
Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 30:359-89
Branch D, and van den Bergh S. 1993. Spectroscopic
differences between supernovae of Type Ia in early-type and in late-type
galaxies.
Astron. J. 105:2231-35
Cappellaro E, Mazzali PA, Benetti S, Danziger IJ,
and Turatto M, et al.1998. SN Ia light curves and radioactive decay.
Astron. Astrophys. 328:203-10
Chiosi C, Wood PR, and Capitanio
N. 1993. Theoretical models of Cepheid variables and their colors and
magnitudes.
Ap. J. Suppl. 86:541-98
Colgate SA, Fryer CL, and Hand KP. 1997. Low mass
SNe Ia and the late light curve. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al 1997b, pp. 273-302
Cristiani S, Cappellaro E, Turatto M, Bergeron J,
and Bues I, et al.1992. The SN 1986G in Centaurus A.
Astron. Astrophys. 259:63-70
Cumming RJ, Lundqvist P, Smith LJ, Pettini M, and
King DL. 1996. Circumstellar
H
stars.
Ap. J. 348:647-67
Bowers EJC, Meikle WPS, Geballe TR, Walton NA, and
Pinto PA, et al.1997. Infrared and optical spectroscopy of Type Ia
supernovae in the nebular phase.
MNRAS 290:663-79
Branch D. 1992. The Hubble constant from nickel
radioactivity in Type Ia supernovae.
Ap J. 392:35-40
Branch D. 1998. Early-time spectra of Type Ia
supernovae and the nature of the peculiar SN 1991T. In
Supernovae and Cosmology, ed. L Labhardt, B Bingelli, R
Buser. Schaub Druck: Sissach. In press
Branch D, Doggett JB, Nomoto K, and Thielemann
F-K. 1985. Accreting white dwarf models for Type I supernovae. IV. The
optical spectra of carbon deflagration supernovae.
Ap. J. 294:619-25
Branch D, Drucker W, and Jeffery
DJ. 1988. Differences among expansion velocities of Type Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 330:L117-18
Branch D, Fisher A, Baron E, and Nugent
P. 1996a. On van den Bergh's method for measuring the Hubble constant
from Type Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 470:L7-L9
Branch D, Fisher A, Herczeg TH, Miller DL, and
Nugent P. 1994. The distance to the Type Ia supernova 1972E and its
parent galaxy NGC 5253: a prediction.
Ap. J. Lett. 421:L87-L90
Branch D, Fisher A, and Nugent P. 1993. On the
relative frequencies of spectroscopically normal and peculiar Type Ia
supernovae.
Astron. J. 106:2383-91
Branch D, Livio M, Yungelson LR, Boffi FR, and
Baron E. 1995. In search of the progenitors of Type Ia supernovae.
Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 107:1019-29
Branch D, Nugent P, and Fisher A. 1997. Type Ia
supernovae as extragalactic distance indicators. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al 1997b, pp. 715-34
Branch D, Romanishin W, and Baron
E. 1996b. Statistical connections between the properties of Type Ia
supernovae and the B - V colors of their parent galaxies,
and the value of H0.
Ap. J. 465:73-78
Branch D, and Tammann GA. 1992. Type Ia supernovae
as standard candles.
Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 30:359-89
Branch D, and van den Bergh S. 1993. Spectroscopic
differences between supernovae of Type Ia in early-type and in late-type
galaxies.
Astron. J. 105:2231-35
Cappellaro E, Mazzali PA, Benetti S, Danziger IJ,
and Turatto M, et al.1998. SN Ia light curves and radioactive decay.
Astron. Astrophys. 328:203-10
Chiosi C, Wood PR, and Capitanio
N. 1993. Theoretical models of Cepheid variables and their colors and
magnitudes.
Ap. J. Suppl. 86:541-98
Colgate SA, Fryer CL, and Hand KP. 1997. Low mass
SNe Ia and the late light curve. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al 1997b, pp. 273-302
Cristiani S, Cappellaro E, Turatto M, Bergeron J,
and Bues I, et al.1992. The SN 1986G in Centaurus A.
Astron. Astrophys. 259:63-70
Cumming RJ, Lundqvist P, Smith LJ, Pettini M, and
King DL. 1996. Circumstellar
H from SN 1994D and
future Type Ia supernovae: an observational test of progenitor models.
MNRAS 283:1355-60
Della Valle M, and Panagia N. 1992. Type Ia
supernovae in late type galaxies: reddening correction, scale height,
and absolute maximum magnitude.
Astron. J. 104:696-703
Eastman RG. 1997. Radiation transport in Type Ia
supernovae. See Ruiz-Lapuente et al
1997b, pp. 571-88
Eck C, Cowan JJ, Roberts D, Boffi FR, and Branch
D. 1996. Radio observations of the Type Ia supernova 1986G as a test of
a symbiotic-star progenitor.
Ap. J. Lett. 451:L53-L55
Feast MW, and Catchpole RM. 1997. The Cepheid
period-luminosity zero-point from Hipparcos trigonometrical parallaxes.
MNRAS 286:L1-L5
Filippenko AV. 1997. Optical spectra of supernovae.
Annu. Rev.
Astron. Astrophys. 35:309-55
Filippenko AV, Richmond MW, Branch D, Gaskell CM,
and Herbst W,
et al.1992a. The subluminous, spectroscopically peculiar Type Ia
supernova 1991bg in the elliptical galaxy NGC 4374.
Astron. J. 104:1543-55
Filippenko AV, Richmond MW, Matheson T, Shields JC,
and Burbidge EM, et al.1992b. The peculiar Type Ia SN 1991T:
detonation of a white dwarf?
Ap. J. 384:L15-L18
Fisher A, Branch D, Höflich PA, and Khokhlov
A. 1995. The minimum ejection velocity of calcium in Type Ia supernovae
and the value of the Hubble constant.
Ap. J. Lett. 447:L73-L76
Fisher A, Branch D, Nugent P, and Baron
E. 1997. Evidence for a high-velocity carbon-rich layer in the Type Ia
SN 1990N.
Ap. J. Lett. 481:L89-L92
Freedman WL. 1997. Determination of the Hubble
constant. In
Critical Dialogues in Cosmology, ed. N Turok,
pp. 92-129. Singapore: World Sci.
Freedman WL, Madore BF, and Kennicutt
RC. 1997. Hubble Space Telescope key project on the extragalactic
distance scale. See
Livio et al, 1997, pp. 171-85
Garnavich PM, Kirshner RP, Challis P, Tonry J, and
Gilliland RL, et al.1998. Constraints on cosmological models from
Hubble Space Telescope observations of high-z supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. In press
Goldhaber G, Deustra S, Gabi S, Groom DE, and Hook I,
et al.1997. Observations of cosmological time dilation using Type
Ia supernovae as clocks. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al, 1997b, pp. 777-84
Gómez G, López R, and Sánchez F.
1996. The Canarias Type Ia supernova archive.
Astron. J. 112:2094-109
Gould A. 1994. The metallicity dependence of
inferred Cepheid distances.
Ap. J. 426:542-52
Hachisu I, Kato M, and Nomoto K. 1996. A new model
for progenitor systems of Type Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 470:L97-100
Hamuy M, Maza J, Phillips MM, Suntzeff NB, and
Wischnjewsky M, et al.1993. The 1990 Calán/Tololo supernova
search.
Astron. J. 106:2392-407
Hamuy M, Phillips MM, Maza J, Suntzeff NB, and
Della Valle M, et al.1995a. SN 1992K: a twin to the subluminous
Type Ia SN 1991bg.
Astron. J. 108:2226-32
Hamuy M, Phillips MM, Maza J, Wischnjewsky M, and
Uomoto A, et al.1991. The optical light curves of SN 1980N and SN
1981D in NGC 1316 (Fornax A).
Astron. J. 102:208-17
Hamuy M, Phillips MM, Schommer RA, Suntzeff NB,
Maza J, and Avilés R. 1996a. The absolute luminosities of the
Calán/Tololo Type Ia supernovae.
Astron. J. 112:2391-97
Hamuy M, Phillips MM, Suntzeff NB, Schommer RA,
Maza J, and Avilés R. 1995b. A Hubble diagram of distant
supernovae.
Astron. J. 109:1-13
Hamuy M, Phillips MM, Suntzeff NB, Schommer RA,
Maza J, and Avilés R. 1996b. The Hubble diagram of the
Calán/Tololo Type Ia supernovae and the value of H0.
Astron. J. 112:2398-407
Hamuy M, Phillips MM, Suntzeff NB, Schommer RA, and
Maza J, et al.1996c. BVRI light curves for 29 Type Ia
supernovae.
Astron. J. 112:2408-37
Hamuy M, Phillips MM, Suntzeff NB, Schommer RA, and
Maza J, et al.1996d. The morphology of Type Ia supernova light
curves.
Astron. J. 112:2438-47
Harkness R.
1991a. A comparison of carbon deflagration models for SNe Ia. In
Supernovae, ed. SE Woosley, pp. 454-63. New York: Springer
Harkness R.
1991b. Type Ia supernovae. In SN 1987A and Other
Supernovae, ed. IJ Danziger, K Kjär, pp. 447-56. Dordrecht:
Kluwer
Hatano K, Deaton J, and Branch D.
1998. Ap. J. Lett. In press
Ho LC, and Filipppenko AV. 1995. Probing the
interstellar medium along the lines of site to supernovae 1994D and
1994I.
Ap. J.444:165-74; Erratum: 463:818
Höflich P. 1995. Analysis of the Type Ia
supernova 1994D.
Ap. J. 443:89-108
Höflich P, and Khokhlov A. 1996. Explosion
models for Type Ia supernovae: a comparison with observed light curves,
distances, H0, and q0.
Ap. J. 457:500-28
Höflich P, Khokhlov A, and Müller
E. 1992. Gamma-ray light curves and spectra of Type Ia supernovae.
Astron. Astrophys. 259:549-66
Höflich P, Khokhlov A, and Müller
E. 1993. Light curve models for Type Ia supernovae: physical
assumptions, their influence and validity.
Astron. Astrophys. 268:570-90
Höflich P, Khokhlov A, Wheeler JC, Nomoto K, and Thielemann F-K. 1997. Explosion models, light curves, spectra, and H
0. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al, 1997b, pp. 659-79
Höflich P, Khokhlov A, Wheeler JC, Phillips
MM, Suntzeff NB, and Hamuy M. 1996. Maximum brightness and postmaximum
decline of light curves of Type Ia supernovae: a comparison of theory
and observations.
Ap. J. 472:L81-L84
Iben II . 1997. Scenarios for Type Ia
supernovae. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al, 1997b, pp. 111-26
Iben II , and Tutukov AV. 1984. Supernovae of Type
I as end products of the evolution of binaries with components of
moderate initial mass (M
from SN 1994D and
future Type Ia supernovae: an observational test of progenitor models.
MNRAS 283:1355-60
Della Valle M, and Panagia N. 1992. Type Ia
supernovae in late type galaxies: reddening correction, scale height,
and absolute maximum magnitude.
Astron. J. 104:696-703
Eastman RG. 1997. Radiation transport in Type Ia
supernovae. See Ruiz-Lapuente et al
1997b, pp. 571-88
Eck C, Cowan JJ, Roberts D, Boffi FR, and Branch
D. 1996. Radio observations of the Type Ia supernova 1986G as a test of
a symbiotic-star progenitor.
Ap. J. Lett. 451:L53-L55
Feast MW, and Catchpole RM. 1997. The Cepheid
period-luminosity zero-point from Hipparcos trigonometrical parallaxes.
MNRAS 286:L1-L5
Filippenko AV. 1997. Optical spectra of supernovae.
Annu. Rev.
Astron. Astrophys. 35:309-55
Filippenko AV, Richmond MW, Branch D, Gaskell CM,
and Herbst W,
et al.1992a. The subluminous, spectroscopically peculiar Type Ia
supernova 1991bg in the elliptical galaxy NGC 4374.
Astron. J. 104:1543-55
Filippenko AV, Richmond MW, Matheson T, Shields JC,
and Burbidge EM, et al.1992b. The peculiar Type Ia SN 1991T:
detonation of a white dwarf?
Ap. J. 384:L15-L18
Fisher A, Branch D, Höflich PA, and Khokhlov
A. 1995. The minimum ejection velocity of calcium in Type Ia supernovae
and the value of the Hubble constant.
Ap. J. Lett. 447:L73-L76
Fisher A, Branch D, Nugent P, and Baron
E. 1997. Evidence for a high-velocity carbon-rich layer in the Type Ia
SN 1990N.
Ap. J. Lett. 481:L89-L92
Freedman WL. 1997. Determination of the Hubble
constant. In
Critical Dialogues in Cosmology, ed. N Turok,
pp. 92-129. Singapore: World Sci.
Freedman WL, Madore BF, and Kennicutt
RC. 1997. Hubble Space Telescope key project on the extragalactic
distance scale. See
Livio et al, 1997, pp. 171-85
Garnavich PM, Kirshner RP, Challis P, Tonry J, and
Gilliland RL, et al.1998. Constraints on cosmological models from
Hubble Space Telescope observations of high-z supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. In press
Goldhaber G, Deustra S, Gabi S, Groom DE, and Hook I,
et al.1997. Observations of cosmological time dilation using Type
Ia supernovae as clocks. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al, 1997b, pp. 777-84
Gómez G, López R, and Sánchez F.
1996. The Canarias Type Ia supernova archive.
Astron. J. 112:2094-109
Gould A. 1994. The metallicity dependence of
inferred Cepheid distances.
Ap. J. 426:542-52
Hachisu I, Kato M, and Nomoto K. 1996. A new model
for progenitor systems of Type Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 470:L97-100
Hamuy M, Maza J, Phillips MM, Suntzeff NB, and
Wischnjewsky M, et al.1993. The 1990 Calán/Tololo supernova
search.
Astron. J. 106:2392-407
Hamuy M, Phillips MM, Maza J, Suntzeff NB, and
Della Valle M, et al.1995a. SN 1992K: a twin to the subluminous
Type Ia SN 1991bg.
Astron. J. 108:2226-32
Hamuy M, Phillips MM, Maza J, Wischnjewsky M, and
Uomoto A, et al.1991. The optical light curves of SN 1980N and SN
1981D in NGC 1316 (Fornax A).
Astron. J. 102:208-17
Hamuy M, Phillips MM, Schommer RA, Suntzeff NB,
Maza J, and Avilés R. 1996a. The absolute luminosities of the
Calán/Tololo Type Ia supernovae.
Astron. J. 112:2391-97
Hamuy M, Phillips MM, Suntzeff NB, Schommer RA,
Maza J, and Avilés R. 1995b. A Hubble diagram of distant
supernovae.
Astron. J. 109:1-13
Hamuy M, Phillips MM, Suntzeff NB, Schommer RA,
Maza J, and Avilés R. 1996b. The Hubble diagram of the
Calán/Tololo Type Ia supernovae and the value of H0.
Astron. J. 112:2398-407
Hamuy M, Phillips MM, Suntzeff NB, Schommer RA, and
Maza J, et al.1996c. BVRI light curves for 29 Type Ia
supernovae.
Astron. J. 112:2408-37
Hamuy M, Phillips MM, Suntzeff NB, Schommer RA, and
Maza J, et al.1996d. The morphology of Type Ia supernova light
curves.
Astron. J. 112:2438-47
Harkness R.
1991a. A comparison of carbon deflagration models for SNe Ia. In
Supernovae, ed. SE Woosley, pp. 454-63. New York: Springer
Harkness R.
1991b. Type Ia supernovae. In SN 1987A and Other
Supernovae, ed. IJ Danziger, K Kjär, pp. 447-56. Dordrecht:
Kluwer
Hatano K, Deaton J, and Branch D.
1998. Ap. J. Lett. In press
Ho LC, and Filipppenko AV. 1995. Probing the
interstellar medium along the lines of site to supernovae 1994D and
1994I.
Ap. J.444:165-74; Erratum: 463:818
Höflich P. 1995. Analysis of the Type Ia
supernova 1994D.
Ap. J. 443:89-108
Höflich P, and Khokhlov A. 1996. Explosion
models for Type Ia supernovae: a comparison with observed light curves,
distances, H0, and q0.
Ap. J. 457:500-28
Höflich P, Khokhlov A, and Müller
E. 1992. Gamma-ray light curves and spectra of Type Ia supernovae.
Astron. Astrophys. 259:549-66
Höflich P, Khokhlov A, and Müller
E. 1993. Light curve models for Type Ia supernovae: physical
assumptions, their influence and validity.
Astron. Astrophys. 268:570-90
Höflich P, Khokhlov A, Wheeler JC, Nomoto K, and Thielemann F-K. 1997. Explosion models, light curves, spectra, and H
0. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al, 1997b, pp. 659-79
Höflich P, Khokhlov A, Wheeler JC, Phillips
MM, Suntzeff NB, and Hamuy M. 1996. Maximum brightness and postmaximum
decline of light curves of Type Ia supernovae: a comparison of theory
and observations.
Ap. J. 472:L81-L84
Iben II . 1997. Scenarios for Type Ia
supernovae. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al, 1997b, pp. 111-26
Iben II , and Tutukov AV. 1984. Supernovae of Type
I as end products of the evolution of binaries with components of
moderate initial mass (M 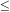 9
M
9
M ).
Ap. J. Suppl. 54:335-72
Jacoby GH, and Pierce MJ. 1996. Response to
Schaefer's comments on Pierce & Jacoby (1995) regarding the Type Ia
supernova
1937C. Astron. J. 112:723-31
Jeffery DJ, Leibundgut B, Kirshner RP, Benetti S,
Branch D, and Sonneborn G. 1992. Analysis of the photospheric epoch
spectra of Type Ia supernovae 1990N and 1991T
Ap. J. 397:304-28
Kennicutt RC, Stetson PB, Saha A, Kelson D, and
Rawson D, et al.
1998. The HST key project on the extragalactic distance scale
XIII. The metallicity dependence of the Cepheid distance
scale. Ap. J. In press
Khokhlov A, Müller E, and Höflich
P. 1993. Light curves of Type Ia supernova models with different
explosion mechanisms.
Astron. Astrophys. 270:223-48
Kim AG, Gabi S, Goldhaber G, Groom DE, and Hook IM,
et al.1997. Implications for the Hubble constant from the first
seven supernovae at z
).
Ap. J. Suppl. 54:335-72
Jacoby GH, and Pierce MJ. 1996. Response to
Schaefer's comments on Pierce & Jacoby (1995) regarding the Type Ia
supernova
1937C. Astron. J. 112:723-31
Jeffery DJ, Leibundgut B, Kirshner RP, Benetti S,
Branch D, and Sonneborn G. 1992. Analysis of the photospheric epoch
spectra of Type Ia supernovae 1990N and 1991T
Ap. J. 397:304-28
Kennicutt RC, Stetson PB, Saha A, Kelson D, and
Rawson D, et al.
1998. The HST key project on the extragalactic distance scale
XIII. The metallicity dependence of the Cepheid distance
scale. Ap. J. In press
Khokhlov A, Müller E, and Höflich
P. 1993. Light curves of Type Ia supernova models with different
explosion mechanisms.
Astron. Astrophys. 270:223-48
Kim AG, Gabi S, Goldhaber G, Groom DE, and Hook IM,
et al.1997. Implications for the Hubble constant from the first
seven supernovae at z
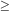 0.35.
Ap. J. Lett. 476:L63-66
Kirshner RP, Jeffery DJ, Leibundgut B, Sonneborn G,
and Phillips MM, et al.1993. SN 1992A: ultraviolet and optical
observations based on HST, IUE, and CTIO observations.
Ap. J. 415:589-615
Kochanek CS. 1997. Rebuilding the Cepheid distance
scale. I. A global analysis of Cepheid mean magnitudes.
Ap. J. 491:13-28
Leibundgut B, Kirshner RP, Filippenko AV, Shields
JC, and Foltz CB, et al.1991a. Premaxium observations of the Type
Ia SN 1990N.
Ap. J. Lett. 371:L23-26
Leibundgut B, Kirshner RP, Phillips MM, Wells LA,
and Suntzeff NB,
et al.1993. SN 1991bg: a Type Ia supernova with a difference.
Astron. J. 105:301-13
Leibundgut B, Schommer R, Phillips MM, Riess A, and
Schmidt B, et al.1996. Time dilation in the light curve of the
distant Type Ia supernova 1995K.
Ap. J. Lett. 466:L21-L24
Leibundgut B, Tammann GA, Cadonau R, and Cerrito
D. 1991b. Supernova studies. VII. An atlas of the light curves of
supernovae Type I.
Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. 89:537-79
Li X-D, and van den Heuvel EPJ. 1997. Evolution of
white dwarf binaries: supersoft X-ray sources and progenitors of Type Ia
supernovae.
Astron. Astrophys. 322:L9-12
Lira P.
1996. Light curves of the supernovae 1990N and 1991T. MS
thesis. Univ. Chile
Lira P, Suntzeff NB, Phillips MM, Hamuy M, and Maza J,
et al.1998. Optical light curves of the Type Ia supernovae 1990N
and 1991T.
Astron. J. 115:234-46
Liu W, Jeffery DJ, and Schultz DR. 1997a. Nebular
spectra of Type Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 483:L107-10
Liu W, Jeffery DJ, and Schultz DR. 1997b. Nebular
spectra of the unusual Type Ia supernova 1991T.
Ap. J. Lett. 486:L35-38
Liu W, Jeffery DJ, Schultz DR, Quinet P, Shaw J,
and Pindzola MS. 1997c. Emission from cobalt in type Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 489:L141-43
Livio M, Donahue M, and Panagia N, eds.
1997. The Extragalactic Distance Scale. Cambridge: Cambridge
Univ. Press
Livne E. 1990. Successive detonations in accreting
white dwarfs as an alternative mechanism for Type Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. 354:L53-55
Livne E, and Arnett WD. 1995. Explosions of
sub-Chandrasekhar mass white dwarfs in two dimensions.
Ap. J. 452:62-74
Lundqvist P, and Cumming RJ.
1997. Supernova progenitor constraints from circumstellar
interaction: Type Ia. In Advances in Stellar Evolution,
ed. RT Rood, A Renzini, pp. 293-97. Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press
Madore BF, and Freedman WL. 1991. The Cepheid
distance scale.
Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 103:933-57
Madore BF, and Freedman WL. 1998. Hipparcos
parallaxes and the Cepheid distance scale.
Ap. J. Lett.492:110-15
Mazzali PA, Chugai N, Turatto M, Lucy LB, and
Danziger IJ, et al.
1997. The properties of the peculiar Type Ia supernova 1991bg. II. The
amount of 56Ni and the total ejecta mass determined from
spectrum synthesis and energetics considerations.
MNRAS 284:151-71
Mazzali PA, Danziger IJ, and Turatto M. 1995. A
study of the properties of the peculiar SN Ia 1991T through models of
its evolving early-time spectra.
Astron. Astrophys. 297:509-34
Mazzali PA, Lucy LB, Danziger IJ, Gouiffes C,
Cappellaro E, and Turatto M. 1993. Models for the early-time spectral
evolution of the standard type Ia supernova 1990N.
Astron. Astrophys. 269:423-45
Meikle WPS, Cumming RJ, Geballe TR, Lewis JR, and
Walton NA, et al.1996. An early-time infrared and optical study
of the Type Ia supernovae 1994D and 1991T.
MNRAS 281:263-80
Milne PA, The L-S, and Leising MD.
1998. Is positron escape seen in the light curves of Type Ia supernovae?
Ap. J. In press
Minkowski R. 1939. The spectra of the supernovae in
IC 4182 and NGC 1003.
Ap. J. 89:156-217
Mochkovitch R, Guerrero J, and Segretain
L. 1997. The merging of white dwarfs. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al, 1997b, pp. 187-204
Mochkovitch R, and Livio M. 1990. The coalescence
of white dwarfs and Type I supernovae. The merged configuration.
Astron. Astrophys. 236:378-84
Nomoto K, Iwamoto K, Nakasato N, Thielemann F-K,
and Brachwitz F, et al.1997. Type Ia supernovae: progenitors and
constraints on nucleosynthesis. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al 1997b, pp. 349-78
Nomoto K, Thielemann F-K, and Yokoi
K. 1984. Accreting white dwarf models for Type Ia
supernovae. III. Carbon deflagration supernovae.
Ap. J. 286:644-58
Nugent P, Baron E, Branch D, Fisher A, and
Hauschildt PH. 1997. Synthetic spectra of hydrodynamical models of Type
Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. 485:812-19
Nugent P, Baron E, Hauschildt PH, and Branch
D. 1995a. Spectrum synthesis of the Type Ia supernovae 1992A and 1981B.
Ap. J. 441:L33-36
Nugent P, Branch D, Baron E, Fisher A, Vaughan TE,
and Hauschildt PH. 1995b. Low Hubble constant from the physics of Type
Ia supernovae.
Phys. Rev. Lett.75:394-97; Erratum: 75:1874
Nugent P, Phillips M, Baron E, Branch D, and
Hauschildt PH. 1995c. Evidence for a spectroscopic sequence among Type
Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 455:L147-50
Patat F, Barbon R, Cappellaro E, and Turatto
M. 1997. Revised photometry and color distribution of Type Ia supernovae
observed at Asiago in the seventies.
Astron. Astrophys. 317:423-31
Patat F, Benetti S, Cappellaro E, Danziger IJ, and
Della Valle M, et al.1996. The Type Ia suppernova 1994D in NGC
4526: the early phases.
MNRAS 278:111-24
Pauldrach AWA, Duschinger M, Mazzali PA, Puls J,
Lennon M, and Miller DL. 1996. NLTE models for synthetic spectra of Type
Ia supernovae.
Astron. Astrophys. 312:525-38
Perlmutter S, Aldering G, Della Valle M, Deustua S, and Ellis RS,
et al.1998. Discovery of a supernova explosion at half the age of
the Universe and its cosmological implications.
Nature 391:51-54
Perlmutter S, Deustua S, Goldhaber G, Groom D, and
Hook I, et al.
1997a. Supernovae. IAU Circ. No. 6621
Perlmutter S, Gabi S, Goldhaber S, Groom DE, and
Hook IM, et al.1997b. Measurements of the cosmological parameters
0.35.
Ap. J. Lett. 476:L63-66
Kirshner RP, Jeffery DJ, Leibundgut B, Sonneborn G,
and Phillips MM, et al.1993. SN 1992A: ultraviolet and optical
observations based on HST, IUE, and CTIO observations.
Ap. J. 415:589-615
Kochanek CS. 1997. Rebuilding the Cepheid distance
scale. I. A global analysis of Cepheid mean magnitudes.
Ap. J. 491:13-28
Leibundgut B, Kirshner RP, Filippenko AV, Shields
JC, and Foltz CB, et al.1991a. Premaxium observations of the Type
Ia SN 1990N.
Ap. J. Lett. 371:L23-26
Leibundgut B, Kirshner RP, Phillips MM, Wells LA,
and Suntzeff NB,
et al.1993. SN 1991bg: a Type Ia supernova with a difference.
Astron. J. 105:301-13
Leibundgut B, Schommer R, Phillips MM, Riess A, and
Schmidt B, et al.1996. Time dilation in the light curve of the
distant Type Ia supernova 1995K.
Ap. J. Lett. 466:L21-L24
Leibundgut B, Tammann GA, Cadonau R, and Cerrito
D. 1991b. Supernova studies. VII. An atlas of the light curves of
supernovae Type I.
Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. 89:537-79
Li X-D, and van den Heuvel EPJ. 1997. Evolution of
white dwarf binaries: supersoft X-ray sources and progenitors of Type Ia
supernovae.
Astron. Astrophys. 322:L9-12
Lira P.
1996. Light curves of the supernovae 1990N and 1991T. MS
thesis. Univ. Chile
Lira P, Suntzeff NB, Phillips MM, Hamuy M, and Maza J,
et al.1998. Optical light curves of the Type Ia supernovae 1990N
and 1991T.
Astron. J. 115:234-46
Liu W, Jeffery DJ, and Schultz DR. 1997a. Nebular
spectra of Type Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 483:L107-10
Liu W, Jeffery DJ, and Schultz DR. 1997b. Nebular
spectra of the unusual Type Ia supernova 1991T.
Ap. J. Lett. 486:L35-38
Liu W, Jeffery DJ, Schultz DR, Quinet P, Shaw J,
and Pindzola MS. 1997c. Emission from cobalt in type Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 489:L141-43
Livio M, Donahue M, and Panagia N, eds.
1997. The Extragalactic Distance Scale. Cambridge: Cambridge
Univ. Press
Livne E. 1990. Successive detonations in accreting
white dwarfs as an alternative mechanism for Type Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. 354:L53-55
Livne E, and Arnett WD. 1995. Explosions of
sub-Chandrasekhar mass white dwarfs in two dimensions.
Ap. J. 452:62-74
Lundqvist P, and Cumming RJ.
1997. Supernova progenitor constraints from circumstellar
interaction: Type Ia. In Advances in Stellar Evolution,
ed. RT Rood, A Renzini, pp. 293-97. Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press
Madore BF, and Freedman WL. 1991. The Cepheid
distance scale.
Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 103:933-57
Madore BF, and Freedman WL. 1998. Hipparcos
parallaxes and the Cepheid distance scale.
Ap. J. Lett.492:110-15
Mazzali PA, Chugai N, Turatto M, Lucy LB, and
Danziger IJ, et al.
1997. The properties of the peculiar Type Ia supernova 1991bg. II. The
amount of 56Ni and the total ejecta mass determined from
spectrum synthesis and energetics considerations.
MNRAS 284:151-71
Mazzali PA, Danziger IJ, and Turatto M. 1995. A
study of the properties of the peculiar SN Ia 1991T through models of
its evolving early-time spectra.
Astron. Astrophys. 297:509-34
Mazzali PA, Lucy LB, Danziger IJ, Gouiffes C,
Cappellaro E, and Turatto M. 1993. Models for the early-time spectral
evolution of the standard type Ia supernova 1990N.
Astron. Astrophys. 269:423-45
Meikle WPS, Cumming RJ, Geballe TR, Lewis JR, and
Walton NA, et al.1996. An early-time infrared and optical study
of the Type Ia supernovae 1994D and 1991T.
MNRAS 281:263-80
Milne PA, The L-S, and Leising MD.
1998. Is positron escape seen in the light curves of Type Ia supernovae?
Ap. J. In press
Minkowski R. 1939. The spectra of the supernovae in
IC 4182 and NGC 1003.
Ap. J. 89:156-217
Mochkovitch R, Guerrero J, and Segretain
L. 1997. The merging of white dwarfs. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al, 1997b, pp. 187-204
Mochkovitch R, and Livio M. 1990. The coalescence
of white dwarfs and Type I supernovae. The merged configuration.
Astron. Astrophys. 236:378-84
Nomoto K, Iwamoto K, Nakasato N, Thielemann F-K,
and Brachwitz F, et al.1997. Type Ia supernovae: progenitors and
constraints on nucleosynthesis. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al 1997b, pp. 349-78
Nomoto K, Thielemann F-K, and Yokoi
K. 1984. Accreting white dwarf models for Type Ia
supernovae. III. Carbon deflagration supernovae.
Ap. J. 286:644-58
Nugent P, Baron E, Branch D, Fisher A, and
Hauschildt PH. 1997. Synthetic spectra of hydrodynamical models of Type
Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. 485:812-19
Nugent P, Baron E, Hauschildt PH, and Branch
D. 1995a. Spectrum synthesis of the Type Ia supernovae 1992A and 1981B.
Ap. J. 441:L33-36
Nugent P, Branch D, Baron E, Fisher A, Vaughan TE,
and Hauschildt PH. 1995b. Low Hubble constant from the physics of Type
Ia supernovae.
Phys. Rev. Lett.75:394-97; Erratum: 75:1874
Nugent P, Phillips M, Baron E, Branch D, and
Hauschildt PH. 1995c. Evidence for a spectroscopic sequence among Type
Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 455:L147-50
Patat F, Barbon R, Cappellaro E, and Turatto
M. 1997. Revised photometry and color distribution of Type Ia supernovae
observed at Asiago in the seventies.
Astron. Astrophys. 317:423-31
Patat F, Benetti S, Cappellaro E, Danziger IJ, and
Della Valle M, et al.1996. The Type Ia suppernova 1994D in NGC
4526: the early phases.
MNRAS 278:111-24
Pauldrach AWA, Duschinger M, Mazzali PA, Puls J,
Lennon M, and Miller DL. 1996. NLTE models for synthetic spectra of Type
Ia supernovae.
Astron. Astrophys. 312:525-38
Perlmutter S, Aldering G, Della Valle M, Deustua S, and Ellis RS,
et al.1998. Discovery of a supernova explosion at half the age of
the Universe and its cosmological implications.
Nature 391:51-54
Perlmutter S, Deustua S, Goldhaber G, Groom D, and
Hook I, et al.
1997a. Supernovae. IAU Circ. No. 6621
Perlmutter S, Gabi S, Goldhaber S, Groom DE, and
Hook IM, et al.1997b. Measurements of the cosmological parameters
 and
and
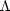 from the first
seven supernovae at z
from the first
seven supernovae at z
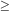 0.35.
Ap. J. 483:565-81
Phillips MM. 1993. The absolute magnitudes of Type
Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 413:L105-8
Phillips MM, Phillips AC, Heathcote SR, Blanco VM,
and Geisler D. 1987. The Type Ia supernova 1986G in NGC 5128: optical
photometry and spectroscopy.
Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 99:592-605
Phillips MM, Wells LA, Suntzeff NB, Hamuy M, and
Leibundgut B, et al.1992. SN 1991T: further evidence of the
heterogeneous nature of Type Ia supernovae.
Astron. J. 103:1632-37
Pierce MJ, and Jacoby GH. 1995. "New" B and
V photometry of the "old" Type Ia supernova 1937C: implications
for H0.
Astron. J. 110:2885-909
Pinto PA. 1997. Time dependence and the opacity of
Type Ia supernovae. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al, 1997b, pp. 607-25
Pskovskii YP. 1977. Brightness, color, and
expansion velocity of SNe I as functions of the rate of brightness
decline.
Sov. Astron. AJ. 21:675
Rappaport SA, Di Stefano R, and Smith
M. 1994. Formation and evolution of supersoft X-ray sources.
Ap. J. 426:692-703
Rasio FA, and Shapiro SL. 1995. Hydrodynamics of
binary coalescence. II. Polytropes with
0.35.
Ap. J. 483:565-81
Phillips MM. 1993. The absolute magnitudes of Type
Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 413:L105-8
Phillips MM, Phillips AC, Heathcote SR, Blanco VM,
and Geisler D. 1987. The Type Ia supernova 1986G in NGC 5128: optical
photometry and spectroscopy.
Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 99:592-605
Phillips MM, Wells LA, Suntzeff NB, Hamuy M, and
Leibundgut B, et al.1992. SN 1991T: further evidence of the
heterogeneous nature of Type Ia supernovae.
Astron. J. 103:1632-37
Pierce MJ, and Jacoby GH. 1995. "New" B and
V photometry of the "old" Type Ia supernova 1937C: implications
for H0.
Astron. J. 110:2885-909
Pinto PA. 1997. Time dependence and the opacity of
Type Ia supernovae. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al, 1997b, pp. 607-25
Pskovskii YP. 1977. Brightness, color, and
expansion velocity of SNe I as functions of the rate of brightness
decline.
Sov. Astron. AJ. 21:675
Rappaport SA, Di Stefano R, and Smith
M. 1994. Formation and evolution of supersoft X-ray sources.
Ap. J. 426:692-703
Rasio FA, and Shapiro SL. 1995. Hydrodynamics of
binary coalescence. II. Polytropes with
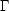 = 5/3.
Ap. J. 438:887-903
Renzini A. 1996. Searching for Type Ia
supernova progenitors. In
Supernovae and Supernova Remnants, ed. R McCray, Z Wang,
pp. 77-85. Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press
Richmond MW, Treffers RR, Filippenko AV, Van Dyk
SD, and Paik Y, et al.1995. UBVRI photometry of the Type
Ia SN 1994D in NGC 4526.
Astron. J. 109:2121-33
Riess AG.
1996. Type Ia supernova multicolor light curve shapes. PhD
thesis. Harvard Univ.
Riess AG, Davis M, Baker J, and Kirshner
RP. 1997a. The velocity field from Type Ia supernovae matches the
gravity field from galaxy surveys.
Ap. J. 488:L1-L5
Riess AG, Filippenko AV, Leonard DC, Schmidt BP,
and Suntzeff N, et al.1997b. Time dilation from spectral feature
age measurements of Type Ia supernovae.
Astron. J. 114:722-29
Riess AG, Nugent P, Filippenko AV, Kirshner RP,
and Perlmutter S. 1998. Snapshot distances to SNe Ia - all in "one"
night's work. Ap. J. In press
Riess AG, Press WH, and Kirshner RP. 1995a. Using
Type Ia supernova light curve shapes to measure the Hubble constant.
Ap. J. Lett. 438:L17-20
Riess AG, Press WH, and Kirshner
RP. 1995b. Determining the motion of the local group using Type Ia
supernova light curve shapes.
Ap. J. Lett. 445:L91-94
Riess AG, Press WH, and Kirshner RP. 1996a. A
precise distance indicator: Type Ia supernova multicolor light-curve
shapes.
Ap. J. 473:88-109
Riess AG, Press WH, and Kirshner RP. 1996b. Is the
dust obscuring supernovae in distant galaxies the same as the dust in
the Milky Way?
Ap. J. 473:588-94
Ruiz-Lapuente P. 1996. The Hubble constant from
56Co-powered nebular candles.
Ap. J. 465:L83-86
Ruiz-Lapuente P, Canal R, and Burkert
A. 1997a. SNe Ia: on the binary progenitors and expected statistics. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al 1997b, pp. 205-30
Ruiz-Lapuente P, Canal R, and Isern J, eds.
1997b. Thermonuclear Supernovae. Dordrecht: Kluwer
Ruiz-Lapuente P, Cappellaro E, Turatto M, Gouiffes
C, and Danziger IJ, et al.1992. Modeling the iron-dominated
spectra of the Type Ia supernova 1991T at premaximum.
Ap. J. Lett. 387:L33-36
Saha A, Labhardt L, Schwengeler H, Macchetto FD,
and Panagia N, et al.1994. Discovery of Cepheids in IC 4182:
absolute peak brightness of SN Ia 1937C and the value of
H0.
Ap. J. 425:14-34
Saha A, Sandage A, Labhardt L, Schwengeler H, and
Tammann GA, et al.1995. Discovery of Cepheids in NGC 5253:
absolute peak brightness of SNe Ia 1895B and 1972E and the value of
H0.
Ap. J. 438:8-26
Saha A, Sandage A, Labhardt L, Tammann GA,
Macchetto FD, and Panagia N. 1996a. Cepheid calibration of the peak
brightness of SNe Ia. V. SN 1981B in NGC 4536.
Ap. J. 466:55-91
Saha A, Sandage A, Labhardt L, Tammann GA,
Macchetto FD, and Panagia N. 1996b. Cepheid calibration of the peak
brightness of Type Ia supernovae. VI. SN 1960F in NGC 4496A.
Ap. J. Suppl. 107:693
Saha A, Sandage A, Labhardt L, Tammann GA,
Macchetto FD, and Panagia N. 1997. Cepheid calibration of the peak
brightness of Type Ia supernovae. VII. SN 1990N in NGC 4639.
Ap. J. 486:1-20
Saio H, and Gautschy A.
1998. On the theoretical period-luminosity relations of
Cepheids. Ap. J. In press
Sandage A. 1996. Annual report of the Carnegie
Observatories.
BAAS 28(1):52
Sandage A, Saha A, Tammann GA, Panagia N, and
Macchetto FD. 1992. The Cepheid distance to IC 4182; calibration of
MV
for SN Ia 1937C and the value of H0.
Ap. J. Lett. 401:L7-10
Sandage A, and Tammann GA. 1982. Steps toward the
Hubble constant. VIII. The global value.
Ap. J. 256:339-45
Sandage A, and Tammann GA. 1993. The Hubble
diagram in V for supernovae of Type Ia and the value of
H0 therefrom.
Ap. J. 415:1-9
Sandage A, and Tammann GA. 1997. The evidence
for the long distance scale with H0 < 65. In
Critical Dialogues in Cosmology, ed. N Turok,
pp. 130-55. Singapore: World Sci.
Sandage A, and Tammann GA.
1998. Confirmation of previous ground-based Cepheid P-L zero-points
using Hipparcos trigonometric parallaxes. MNRAS In press
Sasselov DD, Beaulieu JP, Renault C, Grison P, and
Ferlet R, et al.
1997. Metallicity effects on the Cepheid extragalactic distance
scale from EROS photometry in the Large Magellanic Cloud and the Small
Magellanic Cloud.
Astron. Astrophys. 324:471-82
Schaefer BE. 1994. The peak brightness of SN 1937C
in IC 4182 and the Hubble constant.
Ap. J. 426:493-501
Schaefer BE. 1995a. The peak brightness of SN
1895B in NGC 5253 and the Hubble constant.
Ap. J. Lett. 447:L13-16
Schaefer BE. 1995b. The peak brightness of
supernovae in the U band and the Hubble constant.
Ap. J. Lett. 450:L5-9
Schaefer BE. 1995c. The peak brightness of SN
1981B in NGC 4536 and the Hubble constant.
Ap. J. Lett. 449:L9-12
Schaefer BE. 1996a. The peak brightness of SN
1937C and the Hubble constant: comments on Pierce & Jacoby (1995).
Astron. J. 111:1668-74
Schaefer BE. 1996b. The peak brightness of SN
1960F in NGC 4496 and the Hubble constant.
Ap. J. Lett. 460:L19-23
Schlegel EM, and Petre R. 1993. A ROSAT
upper limit on X-ray emission from SN 1992A.
Ap. J. Lett. 412:L29-32
Schmidt B, Phillips M, Hamuy M, Avilés R, and
Suntzeff N, et al.
1997. Supernovae. IAU Circ. No. 6646
Shigeyama T, Nomoto K, Yamaoka H, and Thielemann
F-K. 1992. Possible models for the type Ia supernova
1990N. Ap. J. Lett. 386:L13-16
Stothers RB. 1988. Abundance effects on the
Cepheid distance scale.
Ap. J. 329:712-19
Tammann GA, and Federspiel M. 1997. Focusing in on
H0. See
Livio et al, 1997, pp. 137-70
Tammann GA, and Sandage A. 1995. The Hubble diagram
for supernovae of Type Ia. II. The effects on the Hubble constant of a
correlation between absolute magnitude and light curve decay rate.
Ap. J. 452:16-24
Teerikorpi P. 1997. Observational selection bias
affecting the determination of the extragalactic distance scale.
Annu. Rev.
Astron. Astrophys. 35:101-36
Tripp R. 1997. Using distant Type Ia supernovae to
measure the cosmological expansion parameters.
Astron. Astrophys. 325:871-76
Tripp R.
1998. A two-parameter luminosity correction for Type Ia
supernovae. Astron. Astrophys. In press
Turatto M, Benetti S, Cappellaro E, Danziger IJ,
and Della Valle M,
et al.1996. The properties of the peculiar Type Ia supernova
1991bg. I. Analysis and discussion of two years of observations.
MNRAS 283:1-17
Tutukov A, and Yungelson LR. 1994. Merging of
binary white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes under the influence
of gravitational wave radiation.
MNRAS 268:871-79
Vacca WD, and Leibundgut B. 1996. The rise times
and bolometric light curve of SN 1994D: constraints on models of Type Ia
supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 471:L37-40
van den Bergh S. 1995. A new method for the
determination of the Hubble parameter.
Ap. J. Lett. 453:L55-56
van den Bergh S. 1996. The luminosities of
supernovae of Type Ia derived from Cepheid calibrations.
Ap. J. 472:431-34
van den Heuvel EPJ, Bhattacharya D, Nomoto K, and
Rappaport SA. 1992. Accreting white dwarf models for CAL83, CAL87, and
other ultrasoft X-ray sources in the LMC.
Astron. Astrophys. 262:97-105
Vaughan TE, Branch D, Miller DL, and Perlmutter
S. 1995. The blue and visual absolute magnitude distributions of Type Ia
supernovae.
Ap. J. 439:558-64
von Hippel T, Bothun GD, and Schommer
RA. 1997. Stellar populations and the white dwarf mass function:
connections to supernova Ia luminosities.
Astron. J. 114:1154-64
Wang L, Höflich P, and Wheeler
JC. 1997a. Supernovae and their host galaxies.
Ap. J. 483:L29-L32
Wang L, Wheeler JC, and Höflich
P. 1997b. Polarimetry of the Type Ia supernova 1996X.
Ap. J. 476:L27-30
Wang L, Wheeler JC, Li Z, and Clocchiatti
A. 1996. Broadband polarimetry of supernovae: 1994D, 1994Y, 1994ae,
1995D, and 1995H.
Ap. J. 467:435-45
Wells LA, Phillips MM, Suntzeff NB, Heathcote SR,
and Hamuy M, et al.1994. The Type Ia supernova 1989B in NGC 3627
(M66).
Astron. J. 108:2233-50
Wheeler JC, Harkness RP, Khokhlov AM, and
Höflich P. 1995. Stirling's supernovae: a survey of the field.
Phys. Rep. 256:211-35
Woosley SE, and Weaver TA. 1986. The physics of
supernova explosions.
Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 24:205-53
Woosley SE, and Weaver TA.
1994a. Sub-Chandrasekhar models for Type Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. 423:371-79
Woosley SE, and Weaver TA.
1994b. Massive stars, supernovae, and nucleosynthesis. In
Supernovae, ed. S Bludman, R Mochkovitch, J Zinn-Justin,
pp. 63-154. Amsterdam: Elsevier
Yungelson LR, and Livio M.
1998. Type Ia supernovae: an examination of potential progenitors and
the redshift distribution. Ap. J. In press
Yungelson LR, Livio M, Truran JW, Tutukov A, and
Fedorova A. 1996. A model for the Galactic population of binary
supersoft X-ray sources.
Ap. J. 466:890-910
Zehavi I, Riess AG, Kirshner RP, and Dekel A.
1998. A local Hubble bubble from SNe Ia? Ap. J. In press
= 5/3.
Ap. J. 438:887-903
Renzini A. 1996. Searching for Type Ia
supernova progenitors. In
Supernovae and Supernova Remnants, ed. R McCray, Z Wang,
pp. 77-85. Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press
Richmond MW, Treffers RR, Filippenko AV, Van Dyk
SD, and Paik Y, et al.1995. UBVRI photometry of the Type
Ia SN 1994D in NGC 4526.
Astron. J. 109:2121-33
Riess AG.
1996. Type Ia supernova multicolor light curve shapes. PhD
thesis. Harvard Univ.
Riess AG, Davis M, Baker J, and Kirshner
RP. 1997a. The velocity field from Type Ia supernovae matches the
gravity field from galaxy surveys.
Ap. J. 488:L1-L5
Riess AG, Filippenko AV, Leonard DC, Schmidt BP,
and Suntzeff N, et al.1997b. Time dilation from spectral feature
age measurements of Type Ia supernovae.
Astron. J. 114:722-29
Riess AG, Nugent P, Filippenko AV, Kirshner RP,
and Perlmutter S. 1998. Snapshot distances to SNe Ia - all in "one"
night's work. Ap. J. In press
Riess AG, Press WH, and Kirshner RP. 1995a. Using
Type Ia supernova light curve shapes to measure the Hubble constant.
Ap. J. Lett. 438:L17-20
Riess AG, Press WH, and Kirshner
RP. 1995b. Determining the motion of the local group using Type Ia
supernova light curve shapes.
Ap. J. Lett. 445:L91-94
Riess AG, Press WH, and Kirshner RP. 1996a. A
precise distance indicator: Type Ia supernova multicolor light-curve
shapes.
Ap. J. 473:88-109
Riess AG, Press WH, and Kirshner RP. 1996b. Is the
dust obscuring supernovae in distant galaxies the same as the dust in
the Milky Way?
Ap. J. 473:588-94
Ruiz-Lapuente P. 1996. The Hubble constant from
56Co-powered nebular candles.
Ap. J. 465:L83-86
Ruiz-Lapuente P, Canal R, and Burkert
A. 1997a. SNe Ia: on the binary progenitors and expected statistics. See
Ruiz-Lapuente et al 1997b, pp. 205-30
Ruiz-Lapuente P, Canal R, and Isern J, eds.
1997b. Thermonuclear Supernovae. Dordrecht: Kluwer
Ruiz-Lapuente P, Cappellaro E, Turatto M, Gouiffes
C, and Danziger IJ, et al.1992. Modeling the iron-dominated
spectra of the Type Ia supernova 1991T at premaximum.
Ap. J. Lett. 387:L33-36
Saha A, Labhardt L, Schwengeler H, Macchetto FD,
and Panagia N, et al.1994. Discovery of Cepheids in IC 4182:
absolute peak brightness of SN Ia 1937C and the value of
H0.
Ap. J. 425:14-34
Saha A, Sandage A, Labhardt L, Schwengeler H, and
Tammann GA, et al.1995. Discovery of Cepheids in NGC 5253:
absolute peak brightness of SNe Ia 1895B and 1972E and the value of
H0.
Ap. J. 438:8-26
Saha A, Sandage A, Labhardt L, Tammann GA,
Macchetto FD, and Panagia N. 1996a. Cepheid calibration of the peak
brightness of SNe Ia. V. SN 1981B in NGC 4536.
Ap. J. 466:55-91
Saha A, Sandage A, Labhardt L, Tammann GA,
Macchetto FD, and Panagia N. 1996b. Cepheid calibration of the peak
brightness of Type Ia supernovae. VI. SN 1960F in NGC 4496A.
Ap. J. Suppl. 107:693
Saha A, Sandage A, Labhardt L, Tammann GA,
Macchetto FD, and Panagia N. 1997. Cepheid calibration of the peak
brightness of Type Ia supernovae. VII. SN 1990N in NGC 4639.
Ap. J. 486:1-20
Saio H, and Gautschy A.
1998. On the theoretical period-luminosity relations of
Cepheids. Ap. J. In press
Sandage A. 1996. Annual report of the Carnegie
Observatories.
BAAS 28(1):52
Sandage A, Saha A, Tammann GA, Panagia N, and
Macchetto FD. 1992. The Cepheid distance to IC 4182; calibration of
MV
for SN Ia 1937C and the value of H0.
Ap. J. Lett. 401:L7-10
Sandage A, and Tammann GA. 1982. Steps toward the
Hubble constant. VIII. The global value.
Ap. J. 256:339-45
Sandage A, and Tammann GA. 1993. The Hubble
diagram in V for supernovae of Type Ia and the value of
H0 therefrom.
Ap. J. 415:1-9
Sandage A, and Tammann GA. 1997. The evidence
for the long distance scale with H0 < 65. In
Critical Dialogues in Cosmology, ed. N Turok,
pp. 130-55. Singapore: World Sci.
Sandage A, and Tammann GA.
1998. Confirmation of previous ground-based Cepheid P-L zero-points
using Hipparcos trigonometric parallaxes. MNRAS In press
Sasselov DD, Beaulieu JP, Renault C, Grison P, and
Ferlet R, et al.
1997. Metallicity effects on the Cepheid extragalactic distance
scale from EROS photometry in the Large Magellanic Cloud and the Small
Magellanic Cloud.
Astron. Astrophys. 324:471-82
Schaefer BE. 1994. The peak brightness of SN 1937C
in IC 4182 and the Hubble constant.
Ap. J. 426:493-501
Schaefer BE. 1995a. The peak brightness of SN
1895B in NGC 5253 and the Hubble constant.
Ap. J. Lett. 447:L13-16
Schaefer BE. 1995b. The peak brightness of
supernovae in the U band and the Hubble constant.
Ap. J. Lett. 450:L5-9
Schaefer BE. 1995c. The peak brightness of SN
1981B in NGC 4536 and the Hubble constant.
Ap. J. Lett. 449:L9-12
Schaefer BE. 1996a. The peak brightness of SN
1937C and the Hubble constant: comments on Pierce & Jacoby (1995).
Astron. J. 111:1668-74
Schaefer BE. 1996b. The peak brightness of SN
1960F in NGC 4496 and the Hubble constant.
Ap. J. Lett. 460:L19-23
Schlegel EM, and Petre R. 1993. A ROSAT
upper limit on X-ray emission from SN 1992A.
Ap. J. Lett. 412:L29-32
Schmidt B, Phillips M, Hamuy M, Avilés R, and
Suntzeff N, et al.
1997. Supernovae. IAU Circ. No. 6646
Shigeyama T, Nomoto K, Yamaoka H, and Thielemann
F-K. 1992. Possible models for the type Ia supernova
1990N. Ap. J. Lett. 386:L13-16
Stothers RB. 1988. Abundance effects on the
Cepheid distance scale.
Ap. J. 329:712-19
Tammann GA, and Federspiel M. 1997. Focusing in on
H0. See
Livio et al, 1997, pp. 137-70
Tammann GA, and Sandage A. 1995. The Hubble diagram
for supernovae of Type Ia. II. The effects on the Hubble constant of a
correlation between absolute magnitude and light curve decay rate.
Ap. J. 452:16-24
Teerikorpi P. 1997. Observational selection bias
affecting the determination of the extragalactic distance scale.
Annu. Rev.
Astron. Astrophys. 35:101-36
Tripp R. 1997. Using distant Type Ia supernovae to
measure the cosmological expansion parameters.
Astron. Astrophys. 325:871-76
Tripp R.
1998. A two-parameter luminosity correction for Type Ia
supernovae. Astron. Astrophys. In press
Turatto M, Benetti S, Cappellaro E, Danziger IJ,
and Della Valle M,
et al.1996. The properties of the peculiar Type Ia supernova
1991bg. I. Analysis and discussion of two years of observations.
MNRAS 283:1-17
Tutukov A, and Yungelson LR. 1994. Merging of
binary white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes under the influence
of gravitational wave radiation.
MNRAS 268:871-79
Vacca WD, and Leibundgut B. 1996. The rise times
and bolometric light curve of SN 1994D: constraints on models of Type Ia
supernovae.
Ap. J. Lett. 471:L37-40
van den Bergh S. 1995. A new method for the
determination of the Hubble parameter.
Ap. J. Lett. 453:L55-56
van den Bergh S. 1996. The luminosities of
supernovae of Type Ia derived from Cepheid calibrations.
Ap. J. 472:431-34
van den Heuvel EPJ, Bhattacharya D, Nomoto K, and
Rappaport SA. 1992. Accreting white dwarf models for CAL83, CAL87, and
other ultrasoft X-ray sources in the LMC.
Astron. Astrophys. 262:97-105
Vaughan TE, Branch D, Miller DL, and Perlmutter
S. 1995. The blue and visual absolute magnitude distributions of Type Ia
supernovae.
Ap. J. 439:558-64
von Hippel T, Bothun GD, and Schommer
RA. 1997. Stellar populations and the white dwarf mass function:
connections to supernova Ia luminosities.
Astron. J. 114:1154-64
Wang L, Höflich P, and Wheeler
JC. 1997a. Supernovae and their host galaxies.
Ap. J. 483:L29-L32
Wang L, Wheeler JC, and Höflich
P. 1997b. Polarimetry of the Type Ia supernova 1996X.
Ap. J. 476:L27-30
Wang L, Wheeler JC, Li Z, and Clocchiatti
A. 1996. Broadband polarimetry of supernovae: 1994D, 1994Y, 1994ae,
1995D, and 1995H.
Ap. J. 467:435-45
Wells LA, Phillips MM, Suntzeff NB, Heathcote SR,
and Hamuy M, et al.1994. The Type Ia supernova 1989B in NGC 3627
(M66).
Astron. J. 108:2233-50
Wheeler JC, Harkness RP, Khokhlov AM, and
Höflich P. 1995. Stirling's supernovae: a survey of the field.
Phys. Rep. 256:211-35
Woosley SE, and Weaver TA. 1986. The physics of
supernova explosions.
Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 24:205-53
Woosley SE, and Weaver TA.
1994a. Sub-Chandrasekhar models for Type Ia supernovae.
Ap. J. 423:371-79
Woosley SE, and Weaver TA.
1994b. Massive stars, supernovae, and nucleosynthesis. In
Supernovae, ed. S Bludman, R Mochkovitch, J Zinn-Justin,
pp. 63-154. Amsterdam: Elsevier
Yungelson LR, and Livio M.
1998. Type Ia supernovae: an examination of potential progenitors and
the redshift distribution. Ap. J. In press
Yungelson LR, Livio M, Truran JW, Tutukov A, and
Fedorova A. 1996. A model for the Galactic population of binary
supersoft X-ray sources.
Ap. J. 466:890-910
Zehavi I, Riess AG, Kirshner RP, and Dekel A.
1998. A local Hubble bubble from SNe Ia? Ap. J. In press