Copyright © 1998 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved
| Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1988. 36:
539-598 Copyright © 1998 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved |
6.3. Acceleration of Cosmic Rays in Extragalactic Radio Sources
Jets and cocoons have also been invoked to
explain the question of production of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays
(UHECRs), E > 4 × 1019 up to 3 ×
1020 eV, revealed by extensive air shower detectors
(Norman et al 1996).
The argument is that large-scale shocks produced inside a jet or by the
expansion of the working surface and cocoon into the ambient plasma can
accelerate already relativistic protons/ions to the maximum
energies. The limiting upper energy cutoff is approximately
Emax 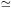 ZeB
ZeB
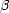 s
Rs,
which yields (in typical units) for hot spots in jets (Rs
~ Rj,
s
Rs,
which yields (in typical units) for hot spots in jets (Rs
~ Rj,
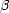 s
~
s
~ 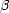 j)
j)
 |
(40) |
and for overpressured cocoons
 |
(41) |
Therefore, hot spots and cocoons appear to be interesting candidates as UHECR sources. Also, the injection problem for ions is less severe than for electrons.