


2.2. The Expansion of the Universe
The expansion of the universe was discovered in 1929 by Edwin Hubble, who measured the distances to a sample of nearby galaxies, and established a correlation between distance and recession velocity. The slope of this relation is the Hubble constant. Large systematic uncertainties in determining distance have made an accurate determination of the Hubble constant a challenge, and only recently have improvements in instrumentation, the launch of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), and the development of several different measurement methods led to a convergence on its value. Accurate distances to nearby galaxies obtained as part of an HST Key Project have allowed calibration of 5 different methods for determining the distances to galaxies out to 500 Mpc (Freedman et al., 2001). All the techniques show good agreement to within their respective uncertainties, and yield a value
 |
where the error bars represent
1- statistical and systematic uncertainties, respectively (see
Figure 3). Because of the importance of its value
to so many cosmological quantities, and because of
its historically large uncertainty, H0 is often written
as H0 = 100h km sec-1 Mpc-1,
so that h = 0.72 ± 0.02 ± 0.07.
statistical and systematic uncertainties, respectively (see
Figure 3). Because of the importance of its value
to so many cosmological quantities, and because of
its historically large uncertainty, H0 is often written
as H0 = 100h km sec-1 Mpc-1,
so that h = 0.72 ± 0.02 ± 0.07.
The largest contributions to these quoted uncertainties result from those due to the metallicity of Cepheids, the distance to the Large Magellanic Cloud (the fiducial nearby galaxy to which all Cepheid distances are measured relative to), and the calibration of the Wide Field Camera on HST. Other groups using similar techniques (Saha et al., 1997) find a lower value of H0 (~ 60 km/sec/Mpc). The reasons for the difference are many, as described further in Freedman et al. (2001), but overall the determinations are consistent to within the measurement uncertainties. Recent measurements of H0 based on two completely independent techniques, the Sunyaev-Zeldovich method and the measurement of time delays for gravitational lenses (Reese et al., 2000, Keeton et al., 2000), are yielding values of H0 ~ 60 km/sec/Mpc with systematic errors currently still at the 20-30% level. New results from the WMAP satellite, discussed in the postscript to this article, give H0 = 71 ± 4 km/sec/Mpc.
Because light from very distance galaxies was emitted long ago, the Hubble diagram also provides a means of probing the expansion at earlier times. For many decades, efforts have been directed toward measuring what was almost universally expected to be a slowing of the expansion over time due to the gravity of all the matter. However, observations by two independent groups have found that supernovae at high redshifts are fainter than predicted for a slowing expansion and indicate that the expansion is actually speeding up (see Figure 4) (Perlmutter et al., 1999, Riess et al., 1998). Although systematic effects due to intervening dust or evolution of the supernovae themselves could explain such a dimming of high-redshift supernovae, several tests have failed to turn up any evidence for such effects. Apparently, the universe is now undergoing an acceleration, with the repulsive gravity of some strange energy form - dark energy - at work. There is weak evidence in the supernova data for an earlier (z > 1/2), decelerating phase (Turner and Riess, 2002). Such a decelerating phase is expected on theoretical grounds (more later), and establishing its existence (or absence!) is an important goal of future supernova observations.
 |
Figure 4. Hubble diagram:
High-redshift type Ia supernovae probe the expansion
history and reveal accelerated expansion. In this differential
Hubble diagram the distance modulus, which is 5 times the logarithm
of the distance, relative to an empty Universe
( |
The remarkable fact that the expansion is speeding up, rather
than slowing down, can be accounted for within Einstein's theory,
as the source of gravity is proportional to
(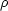 + 3p),
where the pressure p and
energy density
+ 3p),
where the pressure p and
energy density 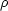 describe the bulk properties of
the "substance". (For ordinary or even nonbaryonic dark
matter, p = 0, while for photons
and relativistic particles, p =
describe the bulk properties of
the "substance". (For ordinary or even nonbaryonic dark
matter, p = 0, while for photons
and relativistic particles, p =
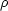 / 3.) A substance
that is very elastic, i.e., with pressure more negative
than one third its energy density, has repulsive gravity
in Einstein's theory (more later). Of course, it could well
be that the root cause of cosmic acceleration
is not new stuff (i.e., dark energy), but involves a
deeper understanding of gravity.
/ 3.) A substance
that is very elastic, i.e., with pressure more negative
than one third its energy density, has repulsive gravity
in Einstein's theory (more later). Of course, it could well
be that the root cause of cosmic acceleration
is not new stuff (i.e., dark energy), but involves a
deeper understanding of gravity.
The deceleration parameter was introduced to quantify the slowing of the expansion; it is related to the mass-energy content of the Universe:
 |
(3) |
where
wX  pX /
pX /
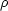 X
characterizes the pressure of the
dark-energy component. (wX need not be constant; for
simplicity,
we shall assume it is.) In the absence of dark energy, a flat Universe
would decelerate by its own self-gravity (i.e., q0 =
0.5), whereas dark energy allows
for acceleration. The supernova measurements are consistent with
wX = - 1 and
X
characterizes the pressure of the
dark-energy component. (wX need not be constant; for
simplicity,
we shall assume it is.) In the absence of dark energy, a flat Universe
would decelerate by its own self-gravity (i.e., q0 =
0.5), whereas dark energy allows
for acceleration. The supernova measurements are consistent with
wX = - 1 and
 X =
0.7. Independent confirmation of such a
startling result is extremely important. As discussed below, strong
indirect evidence for an additional energy component comes from a
comparison of the density of matter with measurements of
X =
0.7. Independent confirmation of such a
startling result is extremely important. As discussed below, strong
indirect evidence for an additional energy component comes from a
comparison of the density of matter with measurements of
 0
from fluctuations in the CMB.
0
from fluctuations in the CMB.
Dark energy, a "mysterious substance" whose pressure is negative and comparable in magntiude to its energy density, apparently accounts for two-thirds of the matter-energy budget of the universe and has no clear explanation. Understanding its nature presents one of the greatest challenges in both cosmology and particle physics.