

REFERENCES
Adelberger K. L. et al. (2003) Galaxies and
Intergalactic Matter at Redshift z ~ 3: Overview,
Ap. J. 584 45
Ahn S.-H., Lee, H.-W., and Lee, H. (2002) P-Cygni
Type Ly from Starburst
Galaxies.
Ap. J. 567 922
Ajiki M., et al. (2002) A New High-Redshift
Ly
from Starburst
Galaxies.
Ap. J. 567 922
Ajiki M., et al. (2002) A New High-Redshift
Ly Emitter: Possible
Superwind Galaxy at z = 5.69.
Ap. J. 576 L25
Andersen M I, et al. (2000) VLT Identification of
the Optical Afterglow of the Gamma-Ray Burst GRB 000131 at z =
4.50
Astron. and Ap. 364 54
Baldwin J et al. (1974) An Analysis of the Apectrum
of the Large-Redshift Quasi-Stellar Object OQ 172
Ap. J. 193 513
Barger A J, et al. (2001) Supermassive Black Hole
Accretion History Inferred From a Large Sample Of Chandra Hard X-Ray
Sources
Astron. J. 122 2177
Barger A J et al. (2002) X-Ray, Optical, and
Infrared Imaging and Spectral Properties of the 1 Ms Chandra Deep Field
North Sources
Astron. J. 124 1839
Baugh C M et al. (1998) The Epoch of Galaxy
Formation
Ap. J. 498 504
Baugh C M et al. (1999) in Photometric Redshifts and
High Redshift Galaxies ed R Weyman, L Storrie-Lombardi, M Sawicki and R
Brunner
ASP Conf. Ser. 191 p. 353
Benitez N, and Broadhurst T (1999) High-z Galaxies
Seen Through Cluster Lenses, in The Hy Redshift Universe, ed A J Bunker
and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 p. 509
Best P, et al. (1999) A 98 per cent
Spectroscopically Complete Sample of the Most Powerful Equatorial Radio
Sources at 408MHz
MNRAS 310, 223
Blain A W., et al. (1999) Submillimeter-Selected
Galaxies, in The Hy Redshift Universe ed A J Bunker and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 p. 425
Blain A W., et al. (2002) The 60µm
Extragalactic Background Radiation Intensity, Dust-Enshrouded Active
Galactic Nuclei and the Assembly of Groups and Clusters of Galaxies
MNRAS 333 222
Brandt W N (2001) The Chandra Deep Field North
Survey. V. 1 Ms Source Catalogs
Astron. J. 122 2810
Brandt W N (2002) The Chandra Deep Field-North
Survey. XI. X-Ray Emission from Luminous Infrared Starburst Galaxies
Ap. J. 568 85
Bunker A J et al. (2003) A Star-Forming Galaxy at
z = 5.78 in the Chandra Deep Field South
MNRAS 342 L47
Calzetti D et al. (2000) The Dust Content and
Opacity of Actively Star-forming Galaxies
Ap. J. 533 682
Chapman S C et al. (2003) Uncoveringt the Redshifrt
Distribution of Submillimetre Galaxies
Nature 422 695
Charlot S and Fall S (1993) Lyman-
Emitter: Possible
Superwind Galaxy at z = 5.69.
Ap. J. 576 L25
Andersen M I, et al. (2000) VLT Identification of
the Optical Afterglow of the Gamma-Ray Burst GRB 000131 at z =
4.50
Astron. and Ap. 364 54
Baldwin J et al. (1974) An Analysis of the Apectrum
of the Large-Redshift Quasi-Stellar Object OQ 172
Ap. J. 193 513
Barger A J, et al. (2001) Supermassive Black Hole
Accretion History Inferred From a Large Sample Of Chandra Hard X-Ray
Sources
Astron. J. 122 2177
Barger A J et al. (2002) X-Ray, Optical, and
Infrared Imaging and Spectral Properties of the 1 Ms Chandra Deep Field
North Sources
Astron. J. 124 1839
Baugh C M et al. (1998) The Epoch of Galaxy
Formation
Ap. J. 498 504
Baugh C M et al. (1999) in Photometric Redshifts and
High Redshift Galaxies ed R Weyman, L Storrie-Lombardi, M Sawicki and R
Brunner
ASP Conf. Ser. 191 p. 353
Benitez N, and Broadhurst T (1999) High-z Galaxies
Seen Through Cluster Lenses, in The Hy Redshift Universe, ed A J Bunker
and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 p. 509
Best P, et al. (1999) A 98 per cent
Spectroscopically Complete Sample of the Most Powerful Equatorial Radio
Sources at 408MHz
MNRAS 310, 223
Blain A W., et al. (1999) Submillimeter-Selected
Galaxies, in The Hy Redshift Universe ed A J Bunker and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 p. 425
Blain A W., et al. (2002) The 60µm
Extragalactic Background Radiation Intensity, Dust-Enshrouded Active
Galactic Nuclei and the Assembly of Groups and Clusters of Galaxies
MNRAS 333 222
Brandt W N (2001) The Chandra Deep Field North
Survey. V. 1 Ms Source Catalogs
Astron. J. 122 2810
Brandt W N (2002) The Chandra Deep Field-North
Survey. XI. X-Ray Emission from Luminous Infrared Starburst Galaxies
Ap. J. 568 85
Bunker A J et al. (2003) A Star-Forming Galaxy at
z = 5.78 in the Chandra Deep Field South
MNRAS 342 L47
Calzetti D et al. (2000) The Dust Content and
Opacity of Actively Star-forming Galaxies
Ap. J. 533 682
Chapman S C et al. (2003) Uncoveringt the Redshifrt
Distribution of Submillimetre Galaxies
Nature 422 695
Charlot S and Fall S (1993) Lyman- Emission from Galaxies
Ap. J. 415 580
Connolly A J et al. (1995) Spectral Classification
of Galaxies: an Orthogonal Approach
Astron. J. 110 1071
Dawson S et al. (2002) A Galactic Wind at z =
5.190
Ap. J. 570 92
de Breuck C et al. (2000) A Sample of 669 Ultra
Steep Spectrum Radio Sources to Find High Redshift Radio Galaxies
Astron. Ap. Sup. 143 303
Dey A et al. (1998) A Galaxy at z = 5.34
Ap. J. 498, L93
Ellis R et al. (2001) A Faint Star-forming System Viewed through the Lensing Cluster Abell 2218: First Light at
Emission from Galaxies
Ap. J. 415 580
Connolly A J et al. (1995) Spectral Classification
of Galaxies: an Orthogonal Approach
Astron. J. 110 1071
Dawson S et al. (2002) A Galactic Wind at z =
5.190
Ap. J. 570 92
de Breuck C et al. (2000) A Sample of 669 Ultra
Steep Spectrum Radio Sources to Find High Redshift Radio Galaxies
Astron. Ap. Sup. 143 303
Dey A et al. (1998) A Galaxy at z = 5.34
Ap. J. 498, L93
Ellis R et al. (2001) A Faint Star-forming System Viewed through the Lensing Cluster Abell 2218: First Light at
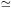 5.6?
Ap. J. 560 L119
Eggen O J, Lynden-Bell D and Sandage A R (1962)
Evidence from the Motions of Old Stars that the Galaxy Collapsed
Ap. J. 136, 748
Fan X et al. (2001) A Survey of z > 5.8
Quasars in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. I. Discovery of Three New
Quasars and the Spatial Density of Luminous Quasars at z ~ 6
Astron. J. 122, 2833
Fan X et al. (2002) Evolution of the Ionizing
Background and the Epoch of Reionization from the Spectra of z ~
6 Quasars
Astron. J. 123 1247
Fernandez-Soto A, Lanzetta K and Yahil A (1999) A
New Catalog of Photometric Redshifts in the Hubble Deep Field
Ap. J. 513 34
Frayer D et al. (1998) Molecular Gas in the z
= 2.8 Submillimeter Galaxy SMM 02399-0136
Ap. J. 506 L7
Frye B et al. (2002) Spectral Evidence for
Widespread Galaxy Outflows at z > 4
Ap. J. 568 558
Fynbo J Möller P, and Thomsen B (2001) Probing
the Faint End of the Galaxy Luminosity Function at z = 3 with
Ly
5.6?
Ap. J. 560 L119
Eggen O J, Lynden-Bell D and Sandage A R (1962)
Evidence from the Motions of Old Stars that the Galaxy Collapsed
Ap. J. 136, 748
Fan X et al. (2001) A Survey of z > 5.8
Quasars in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. I. Discovery of Three New
Quasars and the Spatial Density of Luminous Quasars at z ~ 6
Astron. J. 122, 2833
Fan X et al. (2002) Evolution of the Ionizing
Background and the Epoch of Reionization from the Spectra of z ~
6 Quasars
Astron. J. 123 1247
Fernandez-Soto A, Lanzetta K and Yahil A (1999) A
New Catalog of Photometric Redshifts in the Hubble Deep Field
Ap. J. 513 34
Frayer D et al. (1998) Molecular Gas in the z
= 2.8 Submillimeter Galaxy SMM 02399-0136
Ap. J. 506 L7
Frye B et al. (2002) Spectral Evidence for
Widespread Galaxy Outflows at z > 4
Ap. J. 568 558
Fynbo J Möller P, and Thomsen B (2001) Probing
the Faint End of the Galaxy Luminosity Function at z = 3 with
Ly Emission
Astron. Ap. 374 443
Fynbo J et al. (2002) Deep
Ly
Emission
Astron. Ap. 374 443
Fynbo J et al. (2002) Deep
Ly Imaging of Two z =
2.04 GRB Host Galaxy Fields
Astron. and Ap. 388 425
Genzel R et al (2003) patially Resolved Millimeter
Interferometry of SMM J02399-0136: A Very Massive Galaxy at z =
2.8
Ap. J. 584 633
Giavalisco M (2002) Lyman-Break Galaxies
Ann. Revs. Astron. and Ap. 40 579
Granato G L, et al. (2001) Joint Formation of
QSOs and Spheroids: QSOs as Clocks of Star Formation in Spheroids
MNRAS 324 757
Haiman Z (2002) The Detectability of High-Redshift
Ly
Imaging of Two z =
2.04 GRB Host Galaxy Fields
Astron. and Ap. 388 425
Genzel R et al (2003) patially Resolved Millimeter
Interferometry of SMM J02399-0136: A Very Massive Galaxy at z =
2.8
Ap. J. 584 633
Giavalisco M (2002) Lyman-Break Galaxies
Ann. Revs. Astron. and Ap. 40 579
Granato G L, et al. (2001) Joint Formation of
QSOs and Spheroids: QSOs as Clocks of Star Formation in Spheroids
MNRAS 324 757
Haiman Z (2002) The Detectability of High-Redshift
Ly Emission Lines prior
to the Reionization of the Universe
Ap. J. 576 L1
Hu E, McMahon R G and Cowie L (1999) An Extremely
Luminous Galaxy at z = 5.74
Ap. J. 522 9
Hu E et al. (2002) A Redshift z = 6.56 Galaxy
behind the Cluster Abell 370
Ap. J. (L) 568 L75
Hu E M, Cowie L L and McMahon R G (2002) ERRATUM: A
Redshift z = 6.56 Galaxy behind the Cluster Abell 370
Ap. J. 576 L99
Iwata I et al. (2003) Lyman Break Galaxies at
z ~ 5: Luminosity Function.
P.A.S.J. 55 415
Klypin A et al. (1999) Where Are the Missing
Galactic Satellites?
Ap. J. 522 82
Kodaira K, Taniguchi Y et al. (2003). The Discovery
of Two Ly
Emission Lines prior
to the Reionization of the Universe
Ap. J. 576 L1
Hu E, McMahon R G and Cowie L (1999) An Extremely
Luminous Galaxy at z = 5.74
Ap. J. 522 9
Hu E et al. (2002) A Redshift z = 6.56 Galaxy
behind the Cluster Abell 370
Ap. J. (L) 568 L75
Hu E M, Cowie L L and McMahon R G (2002) ERRATUM: A
Redshift z = 6.56 Galaxy behind the Cluster Abell 370
Ap. J. 576 L99
Iwata I et al. (2003) Lyman Break Galaxies at
z ~ 5: Luminosity Function.
P.A.S.J. 55 415
Klypin A et al. (1999) Where Are the Missing
Galactic Satellites?
Ap. J. 522 82
Kodaira K, Taniguchi Y et al. (2003). The Discovery
of Two Ly Emitters
Beyond Redshift 6 in the Subaru Deep Field
P.A.S.J. 55 L17
Kudritzki R. et al. (2000) Discovery of Nine
Ly
Emitters
Beyond Redshift 6 in the Subaru Deep Field
P.A.S.J. 55 L17
Kudritzki R. et al. (2000) Discovery of Nine
Ly Emitters at Redshift
z ~ 3.1 Using Narrowband Imaging and VLT Spectroscopy
Ap.J. 536 19
Kulkarni S et al. (1998) The Afterglow, Redshift and
Extreme Energetics of the Gamma-Ray Burst of 23 January
1999 Nature 393 35
Kunth D et al. (1998) HST study of
Ly
Emitters at Redshift
z ~ 3.1 Using Narrowband Imaging and VLT Spectroscopy
Ap.J. 536 19
Kulkarni S et al. (1998) The Afterglow, Redshift and
Extreme Energetics of the Gamma-Ray Burst of 23 January
1999 Nature 393 35
Kunth D et al. (1998) HST study of
Ly Emission in Star-Forming
Galaxies: the Effect of Neutral Gas Flows
Astron. and Ap. 334 11
Lanzetta K et al. (1999) in The Hy Redshift Universe
ed A J Bunker and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 p. 544
Lehnert M D and Bremer M (2003) Luminous Lyman Break
Galaxies at z > 5 and the Source of Reionization
Ap. J. 593 in press, astro-ph/0212431
Lilly S and Longair M (1984) Stellar Populations in
Distant Radio Galaxies
MNRAS 211 833
Lilly S et al. (1996) The Canada-France Redshift
Survey: The Luminosity Density and Star Formation History of the
Universe to
z
Emission in Star-Forming
Galaxies: the Effect of Neutral Gas Flows
Astron. and Ap. 334 11
Lanzetta K et al. (1999) in The Hy Redshift Universe
ed A J Bunker and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 p. 544
Lehnert M D and Bremer M (2003) Luminous Lyman Break
Galaxies at z > 5 and the Source of Reionization
Ap. J. 593 in press, astro-ph/0212431
Lilly S and Longair M (1984) Stellar Populations in
Distant Radio Galaxies
MNRAS 211 833
Lilly S et al. (1996) The Canada-France Redshift
Survey: The Luminosity Density and Star Formation History of the
Universe to
z 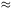 1
Ap. J. 460 L1
Loeb A and Barkana R (2001), The Reionization of the
Universe by the First Stars and Quasars
Ann. Revs. Astron. and Ap. 39 19
Madau P and Pozzetti L and Dickinson M (1998) The
Star Formation History of Field Galaxie
Ap. J. 498 106
Malhotra S and Rhoads J (2002) Large Equivalent
Width Ly
1
Ap. J. 460 L1
Loeb A and Barkana R (2001), The Reionization of the
Universe by the First Stars and Quasars
Ann. Revs. Astron. and Ap. 39 19
Madau P and Pozzetti L and Dickinson M (1998) The
Star Formation History of Field Galaxie
Ap. J. 498 106
Malhotra S and Rhoads J (2002) Large Equivalent
Width Ly ; line Emission
at z = 4.5: Young Galaxies in a Young Universe?
Ap. J. 565 L71
Malhotra S et al. (2003) No X-Ray-bright Type II
Quasars among the Ly
; line Emission
at z = 4.5: Young Galaxies in a Young Universe?
Ap. J. 565 L71
Malhotra S et al. (2003) No X-Ray-bright Type II
Quasars among the Ly Emitters
Ap. J. 585 25
Osmer P S (1999) in The Hy Redshift Universe ed A J
Bunker and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 566
Ouchi M et al. (2002) Subaru Deep
Survey. II. Luminosity Functions and Clustering Properties of
Ly
Emitters
Ap. J. 585 25
Osmer P S (1999) in The Hy Redshift Universe ed A J
Bunker and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 566
Ouchi M et al. (2002) Subaru Deep
Survey. II. Luminosity Functions and Clustering Properties of
Ly Emitters at z
= 4.86 in the Subaru Deep Field
Ap. J. 582, 60
Partridge R B and Peebles P J E (1967) Are Young
Galaxies Visible?
Ap. J. 147 868
Pentericci L et al. (2002a) VLT Optical and
Near-Infrared Observations of the z = 6.28 Quasar SDSS J1030+0524
Astron. J. 123 2151
Pentericci L et al. (2002b) The VLT and the Most
Distant Quasars,
ESO Messinger 108, 24
Pettini M et al. (2001) The Rest-Frame Optical
Spectra of Lyman Break Galaxies: Star Formation, Extinction, Abundances,
and Kinematics
Ap. J. 554 981
Press W H and Schecter P (1974) Formation of
Galaxies and Clusters of Galaxies by Self-Similar Gravitational
Condensation
Ap. J. 187 425
Pritchet C (1994) The Search for Primeval Galaxies
PASP 106 1994
Rhoads J et al. (2003) Spectroscopic Confirmation of
Three Redshift 5.7 Lyman-alpha Emitters from the Large Area Lyman Alpha
Survey
Astron. J. 125 1006
Ridgway S E et al. (2001) NICMOS Imaging of the
Host Galaxies of z 2-3 Radio-quiet Quasars
Astron. J. 550 122
Schaerer D (2002) The Transition from Population III
to Normal Galaxies: Ly
Emitters at z
= 4.86 in the Subaru Deep Field
Ap. J. 582, 60
Partridge R B and Peebles P J E (1967) Are Young
Galaxies Visible?
Ap. J. 147 868
Pentericci L et al. (2002a) VLT Optical and
Near-Infrared Observations of the z = 6.28 Quasar SDSS J1030+0524
Astron. J. 123 2151
Pentericci L et al. (2002b) The VLT and the Most
Distant Quasars,
ESO Messinger 108, 24
Pettini M et al. (2001) The Rest-Frame Optical
Spectra of Lyman Break Galaxies: Star Formation, Extinction, Abundances,
and Kinematics
Ap. J. 554 981
Press W H and Schecter P (1974) Formation of
Galaxies and Clusters of Galaxies by Self-Similar Gravitational
Condensation
Ap. J. 187 425
Pritchet C (1994) The Search for Primeval Galaxies
PASP 106 1994
Rhoads J et al. (2003) Spectroscopic Confirmation of
Three Redshift 5.7 Lyman-alpha Emitters from the Large Area Lyman Alpha
Survey
Astron. J. 125 1006
Ridgway S E et al. (2001) NICMOS Imaging of the
Host Galaxies of z 2-3 Radio-quiet Quasars
Astron. J. 550 122
Schaerer D (2002) The Transition from Population III
to Normal Galaxies: Ly and He II Emission and the Ionising Properties of High Redshift
Starburst Galaxies
Astron. and Ap. 397, 527
Schmidt M (1965) Optical Spectra and Redshifts of 31
Radio Galaxies.
Ap. J. 141 1
Schneider D P, Schmidt M and Gunn J E (1991) PC 1247
+ 3406 - an Optically Selected Quasar with a Redshift of 4.897
Astron. J. 102 837
Searle, L and Zinn, R (1978) Compositions of Halo
Clusters and the Formation of the Galactic Halo
Ap. J. 225 357
Shapley A E et al. (2001) The Rest-Frame Optical
Properties of z
and He II Emission and the Ionising Properties of High Redshift
Starburst Galaxies
Astron. and Ap. 397, 527
Schmidt M (1965) Optical Spectra and Redshifts of 31
Radio Galaxies.
Ap. J. 141 1
Schneider D P, Schmidt M and Gunn J E (1991) PC 1247
+ 3406 - an Optically Selected Quasar with a Redshift of 4.897
Astron. J. 102 837
Searle, L and Zinn, R (1978) Compositions of Halo
Clusters and the Formation of the Galactic Halo
Ap. J. 225 357
Shapley A E et al. (2001) The Rest-Frame Optical
Properties of z 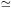 3 Galaxies.
Ap. J. 562 95
Somerville R and Primack J (1999) Semi-Analytic
Modelling of Galaxy Formation: the Local Universe
MNRAS 310 1087
Spinrad H et al. (1998) A z = 5.34 Galaxy
Pair in the Hubble Deep Field
Astron. J. 116, 2617
Spinrad H Stern D, Dawson S and the GOODS team
(2003) work in progress.
Steidel C et al. (1999) Lyman-Break Galaxies at
z
3 Galaxies.
Ap. J. 562 95
Somerville R and Primack J (1999) Semi-Analytic
Modelling of Galaxy Formation: the Local Universe
MNRAS 310 1087
Spinrad H et al. (1998) A z = 5.34 Galaxy
Pair in the Hubble Deep Field
Astron. J. 116, 2617
Spinrad H Stern D, Dawson S and the GOODS team
(2003) work in progress.
Steidel C et al. (1999) Lyman-Break Galaxies at
z 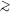 4 and
the Evolution of the Ultraviolet Luminosity Density at High Redshift
Ap. J. 519 1
Stern D and Spinrad H (1999) Search Techniques for
Distant Galaxies
PASP 111 1475
Stern D et al. (2003) Spectroscopic Confirmation of
a Radio-Selected Galaxy Over-Density at z = 1.11
Astron. J. 125 2759
Stiavelli M (2002) Exploring the Cosmic Dark Ages
with the Next Generation of Space and Ground-Based Facilities in Future
Research Directions and Visions for Astronomy, ed A. Dressler, A M
Proceedings of the SPIE,
4835, 122 (astro-ph/0208544)
Taniguchi Y et al. (2003) The Discovery of a Very
Narrow-Line Star Forming Object at a Redshift of 5.66
Ap. J. 585 L97
Thompson D and Djorgovski S G (1995) Serendipitous
Long-Slit Surveys for Primeval Galaxies
Astron. J. 110 982
Tenorio-Tagle G et al. (1999) The Evolution of
Superbubbles and the Detection of
Ly
4 and
the Evolution of the Ultraviolet Luminosity Density at High Redshift
Ap. J. 519 1
Stern D and Spinrad H (1999) Search Techniques for
Distant Galaxies
PASP 111 1475
Stern D et al. (2003) Spectroscopic Confirmation of
a Radio-Selected Galaxy Over-Density at z = 1.11
Astron. J. 125 2759
Stiavelli M (2002) Exploring the Cosmic Dark Ages
with the Next Generation of Space and Ground-Based Facilities in Future
Research Directions and Visions for Astronomy, ed A. Dressler, A M
Proceedings of the SPIE,
4835, 122 (astro-ph/0208544)
Taniguchi Y et al. (2003) The Discovery of a Very
Narrow-Line Star Forming Object at a Redshift of 5.66
Ap. J. 585 L97
Thompson D and Djorgovski S G (1995) Serendipitous
Long-Slit Surveys for Primeval Galaxies
Astron. J. 110 982
Tenorio-Tagle G et al. (1999) The Evolution of
Superbubbles and the Detection of
Ly ; in Star-Forming Galaxies
MNRAS 309 332
van Breugel W et al. (1999) A Radio Galaxy at
z = 5.19
Ap. J. 518 61
Venemans B P et al. (2002) The Most Distant
Structure of Galaxies Known: A Protocluster at z = 4.1
Ap. J. 569 L11
Weinberg D H et al. (1999) in Photometric Redshifts
and High Redshift Galaxies ed R J Weymann, L Storrie-Lombardi, M Sawicki
and R Brunner
ASP Conf. Ser. 191 341
Weymann R J et al. (1998) Keck Spectroscopy and
NICMOS Photometry of a Redshift z = 5.60 Galaxy.
Ap. J. 505 L95
White S and Rees M (1978) Core Condensation in Heavy
Halos - A Two-Stage Theory for Galaxy Formation and Clustering
MNRAS 183 341
; in Star-Forming Galaxies
MNRAS 309 332
van Breugel W et al. (1999) A Radio Galaxy at
z = 5.19
Ap. J. 518 61
Venemans B P et al. (2002) The Most Distant
Structure of Galaxies Known: A Protocluster at z = 4.1
Ap. J. 569 L11
Weinberg D H et al. (1999) in Photometric Redshifts
and High Redshift Galaxies ed R J Weymann, L Storrie-Lombardi, M Sawicki
and R Brunner
ASP Conf. Ser. 191 341
Weymann R J et al. (1998) Keck Spectroscopy and
NICMOS Photometry of a Redshift z = 5.60 Galaxy.
Ap. J. 505 L95
White S and Rees M (1978) Core Condensation in Heavy
Halos - A Two-Stage Theory for Galaxy Formation and Clustering
MNRAS 183 341




 from Starburst
Galaxies.
Ap. J. 567 922
Ajiki M., et al. (2002) A New High-Redshift
Ly
from Starburst
Galaxies.
Ap. J. 567 922
Ajiki M., et al. (2002) A New High-Redshift
Ly Emitter: Possible
Superwind Galaxy at z = 5.69.
Ap. J. 576 L25
Andersen M I, et al. (2000) VLT Identification of
the Optical Afterglow of the Gamma-Ray Burst GRB 000131 at z =
4.50
Astron. and Ap. 364 54
Baldwin J et al. (1974) An Analysis of the Apectrum
of the Large-Redshift Quasi-Stellar Object OQ 172
Ap. J. 193 513
Barger A J, et al. (2001) Supermassive Black Hole
Accretion History Inferred From a Large Sample Of Chandra Hard X-Ray
Sources
Astron. J. 122 2177
Barger A J et al. (2002) X-Ray, Optical, and
Infrared Imaging and Spectral Properties of the 1 Ms Chandra Deep Field
North Sources
Astron. J. 124 1839
Baugh C M et al. (1998) The Epoch of Galaxy
Formation
Ap. J. 498 504
Baugh C M et al. (1999) in Photometric Redshifts and
High Redshift Galaxies ed R Weyman, L Storrie-Lombardi, M Sawicki and R
Brunner
ASP Conf. Ser. 191 p. 353
Benitez N, and Broadhurst T (1999) High-z Galaxies
Seen Through Cluster Lenses, in The Hy Redshift Universe, ed A J Bunker
and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 p. 509
Best P, et al. (1999) A 98 per cent
Spectroscopically Complete Sample of the Most Powerful Equatorial Radio
Sources at 408MHz
MNRAS 310, 223
Blain A W., et al. (1999) Submillimeter-Selected
Galaxies, in The Hy Redshift Universe ed A J Bunker and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 p. 425
Blain A W., et al. (2002) The 60µm
Extragalactic Background Radiation Intensity, Dust-Enshrouded Active
Galactic Nuclei and the Assembly of Groups and Clusters of Galaxies
MNRAS 333 222
Brandt W N (2001) The Chandra Deep Field North
Survey. V. 1 Ms Source Catalogs
Astron. J. 122 2810
Brandt W N (2002) The Chandra Deep Field-North
Survey. XI. X-Ray Emission from Luminous Infrared Starburst Galaxies
Ap. J. 568 85
Bunker A J et al. (2003) A Star-Forming Galaxy at
z = 5.78 in the Chandra Deep Field South
MNRAS 342 L47
Calzetti D et al. (2000) The Dust Content and
Opacity of Actively Star-forming Galaxies
Ap. J. 533 682
Chapman S C et al. (2003) Uncoveringt the Redshifrt
Distribution of Submillimetre Galaxies
Nature 422 695
Charlot S and Fall S (1993) Lyman-
Emitter: Possible
Superwind Galaxy at z = 5.69.
Ap. J. 576 L25
Andersen M I, et al. (2000) VLT Identification of
the Optical Afterglow of the Gamma-Ray Burst GRB 000131 at z =
4.50
Astron. and Ap. 364 54
Baldwin J et al. (1974) An Analysis of the Apectrum
of the Large-Redshift Quasi-Stellar Object OQ 172
Ap. J. 193 513
Barger A J, et al. (2001) Supermassive Black Hole
Accretion History Inferred From a Large Sample Of Chandra Hard X-Ray
Sources
Astron. J. 122 2177
Barger A J et al. (2002) X-Ray, Optical, and
Infrared Imaging and Spectral Properties of the 1 Ms Chandra Deep Field
North Sources
Astron. J. 124 1839
Baugh C M et al. (1998) The Epoch of Galaxy
Formation
Ap. J. 498 504
Baugh C M et al. (1999) in Photometric Redshifts and
High Redshift Galaxies ed R Weyman, L Storrie-Lombardi, M Sawicki and R
Brunner
ASP Conf. Ser. 191 p. 353
Benitez N, and Broadhurst T (1999) High-z Galaxies
Seen Through Cluster Lenses, in The Hy Redshift Universe, ed A J Bunker
and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 p. 509
Best P, et al. (1999) A 98 per cent
Spectroscopically Complete Sample of the Most Powerful Equatorial Radio
Sources at 408MHz
MNRAS 310, 223
Blain A W., et al. (1999) Submillimeter-Selected
Galaxies, in The Hy Redshift Universe ed A J Bunker and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 p. 425
Blain A W., et al. (2002) The 60µm
Extragalactic Background Radiation Intensity, Dust-Enshrouded Active
Galactic Nuclei and the Assembly of Groups and Clusters of Galaxies
MNRAS 333 222
Brandt W N (2001) The Chandra Deep Field North
Survey. V. 1 Ms Source Catalogs
Astron. J. 122 2810
Brandt W N (2002) The Chandra Deep Field-North
Survey. XI. X-Ray Emission from Luminous Infrared Starburst Galaxies
Ap. J. 568 85
Bunker A J et al. (2003) A Star-Forming Galaxy at
z = 5.78 in the Chandra Deep Field South
MNRAS 342 L47
Calzetti D et al. (2000) The Dust Content and
Opacity of Actively Star-forming Galaxies
Ap. J. 533 682
Chapman S C et al. (2003) Uncoveringt the Redshifrt
Distribution of Submillimetre Galaxies
Nature 422 695
Charlot S and Fall S (1993) Lyman- Emission from Galaxies
Ap. J. 415 580
Connolly A J et al. (1995) Spectral Classification
of Galaxies: an Orthogonal Approach
Astron. J. 110 1071
Dawson S et al. (2002) A Galactic Wind at z =
5.190
Ap. J. 570 92
de Breuck C et al. (2000) A Sample of 669 Ultra
Steep Spectrum Radio Sources to Find High Redshift Radio Galaxies
Astron. Ap. Sup. 143 303
Dey A et al. (1998) A Galaxy at z = 5.34
Ap. J. 498, L93
Ellis R et al. (2001) A Faint Star-forming System Viewed through the Lensing Cluster Abell 2218: First Light at
Emission from Galaxies
Ap. J. 415 580
Connolly A J et al. (1995) Spectral Classification
of Galaxies: an Orthogonal Approach
Astron. J. 110 1071
Dawson S et al. (2002) A Galactic Wind at z =
5.190
Ap. J. 570 92
de Breuck C et al. (2000) A Sample of 669 Ultra
Steep Spectrum Radio Sources to Find High Redshift Radio Galaxies
Astron. Ap. Sup. 143 303
Dey A et al. (1998) A Galaxy at z = 5.34
Ap. J. 498, L93
Ellis R et al. (2001) A Faint Star-forming System Viewed through the Lensing Cluster Abell 2218: First Light at
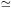 5.6?
Ap. J. 560 L119
Eggen O J, Lynden-Bell D and Sandage A R (1962)
Evidence from the Motions of Old Stars that the Galaxy Collapsed
Ap. J. 136, 748
Fan X et al. (2001) A Survey of z > 5.8
Quasars in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. I. Discovery of Three New
Quasars and the Spatial Density of Luminous Quasars at z ~ 6
Astron. J. 122, 2833
Fan X et al. (2002) Evolution of the Ionizing
Background and the Epoch of Reionization from the Spectra of z ~
6 Quasars
Astron. J. 123 1247
Fernandez-Soto A, Lanzetta K and Yahil A (1999) A
New Catalog of Photometric Redshifts in the Hubble Deep Field
Ap. J. 513 34
Frayer D et al. (1998) Molecular Gas in the z
= 2.8 Submillimeter Galaxy SMM 02399-0136
Ap. J. 506 L7
Frye B et al. (2002) Spectral Evidence for
Widespread Galaxy Outflows at z > 4
Ap. J. 568 558
Fynbo J Möller P, and Thomsen B (2001) Probing
the Faint End of the Galaxy Luminosity Function at z = 3 with
Ly
5.6?
Ap. J. 560 L119
Eggen O J, Lynden-Bell D and Sandage A R (1962)
Evidence from the Motions of Old Stars that the Galaxy Collapsed
Ap. J. 136, 748
Fan X et al. (2001) A Survey of z > 5.8
Quasars in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. I. Discovery of Three New
Quasars and the Spatial Density of Luminous Quasars at z ~ 6
Astron. J. 122, 2833
Fan X et al. (2002) Evolution of the Ionizing
Background and the Epoch of Reionization from the Spectra of z ~
6 Quasars
Astron. J. 123 1247
Fernandez-Soto A, Lanzetta K and Yahil A (1999) A
New Catalog of Photometric Redshifts in the Hubble Deep Field
Ap. J. 513 34
Frayer D et al. (1998) Molecular Gas in the z
= 2.8 Submillimeter Galaxy SMM 02399-0136
Ap. J. 506 L7
Frye B et al. (2002) Spectral Evidence for
Widespread Galaxy Outflows at z > 4
Ap. J. 568 558
Fynbo J Möller P, and Thomsen B (2001) Probing
the Faint End of the Galaxy Luminosity Function at z = 3 with
Ly Emission
Astron. Ap. 374 443
Fynbo J et al. (2002) Deep
Ly
Emission
Astron. Ap. 374 443
Fynbo J et al. (2002) Deep
Ly Imaging of Two z =
2.04 GRB Host Galaxy Fields
Astron. and Ap. 388 425
Genzel R et al (2003) patially Resolved Millimeter
Interferometry of SMM J02399-0136: A Very Massive Galaxy at z =
2.8
Ap. J. 584 633
Giavalisco M (2002) Lyman-Break Galaxies
Ann. Revs. Astron. and Ap. 40 579
Granato G L, et al. (2001) Joint Formation of
QSOs and Spheroids: QSOs as Clocks of Star Formation in Spheroids
MNRAS 324 757
Haiman Z (2002) The Detectability of High-Redshift
Ly
Imaging of Two z =
2.04 GRB Host Galaxy Fields
Astron. and Ap. 388 425
Genzel R et al (2003) patially Resolved Millimeter
Interferometry of SMM J02399-0136: A Very Massive Galaxy at z =
2.8
Ap. J. 584 633
Giavalisco M (2002) Lyman-Break Galaxies
Ann. Revs. Astron. and Ap. 40 579
Granato G L, et al. (2001) Joint Formation of
QSOs and Spheroids: QSOs as Clocks of Star Formation in Spheroids
MNRAS 324 757
Haiman Z (2002) The Detectability of High-Redshift
Ly Emission Lines prior
to the Reionization of the Universe
Ap. J. 576 L1
Hu E, McMahon R G and Cowie L (1999) An Extremely
Luminous Galaxy at z = 5.74
Ap. J. 522 9
Hu E et al. (2002) A Redshift z = 6.56 Galaxy
behind the Cluster Abell 370
Ap. J. (L) 568 L75
Hu E M, Cowie L L and McMahon R G (2002) ERRATUM: A
Redshift z = 6.56 Galaxy behind the Cluster Abell 370
Ap. J. 576 L99
Iwata I et al. (2003) Lyman Break Galaxies at
z ~ 5: Luminosity Function.
P.A.S.J. 55 415
Klypin A et al. (1999) Where Are the Missing
Galactic Satellites?
Ap. J. 522 82
Kodaira K, Taniguchi Y et al. (2003). The Discovery
of Two Ly
Emission Lines prior
to the Reionization of the Universe
Ap. J. 576 L1
Hu E, McMahon R G and Cowie L (1999) An Extremely
Luminous Galaxy at z = 5.74
Ap. J. 522 9
Hu E et al. (2002) A Redshift z = 6.56 Galaxy
behind the Cluster Abell 370
Ap. J. (L) 568 L75
Hu E M, Cowie L L and McMahon R G (2002) ERRATUM: A
Redshift z = 6.56 Galaxy behind the Cluster Abell 370
Ap. J. 576 L99
Iwata I et al. (2003) Lyman Break Galaxies at
z ~ 5: Luminosity Function.
P.A.S.J. 55 415
Klypin A et al. (1999) Where Are the Missing
Galactic Satellites?
Ap. J. 522 82
Kodaira K, Taniguchi Y et al. (2003). The Discovery
of Two Ly Emitters
Beyond Redshift 6 in the Subaru Deep Field
P.A.S.J. 55 L17
Kudritzki R. et al. (2000) Discovery of Nine
Ly
Emitters
Beyond Redshift 6 in the Subaru Deep Field
P.A.S.J. 55 L17
Kudritzki R. et al. (2000) Discovery of Nine
Ly Emitters at Redshift
z ~ 3.1 Using Narrowband Imaging and VLT Spectroscopy
Ap.J. 536 19
Kulkarni S et al. (1998) The Afterglow, Redshift and
Extreme Energetics of the Gamma-Ray Burst of 23 January
1999 Nature 393 35
Kunth D et al. (1998) HST study of
Ly
Emitters at Redshift
z ~ 3.1 Using Narrowband Imaging and VLT Spectroscopy
Ap.J. 536 19
Kulkarni S et al. (1998) The Afterglow, Redshift and
Extreme Energetics of the Gamma-Ray Burst of 23 January
1999 Nature 393 35
Kunth D et al. (1998) HST study of
Ly Emission in Star-Forming
Galaxies: the Effect of Neutral Gas Flows
Astron. and Ap. 334 11
Lanzetta K et al. (1999) in The Hy Redshift Universe
ed A J Bunker and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 p. 544
Lehnert M D and Bremer M (2003) Luminous Lyman Break
Galaxies at z > 5 and the Source of Reionization
Ap. J. 593 in press, astro-ph/0212431
Lilly S and Longair M (1984) Stellar Populations in
Distant Radio Galaxies
MNRAS 211 833
Lilly S et al. (1996) The Canada-France Redshift
Survey: The Luminosity Density and Star Formation History of the
Universe to
z
Emission in Star-Forming
Galaxies: the Effect of Neutral Gas Flows
Astron. and Ap. 334 11
Lanzetta K et al. (1999) in The Hy Redshift Universe
ed A J Bunker and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 p. 544
Lehnert M D and Bremer M (2003) Luminous Lyman Break
Galaxies at z > 5 and the Source of Reionization
Ap. J. 593 in press, astro-ph/0212431
Lilly S and Longair M (1984) Stellar Populations in
Distant Radio Galaxies
MNRAS 211 833
Lilly S et al. (1996) The Canada-France Redshift
Survey: The Luminosity Density and Star Formation History of the
Universe to
z 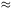 1
Ap. J. 460 L1
Loeb A and Barkana R (2001), The Reionization of the
Universe by the First Stars and Quasars
Ann. Revs. Astron. and Ap. 39 19
Madau P and Pozzetti L and Dickinson M (1998) The
Star Formation History of Field Galaxie
Ap. J. 498 106
Malhotra S and Rhoads J (2002) Large Equivalent
Width Ly
1
Ap. J. 460 L1
Loeb A and Barkana R (2001), The Reionization of the
Universe by the First Stars and Quasars
Ann. Revs. Astron. and Ap. 39 19
Madau P and Pozzetti L and Dickinson M (1998) The
Star Formation History of Field Galaxie
Ap. J. 498 106
Malhotra S and Rhoads J (2002) Large Equivalent
Width Ly ; line Emission
at z = 4.5: Young Galaxies in a Young Universe?
Ap. J. 565 L71
Malhotra S et al. (2003) No X-Ray-bright Type II
Quasars among the Ly
; line Emission
at z = 4.5: Young Galaxies in a Young Universe?
Ap. J. 565 L71
Malhotra S et al. (2003) No X-Ray-bright Type II
Quasars among the Ly Emitters
Ap. J. 585 25
Osmer P S (1999) in The Hy Redshift Universe ed A J
Bunker and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 566
Ouchi M et al. (2002) Subaru Deep
Survey. II. Luminosity Functions and Clustering Properties of
Ly
Emitters
Ap. J. 585 25
Osmer P S (1999) in The Hy Redshift Universe ed A J
Bunker and W van Breugel
ASP Conf. Ser. 193 566
Ouchi M et al. (2002) Subaru Deep
Survey. II. Luminosity Functions and Clustering Properties of
Ly Emitters at z
= 4.86 in the Subaru Deep Field
Ap. J. 582, 60
Partridge R B and Peebles P J E (1967) Are Young
Galaxies Visible?
Ap. J. 147 868
Pentericci L et al. (2002a) VLT Optical and
Near-Infrared Observations of the z = 6.28 Quasar SDSS J1030+0524
Astron. J. 123 2151
Pentericci L et al. (2002b) The VLT and the Most
Distant Quasars,
ESO Messinger 108, 24
Pettini M et al. (2001) The Rest-Frame Optical
Spectra of Lyman Break Galaxies: Star Formation, Extinction, Abundances,
and Kinematics
Ap. J. 554 981
Press W H and Schecter P (1974) Formation of
Galaxies and Clusters of Galaxies by Self-Similar Gravitational
Condensation
Ap. J. 187 425
Pritchet C (1994) The Search for Primeval Galaxies
PASP 106 1994
Rhoads J et al. (2003) Spectroscopic Confirmation of
Three Redshift 5.7 Lyman-alpha Emitters from the Large Area Lyman Alpha
Survey
Astron. J. 125 1006
Ridgway S E et al. (2001) NICMOS Imaging of the
Host Galaxies of z 2-3 Radio-quiet Quasars
Astron. J. 550 122
Schaerer D (2002) The Transition from Population III
to Normal Galaxies: Ly
Emitters at z
= 4.86 in the Subaru Deep Field
Ap. J. 582, 60
Partridge R B and Peebles P J E (1967) Are Young
Galaxies Visible?
Ap. J. 147 868
Pentericci L et al. (2002a) VLT Optical and
Near-Infrared Observations of the z = 6.28 Quasar SDSS J1030+0524
Astron. J. 123 2151
Pentericci L et al. (2002b) The VLT and the Most
Distant Quasars,
ESO Messinger 108, 24
Pettini M et al. (2001) The Rest-Frame Optical
Spectra of Lyman Break Galaxies: Star Formation, Extinction, Abundances,
and Kinematics
Ap. J. 554 981
Press W H and Schecter P (1974) Formation of
Galaxies and Clusters of Galaxies by Self-Similar Gravitational
Condensation
Ap. J. 187 425
Pritchet C (1994) The Search for Primeval Galaxies
PASP 106 1994
Rhoads J et al. (2003) Spectroscopic Confirmation of
Three Redshift 5.7 Lyman-alpha Emitters from the Large Area Lyman Alpha
Survey
Astron. J. 125 1006
Ridgway S E et al. (2001) NICMOS Imaging of the
Host Galaxies of z 2-3 Radio-quiet Quasars
Astron. J. 550 122
Schaerer D (2002) The Transition from Population III
to Normal Galaxies: Ly and He II Emission and the Ionising Properties of High Redshift
Starburst Galaxies
Astron. and Ap. 397, 527
Schmidt M (1965) Optical Spectra and Redshifts of 31
Radio Galaxies.
Ap. J. 141 1
Schneider D P, Schmidt M and Gunn J E (1991) PC 1247
+ 3406 - an Optically Selected Quasar with a Redshift of 4.897
Astron. J. 102 837
Searle, L and Zinn, R (1978) Compositions of Halo
Clusters and the Formation of the Galactic Halo
Ap. J. 225 357
Shapley A E et al. (2001) The Rest-Frame Optical
Properties of z
and He II Emission and the Ionising Properties of High Redshift
Starburst Galaxies
Astron. and Ap. 397, 527
Schmidt M (1965) Optical Spectra and Redshifts of 31
Radio Galaxies.
Ap. J. 141 1
Schneider D P, Schmidt M and Gunn J E (1991) PC 1247
+ 3406 - an Optically Selected Quasar with a Redshift of 4.897
Astron. J. 102 837
Searle, L and Zinn, R (1978) Compositions of Halo
Clusters and the Formation of the Galactic Halo
Ap. J. 225 357
Shapley A E et al. (2001) The Rest-Frame Optical
Properties of z 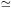 3 Galaxies.
Ap. J. 562 95
Somerville R and Primack J (1999) Semi-Analytic
Modelling of Galaxy Formation: the Local Universe
MNRAS 310 1087
Spinrad H et al. (1998) A z = 5.34 Galaxy
Pair in the Hubble Deep Field
Astron. J. 116, 2617
Spinrad H Stern D, Dawson S and the GOODS team
(2003) work in progress.
Steidel C et al. (1999) Lyman-Break Galaxies at
z
3 Galaxies.
Ap. J. 562 95
Somerville R and Primack J (1999) Semi-Analytic
Modelling of Galaxy Formation: the Local Universe
MNRAS 310 1087
Spinrad H et al. (1998) A z = 5.34 Galaxy
Pair in the Hubble Deep Field
Astron. J. 116, 2617
Spinrad H Stern D, Dawson S and the GOODS team
(2003) work in progress.
Steidel C et al. (1999) Lyman-Break Galaxies at
z 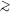 4 and
the Evolution of the Ultraviolet Luminosity Density at High Redshift
Ap. J. 519 1
Stern D and Spinrad H (1999) Search Techniques for
Distant Galaxies
PASP 111 1475
Stern D et al. (2003) Spectroscopic Confirmation of
a Radio-Selected Galaxy Over-Density at z = 1.11
Astron. J. 125 2759
Stiavelli M (2002) Exploring the Cosmic Dark Ages
with the Next Generation of Space and Ground-Based Facilities in Future
Research Directions and Visions for Astronomy, ed A. Dressler, A M
Proceedings of the SPIE,
4835, 122 (astro-ph/0208544)
Taniguchi Y et al. (2003) The Discovery of a Very
Narrow-Line Star Forming Object at a Redshift of 5.66
Ap. J. 585 L97
Thompson D and Djorgovski S G (1995) Serendipitous
Long-Slit Surveys for Primeval Galaxies
Astron. J. 110 982
Tenorio-Tagle G et al. (1999) The Evolution of
Superbubbles and the Detection of
Ly
4 and
the Evolution of the Ultraviolet Luminosity Density at High Redshift
Ap. J. 519 1
Stern D and Spinrad H (1999) Search Techniques for
Distant Galaxies
PASP 111 1475
Stern D et al. (2003) Spectroscopic Confirmation of
a Radio-Selected Galaxy Over-Density at z = 1.11
Astron. J. 125 2759
Stiavelli M (2002) Exploring the Cosmic Dark Ages
with the Next Generation of Space and Ground-Based Facilities in Future
Research Directions and Visions for Astronomy, ed A. Dressler, A M
Proceedings of the SPIE,
4835, 122 (astro-ph/0208544)
Taniguchi Y et al. (2003) The Discovery of a Very
Narrow-Line Star Forming Object at a Redshift of 5.66
Ap. J. 585 L97
Thompson D and Djorgovski S G (1995) Serendipitous
Long-Slit Surveys for Primeval Galaxies
Astron. J. 110 982
Tenorio-Tagle G et al. (1999) The Evolution of
Superbubbles and the Detection of
Ly ; in Star-Forming Galaxies
MNRAS 309 332
van Breugel W et al. (1999) A Radio Galaxy at
z = 5.19
Ap. J. 518 61
Venemans B P et al. (2002) The Most Distant
Structure of Galaxies Known: A Protocluster at z = 4.1
Ap. J. 569 L11
Weinberg D H et al. (1999) in Photometric Redshifts
and High Redshift Galaxies ed R J Weymann, L Storrie-Lombardi, M Sawicki
and R Brunner
ASP Conf. Ser. 191 341
Weymann R J et al. (1998) Keck Spectroscopy and
NICMOS Photometry of a Redshift z = 5.60 Galaxy.
Ap. J. 505 L95
White S and Rees M (1978) Core Condensation in Heavy
Halos - A Two-Stage Theory for Galaxy Formation and Clustering
MNRAS 183 341
; in Star-Forming Galaxies
MNRAS 309 332
van Breugel W et al. (1999) A Radio Galaxy at
z = 5.19
Ap. J. 518 61
Venemans B P et al. (2002) The Most Distant
Structure of Galaxies Known: A Protocluster at z = 4.1
Ap. J. 569 L11
Weinberg D H et al. (1999) in Photometric Redshifts
and High Redshift Galaxies ed R J Weymann, L Storrie-Lombardi, M Sawicki
and R Brunner
ASP Conf. Ser. 191 341
Weymann R J et al. (1998) Keck Spectroscopy and
NICMOS Photometry of a Redshift z = 5.60 Galaxy.
Ap. J. 505 L95
White S and Rees M (1978) Core Condensation in Heavy
Halos - A Two-Stage Theory for Galaxy Formation and Clustering
MNRAS 183 341