In Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Disks ASP
Conference Series, Vol. 396, Proceedings of the conference held 1-5
October, 2007 at the Centro Convegni Matteo Ricci, Rome, Italy. Edited
by José G. Funes, S.J., and Enrico Maria Corsini. San Francisco:
Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 2008., p.297
astro-ph/0810.2534
For a PDF version of the article, click here.
SECULAR EVOLUTION IN DISK GALAXIES: PSEUDOBULGE GROWTH AND THE
FORMATION OF SPHEROIDAL GALAXIES
John Kormendy and David B. Fisher
Department of
Astronomy,
University of Texas at
Austin,
1 University Station C1400, Austin, TX 78712-0259, USA;
MPI für
Extraterr. Physik, Postfach 1312, 85741 Garching, Germany;
Universitäts-Sternwarte, Scheinerstrasse 1, 81679 Munich, Germany
Abstract. Updating Kormendy & Kennicutt (2004, ARA&A, 42,
603), we review internal secular evolution of galaxy disks. One
consequence is the growth of pseudobulges that often are mistaken for
true (merger-built) bulges. Many pseudobulges are recognizable as cold,
rapidly rotating, disky structures. Bulges have Sérsic function
brightness profiles with index n
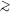 2 while most pseudobulges have n
2 while most pseudobulges have n
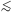 2. Recognition of pseudobulges makes the biggest problem with cold dark
matter galaxy formation more acute: How can hierarchical clustering make
so many pure disk galaxies with no evidence for merger-built bulges?
E. g., the giant Scd galaxies M 101 and NGC 6946 have rotation
velocities of Vcirc ~ 200
km s-1 but nuclear star clusters with velocity
dispersions of 25 to 40 km s-1. Within 8 Mpc of us, 11
of 19 galaxies with Vcirc > 150
km s-1 show no evidence for a classical bulge, one
may contain a classical plus a pseudo bulge, and 7 are ellipticals or
have classical bulges. So it is hard to understand how bulgeless
galaxies could form as the quiescent tail of a distribution of merger
histories.
2. Recognition of pseudobulges makes the biggest problem with cold dark
matter galaxy formation more acute: How can hierarchical clustering make
so many pure disk galaxies with no evidence for merger-built bulges?
E. g., the giant Scd galaxies M 101 and NGC 6946 have rotation
velocities of Vcirc ~ 200
km s-1 but nuclear star clusters with velocity
dispersions of 25 to 40 km s-1. Within 8 Mpc of us, 11
of 19 galaxies with Vcirc > 150
km s-1 show no evidence for a classical bulge, one
may contain a classical plus a pseudo bulge, and 7 are ellipticals or
have classical bulges. So it is hard to understand how bulgeless
galaxies could form as the quiescent tail of a distribution of merger
histories.
Our second theme is environmental secular evolution. We confirm that
spheroidal galaxies have fundamental plane correlations that are almost
perpendicular to those for bulges and elliptical galaxies. Spheroidals
are not dwarf ellipticals. Rather, their structural parameters are
similar to those of late-type galaxies. We suggest that spheroidals are
defunct late-type galaxies transformed by internal processes such as
supernova-driven gas ejection and environmental processes such as
secular harassment and ram-pressure stripping.
Minus spheroidals, the fundamental plane correlations for ellipticals
and bulges have small scatter. With respect to these, pseudobulges are
larger and less dense. They fade out by becoming fluffy, not by
becoming compact, like nuclei. Pseudobulges and nuclear star clusters
appear to have different origins.
Keywords galaxies: bulges, galaxies: evolution, galaxies:
formation, galaxies: photometry, galaxies: kinematics and dynamics,
galaxies: nuclei, galaxies: structure
Table of Contents

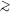 2 while most pseudobulges have n
2 while most pseudobulges have n
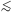 2. Recognition of pseudobulges makes the biggest problem with cold dark
matter galaxy formation more acute: How can hierarchical clustering make
so many pure disk galaxies with no evidence for merger-built bulges?
E. g., the giant Scd galaxies M 101 and NGC 6946 have rotation
velocities of Vcirc ~ 200
km s-1 but nuclear star clusters with velocity
dispersions of 25 to 40 km s-1. Within 8 Mpc of us, 11
of 19 galaxies with Vcirc > 150
km s-1 show no evidence for a classical bulge, one
may contain a classical plus a pseudo bulge, and 7 are ellipticals or
have classical bulges. So it is hard to understand how bulgeless
galaxies could form as the quiescent tail of a distribution of merger
histories.
2. Recognition of pseudobulges makes the biggest problem with cold dark
matter galaxy formation more acute: How can hierarchical clustering make
so many pure disk galaxies with no evidence for merger-built bulges?
E. g., the giant Scd galaxies M 101 and NGC 6946 have rotation
velocities of Vcirc ~ 200
km s-1 but nuclear star clusters with velocity
dispersions of 25 to 40 km s-1. Within 8 Mpc of us, 11
of 19 galaxies with Vcirc > 150
km s-1 show no evidence for a classical bulge, one
may contain a classical plus a pseudo bulge, and 7 are ellipticals or
have classical bulges. So it is hard to understand how bulgeless
galaxies could form as the quiescent tail of a distribution of merger
histories.
