


3.5. Dark Energy, or Worse?
If general relativity is correct, cosmic acceleration implies there must be a dark energy density which diminishes relatively slowly as the universe expands. This can be seen directly from the Friedmann equation (17), which implies
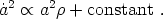 |
(77) |
From this relation, it is clear that the only way to get
acceleration (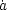 increasing) in an expanding universe
is if
increasing) in an expanding universe
is if 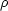 falls
off more slowly than a-2; neither matter
(
falls
off more slowly than a-2; neither matter
(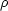 M
M
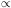 a-3)
nor radiation
(
a-3)
nor radiation
(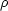 R
R
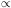 a-4) will do the trick.
Vacuum energy is, of course, strictly constant; but the data
are consistent with smoothly-distributed sources of dark energy
that vary slowly with time.
a-4) will do the trick.
Vacuum energy is, of course, strictly constant; but the data
are consistent with smoothly-distributed sources of dark energy
that vary slowly with time.
There are good reasons to consider dynamical dark energy as an alternative to an honest cosmological constant. First, a dynamical energy density can be evolving slowly to zero, allowing for a solution to the cosmological constant problem which makes the ultimate vacuum energy vanish exactly. Second, it poses an interesting and challenging observational problem to study the evolution of the dark energy, from which we might learn something about the underlying physical mechanism. Perhaps most intriguingly, allowing the dark energy to evolve opens the possibility of finding a dynamical solution to the coincidence problem, if the dynamics are such as to trigger a recent takeover by the dark energy (independently of, or at least for a wide range of, the parameters in the theory). To date this hope has not quite been met, but dynamical mechanisms at least allow for the possibility (unlike a true cosmological constant).
The simplest possibility along these lines
involves the same kind of source
typically invoked in models of inflation in the very early universe:
a scalar field  rolling slowly in a potential, sometimes known as "quintessence"
[92,
93,
94,
95,
96,
97].
The energy density of a scalar field is a sum of kinetic, gradient,
and potential energies,
rolling slowly in a potential, sometimes known as "quintessence"
[92,
93,
94,
95,
96,
97].
The energy density of a scalar field is a sum of kinetic, gradient,
and potential energies,
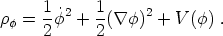 |
(78) |
For a homogeneous field (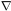

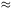 0),
the equation of motion in an expanding universe is
0),
the equation of motion in an expanding universe is
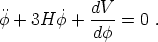 |
(79) |
If the slope of the potential V is quite flat, we will have
solutions for which
 is nearly
constant throughout space and
only evolving very gradually with time; the energy density in
such a configuration is
is nearly
constant throughout space and
only evolving very gradually with time; the energy density in
such a configuration is
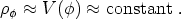 |
(80) |
Thus, a slowly-rolling scalar field is an appropriate candidate for dark energy.
However, introducing dynamics opens up the possibility
of introducing new problems, the form and severity of which will depend
on the specific kind of model being considered. Most quintessence
models feature scalar fields
 with masses of
order the current Hubble scale,
with masses of
order the current Hubble scale,
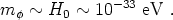 |
(81) |
(Fields with larger masses would typically have already rolled to the minimum of their potentials.) In quantum field theory, light scalar fields are unnatural; renormalization effects tend to drive scalar masses up to the scale of new physics. The well-known hierarchy problem of particle physics amounts to asking why the Higgs mass, thought to be of order 1011eV, should be so much smaller than the grand unification/Planck scale, 1025 - 1027 eV. Masses of 10-33 eV are correspondingly harder to understand. On top of that, light scalar fields give rise to long-range forces and time-dependent coupling constants that should be observable even if couplings to ordinary matter are suppressed by the Planck scale [98, 99]; we therefore need to invoke additional fine-tunings to explain why the quintessence field has not already been experimentally detected.
Nevertheless, these apparent fine-tunings might be worth the
price, if we were somehow able to explain the coincidence problem.
To date, many investigations have considered scalar fields with
potentials that asymptote gradually to zero, of the form
e1/ or
1 /
or
1 /  . These can
have cosmologically interesting
properties, including "tracking" behavior that makes the current
energy density largely independent of the initial conditions
[100].
They do not, however,
provide a solution to the coincidence problem, as the era in which
the scalar field begins to dominate is still set by finely-tuned
parameters in the theory. One way to address the coincidence
problem is to take advantage of the fact that matter/radiation
equality was a relatively recent occurrence (at least on a
logarithmic scale); if a scalar field has dynamics which are
sensitive to the difference between matter- and radiation-dominated
universes, we might hope that its energy density becomes constant
only after matter/radiation equality. An approach which takes this
route is k-essence
[101],
which modifies the form of the kinetic energy for the scalar field.
Instead of a conventional kinetic energy K = 1/2
(
. These can
have cosmologically interesting
properties, including "tracking" behavior that makes the current
energy density largely independent of the initial conditions
[100].
They do not, however,
provide a solution to the coincidence problem, as the era in which
the scalar field begins to dominate is still set by finely-tuned
parameters in the theory. One way to address the coincidence
problem is to take advantage of the fact that matter/radiation
equality was a relatively recent occurrence (at least on a
logarithmic scale); if a scalar field has dynamics which are
sensitive to the difference between matter- and radiation-dominated
universes, we might hope that its energy density becomes constant
only after matter/radiation equality. An approach which takes this
route is k-essence
[101],
which modifies the form of the kinetic energy for the scalar field.
Instead of a conventional kinetic energy K = 1/2
(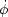 )2, in k-essence we posit a form
)2, in k-essence we posit a form
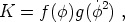 |
(82) |
where f and g are functions specified by the model. For certain choices of these functions, the k-essence field naturally tracks the evolution of the total radiation energy density during radiation domination, but switches to being almost constant once matter begins to dominate. Unfortunately, it seems necessary to choose a finely-tuned kinetic term to get the desired behavior [102].
An alternative possibility is that there is nothing special about the present era; rather, acceleration is just something that happens from time to time. This can be accomplished by oscillating dark energy [103]. In these models the potential takes the form of a decaying exponential (which by itself would give scaling behavior, so that the dark energy remained proportional to the background density) with small perturbations superimposed:
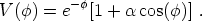 |
(83) |
On average, the dark energy in such a model will track that of the dominant matter/radiation component; however, there will be gradual oscillations from a negligible density to a dominant density and back, on a timescale set by the Hubble parameter, leading to occasional periods of acceleration. Unfortunately, in neither the k-essence models nor the oscillating models do we have a compelling particle-physics motivation for the chosen dynamics, and in both cases the behavior still depends sensitively on the precise form of parameters and interactions chosen. Nevertheless, these theories stand as interesting attempts to address the coincidence problem by dynamical means.
One of the interesting features of dynamical dark energy is that it is experimentally testable. In principle, different dark energy models can yield different cosmic histories, and, in particular, a different value for the equation of state parameter, both today and its redshift-dependence. Since the CMB strongly constrains the total density to be near the critical value, it is sensible to assume a perfectly flat universe and determine constraints on the matter density and dark energy equation of state; see figure (3.8) for some recent limits.
 |
Figure 3.8. Constraints on the dark-energy
equation-of-state parameter, as a function of
|
As can be seen in (3.8), one possibility that is consistent with the data is that w < - 1. Such a possibility violates the dominant energy condition, but possible models have been proposed [105]. However, such models run into serious problems when one takes them seriously as a particle physics theory [106, 107]. Even if one restricts one's attention to more conventional matter sources, making dark energy compatible with sensible particle physics has proven tremendously difficult.
Given the challenge of this problem, it is worthwhile considering the possibility that cosmic acceleration is not due to some kind of stuff, but rather arises from new gravitational physics. there are a number of different approaches to this [108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113] and we will not review them all here. Instead we will provide an example drawn from our own proposal [112].
As a first attempt, consider the simplest correction to the Einstein-Hilbert action,
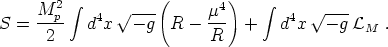 |
(84) |
Here µ is a new parameter with units of [mass] and
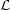 M is the
Lagrangian density for matter.
M is the
Lagrangian density for matter.
The fourth-order equations arising from this action are complicated
and it is difficult to extract details about cosmological evolution
from them. It is therefore convenient to transform from the frame
used in 84, which we call the matter frame, to the
Einstein frame, where the gravitational Lagrangian takes the
Einstein-Hilbert form and the additional degrees of freedom
( and
and  ) are represented by
a fictitious scalar field
) are represented by
a fictitious scalar field
 .
The details of this can be found in
[112]. Here we
just state that, performing a simultaneous redefinition of the time
coordinate, in terms of the new metric
.
The details of this can be found in
[112]. Here we
just state that, performing a simultaneous redefinition of the time
coordinate, in terms of the new metric
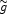 µ
µ , our theory is that of a scalar field
, our theory is that of a scalar field
 (xµ) minimally coupled to
Einstein gravity, and non-minimally coupled to matter, with potential
(xµ) minimally coupled to
Einstein gravity, and non-minimally coupled to matter, with potential
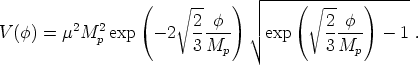 |
(85) |
Now let us first focus on vacuum cosmological solutions.
The beginning of the Universe corresponds to
R 
 and
and

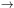 0. The initial
conditions we must specify are the initial values of
0. The initial
conditions we must specify are the initial values of
 and
and
 ', denoted
as
', denoted
as  i
and
i
and  'i.
For simplicity we take
'i.
For simplicity we take
 i
<< Mp. There are then three qualitatively
distinct outcomes, depending on the value of
i
<< Mp. There are then three qualitatively
distinct outcomes, depending on the value of
 'i.
'i.
1. Eternal de Sitter. There is a critical value of
 'i
'i

 'C
for which
'C
for which  just
reaches the maximum of the potential
V(
just
reaches the maximum of the potential
V( ) and
comes to rest. In this case the Universe
asymptotically evolves to a de Sitter solution. This
solution requires tuning and is unstable, since any perturbation will
induce the field to roll away from the maximum of its potential.
) and
comes to rest. In this case the Universe
asymptotically evolves to a de Sitter solution. This
solution requires tuning and is unstable, since any perturbation will
induce the field to roll away from the maximum of its potential.
2. Power-Law Acceleration. For
 'i >
'i >
 'C, the
field overshoots the maximum of
V(
'C, the
field overshoots the maximum of
V( ) and
the Universe evolves to
late-time power-law inflation, with observational consequences similar
to dark energy with equation-of-state parameter wDE =
-2/3.
) and
the Universe evolves to
late-time power-law inflation, with observational consequences similar
to dark energy with equation-of-state parameter wDE =
-2/3.
3. Future Singularity. For
 'i
<
'i
<
 'C,
'C,
 does not reach the maximum of its potential and rolls back down to
does not reach the maximum of its potential and rolls back down to
 = 0. This
yields a future curvature singularity.
= 0. This
yields a future curvature singularity.
In the more interesting case in which the Universe contains matter, it is possible to show that the three possible cosmic futures identified in the vacuum case remain in the presence of matter.
By choosing µ ~ 10-33 eV, the corrections to the standard cosmology only become important at the present epoch, making this theory a candidate to explain the observed acceleration of the Universe without recourse to dark energy. Since we have no particular reason for this choice, such a tuning appears no more attractive than the traditional choice of the cosmological constant.
Clearly our choice of correction to the gravitational action can be generalized. Terms of the form - µ2(n+1) / Rn, with n > 1, lead to similar late-time self acceleration, with behavior similar to a dark energy component with equation of state parameter
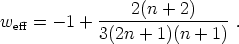 |
(86) |
Clearly therefore, such modifications can
easily accommodate current observational bounds
[104,
73]
on the equation of state parameter
-1.45 < wDE < - 0.74 (95% confidence level).
In the asymptotic regime n = 1 is ruled out at this level, while
n 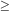 2 is allowed; even
n = 1 is permitted if we are near the top of the potential.
2 is allowed; even
n = 1 is permitted if we are near the top of the potential.
Finally, any modification of the Einstein-Hilbert action must, of
course, be consistent with the classic solar system tests of gravity
theory, as well as numerous other astrophysical dynamical tests.
We have chosen the coupling constant µ to be very small, but
we have also introduced a new light degree of freedom. Chiba
[114] has
pointed out
that the model with n = 1 is equivalent to Brans-Dicke
theory with  = 0 in the
approximation where the potential
was neglected, and would therefore be inconsistent with experiment.
It is not yet clear whether including the potential, or considering
extensions of the original model, could alter this conclusion.
= 0 in the
approximation where the potential
was neglected, and would therefore be inconsistent with experiment.
It is not yet clear whether including the potential, or considering
extensions of the original model, could alter this conclusion.