


3. The Open Model
The so-called Open Model (13) is the case where k = -1 and the geometry is said to be hyperbolic. Taking k = -1 in the Friedmann equations (29), (28),
Solving these equations
(39), (40) yields the same value
of the density (37) as the closed model, but in this
case q < 1/2 and
13 Although it is a standard practice to
refer to this case
(k = -1) as the `Open' Model, it should be noted that the model
can actually correspond to a closed universe. This is the result
of a non-trivial topology, which results in geometry that can be
hyperbolic; but, the topology can cause it to be contained in a
finite space [16,
17].
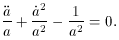
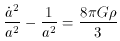
 < 1, as previously discussed.
< 1, as previously discussed.