Redshifts of Galaxies
Stromberg's original list
[258] of optical radial velocities
contained 41 galaxies. Some forty years later optical redshifts for
583 galaxies were published
[146]. In the RC1 and RC2
([7,
8] in
Secondary Galaxy Catalogs) some
280 references to sources of optical velocity data are
listed (Tables 12 and 13, respectively), with an additional 538
references to optical redshifts being found in RC3
([9] in
Secondary Galaxy Catalogs).
Velocity data is no longer restricted to the optical measurements but
includes derivations from 21-cm radio observations (see for instance
[148,
262], Table V2 in RC2, and
209 references to radio wavelength redshifts in RC3, complete to 1987);
corrections for errors in redshifts
[232].
A major compilation
[206] contains redshifts and
original references for 8,250 galaxies, complete to 1980 and supersedes
[121];
cross-correlation redshifts are discussed for
59 galaxies in [167];
redshifts for 115 galaxies
[248];
a study of a complete sample of field galaxies
[174];
data for 1093 galaxies with mpg
< 15.5 mag in a 6 degree strip across the North Galactic Cap
[145]; the southern
sky redshift survey
[63]; radial velocities
for 301 pairs
of galaxies
[158]; 44 galaxies in Perseus
[106];
359 galaxies in Abell clusters
[280]; 285 galaxies
observed for bulge-to-disk ratio estimates
[241];
IRAS galaxies in the Bootes Void area
[268]; a deep
survey of 280 galaxies
[175]; deep survey of IRAS
galaxies towards the Bootes Void
[89]; 5 suspected
superclusters [53]; s-type Markarian galaxies
[149];
multi-object spectroscopy of galaxies in
Abell 400, 576, 1767 and 2124
[135]; 102 dwarf galaxies
[96]; 75
galaxies in Abell 2256
[172]; 387 southern compact
and bright-nuclei galaxies
[102,
103];
84 brightest Abell cluster galaxies
[242]; 100
galaxies in 10 clusters
[219]; 161 galaxies in 11
clusters [101];
71 galaxies in the Indus region
[62]; galaxies in
Abell 496 and 2052
[220]; Tololo
emission-line galaxies
[28]; 298 late-type
galaxies in the
Virgo Cluster
[137]; 155 galaxies in
the winter Galactic Plane
[196]; 135 galaxies in the
Virgo region
[97]; 472 galaxies in the
Pisces-Perseus supercluster
[120]; 100 galaxies in the
Coma Cluster
[263]; high-precision
21cm redshifts
for 625 galaxies
[264]; low surface
brightness objects
[244]; 150 galaxies in the
Hercules supercluster
[260]; 123 galaxies in the
Cancer cluster
[12]; 83 galaxies in
poor cD clusters
[18]; 21cm velocities
for 440 galaxies betwen the Local
supercluster and the Hydra-Centaurus supercluster
[228];
71 galaxies in the Hydra I (Abell 1060) cluster
[229];
469 elliptical galaxies
[67]; 342 galaxies
toward the Bootes Void
[257]; 88 image-tube
spectra of 79 galaxies
[165]; flux-limited
sample of 72 IRAS galaxies
[249];
21cm velocities for 342 out of 415 galaxies, and
383 galaxies observed in the Pisces-Perseus supercluster
[118,
119,
127]; 228
southern galaxies
[64]; Medium Sensitivity
Survey X-ray sources
[116]; several hundred
spiral galaxies in 10 clusters
[31]; 21cm redshifts
for 324 isolated galaxies
[126]; 26 galaxies in the
direction of the Coma/Abell 1367 supercluster
[123];
92 galaxies in the direction of the
Coma cluster
[265]; flux-limited
sample of IRAS galaxies
[269]; 129 galaxies in
groups and clusters
[51];
approximately 40 galaxy redshifts in each of 14 rich
clusters [55];
1,268 radial velocities in 15 rich
clusters [95]; 157
galaxies in 54 triplets
[161]; galaxies in the
Horologium region
[52]; 559 Selected Area
94 objects
[17];
719 bright galaxies
[235]; 21cm observations
of 1787 nearby galaxies
[105]; 21cm observations for
183 galaxies
[262]; 164 field
galaxies brighter than
B ~ 15.5 mag
[174]; 90 IRAS galaxies
[133]; 172 central
galaxies and companions
[7]; 530 IRAS galaxies
[184]; 70
peculiar objects
[191]; redshifts in
Klemola 27
[225];
21cm observations for galaxies in the Pegasus I cluster
[226];
156 binary systems [275];
145 blue Zwicky compact galaxies
[179]; 160 galaxies
in Abell 194
[50]; 289 galaxies in
Abell 539
[201];
107 southern galaxies
[207];
266 galaxies in the Hydra-Centaurus region
[104]; the
Fornax cluster
[154,
227]; 300
galaxies in a strip crossing the Coma cluster
[160];
galaxies with supernovae
[13,
14,
15,
16]; compilation of
double galaxy
redshifts [215];
radial velocities of isolated
galaxies [162];
39 peculiar ESO galaxies
[29];
redshifts for Karachensteva isolated galaxies
[163],
and for Karachentsev isolated triples
[164];
radial velocities for 21 interacting double
galaxies [159]; Zwicky
compact galaxies
[239].
Accidental and systematic errors in various sets of velocity
measurements are discussed in
[10,
86,
141,
185,
203,
230,
232]. A
total of 2,713 velocities are reduced to a standard system in RC2; this
was increased to 16,693 in RC3.
Corrections for the Solar Motion:
Radial velocities, V, when referred to the Galactic centre, must be
corrected for the orbital motion of the Sun. Most researchers in the
field (e.g.,
[236] or RC2) adopt
the standard correction of
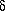 V =
300sinl x cosb km/s
V =
300sinl x cosb km/s
where it is assumed that the Sun is moving at 300 km s-1 toward l
= 90 , b = 0, which is in good agreement with the estimate of V = (315 ± 15) km s-1 toward l = 95, b = -8 for the Local Group
velocity centroid
[88].
= (315 ± 15) km s-1 toward l = 95, b = -8 for the Local Group
velocity centroid
[88].
Main |
Introduction |
Basic Data |
Galaxies
| Cosmology
| Particle Physics
Spectroscopy |
Glossary and Lexicon of Term |
Tabular Information
Graphical Relations |
Annual Review Articles |
Astrostatistics
CUP Monographs |
Author Index |
New Additions |
Catalogs
Table of Contents |
Text
Search |
Web Links
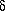 V =
300sinl x cosb km/s
V =
300sinl x cosb km/s
 = (315 ± 15) km s-1 toward l = 95, b = -8 for the Local Group
velocity centroid
[88].
= (315 ± 15) km s-1 toward l = 95, b = -8 for the Local Group
velocity centroid
[88].