


4.1. Measured Peculiar Velocities
These methods use data that include both redshifts and redshift-independent
distances to galaxies via POTENT-like reconstructions of the underlying
velocity and mass-density fields
[34],
independently of whole-sky redshift surveys.
Combined with the assumption of Gaussian initial fluctuations,
these methods provide lower bounds on
 m in various ways
[35],
such as
(a) using the fact that diverging flows in voids cannot be large
when
m in various ways
[35],
such as
(a) using the fact that diverging flows in voids cannot be large
when  m is low
because the voids cannot be more empty than empty
[36],
(b) using the skewness of
m is low
because the voids cannot be more empty than empty
[36],
(b) using the skewness of
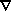 . v
as induced by
. v
as induced by  m-dependent
nonlinear gravity
[37],
and
(c) appealing to the mass-density initial probability distribution function
via a Zel'dovich ``time machine''
[38].
m-dependent
nonlinear gravity
[37],
and
(c) appealing to the mass-density initial probability distribution function
via a Zel'dovich ``time machine''
[38].
New developments:
The Mark III catalog of Tully-Fisher and
Dn -  peculiar velocities with more than 3000 galaxies has been completed
[39],
and several new samples are coming up soon.
peculiar velocities with more than 3000 galaxies has been completed
[39],
and several new samples are coming up soon.
 New, more accurate distance
indicators are being developed and implemented to larger samples.
Most promising are the methods based on surface-brightness fluctuations
for nearby galaxies, and supernovae type Ia for large-scale coverage
([40] for a review).
New, more accurate distance
indicators are being developed and implemented to larger samples.
Most promising are the methods based on surface-brightness fluctuations
for nearby galaxies, and supernovae type Ia for large-scale coverage
([40] for a review).
 The understanding of the systematic biases in the data and the analysis
is improving, and new methods for correcting them are being developed.
The understanding of the systematic biases in the data and the analysis
is improving, and new methods for correcting them are being developed.
Pro: These methods allow direct dynamical measures of
 m
independent of galaxy density biasing.
m
independent of galaxy density biasing.
Con:
The measurement of redshift-independent distances involves large errors
that grow in proportion to distance, and the analysis is therefore
limited to the relatively local cosmological volume, out to
~ 100 h-1Mpc in the best cases. The associated
cosmic scatter is inevitably large.
 Some of the distance indicators may be subject to systematic environmental
effects that are hard to identify.
Some of the distance indicators may be subject to systematic environmental
effects that are hard to identify.
 These methods ignore possible velocity biasing.
These methods ignore possible velocity biasing.
 The methods assume potential flow and Gaussian initial conditions.
These are valid hypotheses for the standard scenarios of structure formations,
but they might be invalid in more esoteric models, such as those based
on topological defects as seeds for structure formation.
The methods assume potential flow and Gaussian initial conditions.
These are valid hypotheses for the standard scenarios of structure formations,
but they might be invalid in more esoteric models, such as those based
on topological defects as seeds for structure formation.
Current Results: From
Mark III peculiar velocities using several methods:
 m > 0.3 at more
than 95% confidence (reviews:
[35]). From
the extracted mass power spectrum under the general CDM family of models
[41]:
m > 0.3 at more
than 95% confidence (reviews:
[35]). From
the extracted mass power spectrum under the general CDM family of models
[41]:
 8
8
 m0.6
= 0.8 ± 0.2.
m0.6
= 0.8 ± 0.2.