


1.2.2. "Extra" Relativistic Energy
Suppose there is some new physics beyond the standard model of
particle physics which leads to "extra" relativistic energy so that
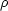 R
R
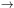
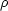 R'
R'

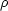 R
+
R
+ 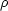 X;
hereafter, for convenience of notation, the subscript
R will be dropped. It is useful, and conventional, to account
for this extra energy in terms of the equivalent number of extra
neutrinos:
X;
hereafter, for convenience of notation, the subscript
R will be dropped. It is useful, and conventional, to account
for this extra energy in terms of the equivalent number of extra
neutrinos: 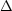 N
N

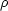 X /
X /
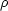
 (Steigman, Schramm,
& Gunn 1977
(SSG); see also
Hoyle & Tayler 1964,
Peebles 1966,
Shvartsman 1969).
In the presence of this extra energy,
prior to e± annihilation
(Steigman, Schramm,
& Gunn 1977
(SSG); see also
Hoyle & Tayler 1964,
Peebles 1966,
Shvartsman 1969).
In the presence of this extra energy,
prior to e± annihilation
 |
(1.21) |
In this case the early universe would expand faster than in the standard model. The pre-e± annihilation speedup in the expansion rate is
 |
(1.22) |
After e± annihilation there are similar, but
quantitatively different changes
 |
(1.23) |
Armed with an understanding of the evolution of the early universe and its particle content, we may now proceed to the main subject of these lectures, primordial nucleosynthesis.