

REFERENCES
A. H. Guth, "The inflationary universe: A
possible solution to the horizon and flatness problems,"
Phys. Rev. D 23, 347 (1981).
A. D. Linde, "A new inflationary universe
scenario:
A possible solution of the horizon, flatness, homogeneity, isotropy and
primordial monopole problems,"
Phys. Lett. B 108, 389 (1982).
A. Albrecht, P. J. Steinhardt,
"Cosmology for grand unified theories with radiatively induced symmetry
breaking,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 48, 1220 (1982).
A. D. Linde,
Particle Physics and Inflationary Cosmology
(Harwood, Philadelphia, 1990).
E. W. Kolb, M. S. Turner,
The Early Universe (Addison-Wesley, Reading,
MA, 1990).
A. R. Liddle, D. H. Lyth,
Cosmological Inflation and Large-Scale
Structure (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 2000).
A. H. Guth,
The Inflationary Universe: The Quest for a New Theory
of Cosmic Origins (Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 1997).
R. C. Tolman, "Possibilities in relativistic
thermodynamics for irreversible processes without exhaustion of free
energy,"
Phys. Rev. 39, 320 (1932).
D. H. Lyth, A. Riotto, "Particle
physics models of inflation and the cosmological density perturbation,"
Phys. Rep. 314, 1 (1999)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9807278].
M. Tegmark et al., "Cosmological
parameters from SDSS and WMAP,"
Phys. Rev. D 69, 103501 (2004)
[arXiv: astro-ph/0310723].
D. J. Fixsen et al., "The cosmic
microwave background spectrum from the full COBE FIRAS data set,"
Astrophys. J. 473, 576 (1996)
[arXiv: astro-ph/9605054].
D. N. Spergel et al., "First year
Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) observations: Determination
of cosmological parameters,"
Astrophys. J. Suppl. 148, 175 (2003)
[arXiv: astro-ph/0302209].
For a review, see V. F. Mukhanov,
H. A. Feldman, R. H. Brandenberger, "Theory of cosmological
perturbations,"
Phys. Rep. 215, 203 (1992)
and also [6].
For a review, see R. P. Kirshner, "Throwing
light on dark energy,"
Science 300, 1914 (2003).
A. Vilenkin, E. P. S. Shellard,
Cosmic Strings and other Topological Defects
(Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 1994).
U.-L. Pen, U. Seljak, N. Turok, "Power spectra
in global defect theories of cosmic structure formation,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 1611 (1997)
[arXiv: astro-ph/9704165].
For a review, see J. Polchinski,
"Introduction to cosmic F- and D-strings,"
arXiv: hep-th/0412244.
We thank Max Tegmark for providing this graph,
which shows the most precise data points for each range of
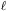 from recent observations, as summarized in
[10].
The cosmic string prediction is taken from
[16]. The
other curves were all calculated for ns = 1,
from recent observations, as summarized in
[10].
The cosmic string prediction is taken from
[16]. The
other curves were all calculated for ns = 1,
 baryon =
0.05, and H = 70 km s-1 Mpc-1, with the
remaining parameters fixed as follows. "Inflation with
baryon =
0.05, and H = 70 km s-1 Mpc-1, with the
remaining parameters fixed as follows. "Inflation with
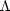 ":
":
 DM(dark
matter) = 0.23,
DM(dark
matter) = 0.23,

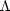 =
0.72, and optical depth parameter
=
0.72, and optical depth parameter
 = 0.17; "Inflation without
= 0.17; "Inflation without
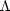 ":
":
 DM = 0.95,
DM = 0.95,

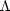 =
0,
=
0,  = 0.06; "Open universe":
= 0.06; "Open universe":
 DM =
0.25,
DM =
0.25,

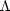 =
0,
=
0,  = 0.06. The
1-SD error bars include both observational uncertainty and
"cosmic variance," the intrinsic quantum uncertainty in the
predictions, as calculated from the "Inflation with
= 0.06. The
1-SD error bars include both observational uncertainty and
"cosmic variance," the intrinsic quantum uncertainty in the
predictions, as calculated from the "Inflation with
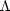 "
model. With our current ignorance of the underlying physics, none
of these theories predicts the overall amplitude of the
fluctuations; the "Inflation with
"
model. With our current ignorance of the underlying physics, none
of these theories predicts the overall amplitude of the
fluctuations; the "Inflation with
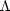 " curve was
normalized for a best fit, and the others were normalized arbitrarily.
P. J. Steinhardt,
"Natural inflation",
in The Very Early Universe, G. W. Gibbons, S. W. Hawking, S. T. C.
Siklos, Eds. (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 1983), p. 251.
A. Vilenkin, "The birth of inflationary
universes,"
Phys. Rev. D 27, 2848 (1983).
A. D. Linde, "Eternally existing
self-reproducing chaotic inflationary universe,"
Phys. Lett. B 175, 395 (1986).
For a review, see A. H. Guth, "Inflation and
eternal inflation,"
Phys. Rep. 333-334, 555 (2000)
[arXiv: astro-ph/0002156].
A. Borde, A. H. Guth,
A. Vilenkin, "Inflationary space-times are incomplete in past
directions,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 151301 (2003)
[arXiv: gr-qc/0110012].
L. A. Kofman, A. D. Linde, A. A. Starobinsky,
"Reheating after inflation,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 3195 (1994)
[arXiv: hep-th/9405187].
Y. Shtanov, J. H. Traschen, R. H. Brandenberger,
"Universe reheating after inflation,"
Phys. Rev. D 51, 5438 (1995)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9407247].
D. Boyanovsky, H. J. de Vega, R. Holman,
D. S. Lee, A. Singh, "Dissipation via particle production in scalar field
theories",
Phys. Rev. D 51, 4419 (1995)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9408214].
D. I. Kaiser, "Post-inflation reheating in an
expanding universe,"
Phys. Rev. D 53, 1776 (1996)
[arXiv: astro-ph/9507108].
For a review, see L. A. Kofman,
"Preheating after inflation", in COSMO-97:
Proceedings, L. Roszkowski, Ed. (World Scientific, Singapore, 1998),
pp. 312-321
[arXiv: astro-ph/9802221].
B. A. Bassett, D. I. Kaiser, R. Maartens,
"General relativistic effects in preheating,"
Phys. Lett. B 455, 84 (1999)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9808404].
Clifford Will,
Theory and Experiment in Gravitational
Physics (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, ed. 2, 1993).
C. D. Hoyle et al., "Sub-millimeter
tests of the gravitational inverse-square law,"
Phys. Rev. D 70, 042004 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-ph/0405262].
See, for example, J. Polchinski, String
Theory (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 1998), vol. 1.
N. Arkani-Hamed, S. Dimopoulos,
G. Dvali, "The hierarchy problem and new dimensions at a millimeter,"
Phys. Lett. B 429, 263 (1998)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9803315].
L. Randall, R. Sundrum, "An alternative to
compactification,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 4690 (1999)
[arXiv: hep-th/9906064].
For a review, see L. Randall, "Extra dimensions
and warped geometries,"
Science 296, 1422 (2002).
J. Garriga, T. Tanaka, "Gravity in the
Randall-Sundrum brane world,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 2778 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/9911055].
S. B. Giddings, E. Katz, L. Randall, "Linearized
gravity in brane backgrounds,"
J. High Energy Phys. 3, 23 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/0002091].
P. Binetruy, C. Deffayet, D. Langlois,
"Non-conventional cosmology from a brane universe,"
Nucl. Phys. B 565, 269 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/9905012].
R. Maartens, D. Wands, B. A.
Bassett, I. P. C. Heard, "Chaotic inflation on the brane,"
Phys. Rev. D 62, 041301 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9912464].
For a review, see D. Langlois,
"Gravitation and cosmology in brane-worlds,"
arXiv: gr-qc/0410129.
F. Quevedo, "Lectures on string/brane cosmology,"
Class. Quant. Grav. 19, 5721 (2002)
[arXiv: hep-th/0210292].
A. D. Linde, "Prospects of inflation,"
arXiv: hep-th/0402051.
C. P. Burgess, "Inflationary string theory?,"
Pramana 63, 1269 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-th/0408037].
G. R. Dvali, S.-H. H. Tye, "Brane inflation,"
Phys. Lett. B 450, 72 (1999)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9812483].
S. Kachru, R. Kallosh, A. Linde, S. P. Trivedi,
"De Sitter vacua in string theory,"
Phys. Rev. D 68, 046005 (2003)
[arXiv: hep-th/0301240].
S. Kachru, R. Kallosh, A. Linde, J. Maldacena, L.
McAllister, and S. P. Trivedi, "Towards inflation in string theory,"
J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 10, 013 (2003)
[arXiv: hep-th/0308055].
N. Iizuka, S. P. Trivedi, "An inflationary model
in string theory,"
Phys. Rev. D 70, 043519 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-th/0403203].
R. Bousso, J. Polchinski, "Quantization of
four-form fluxes and dynamical neutralization of the cosmological constant,"
J. High Energy Phys. 0006, 006 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/0004134].
L. Susskind, "The anthropic landscape of string
theory,"
arXiv: hep-th/0302219.
R. Bousso, J. Polchinski, "The string theory
landscape,"
Sci. Am. 291, 60 (Sept. 2004).
A. D. Linde, D. Linde, A. Mezhlumian, "Do we
live in the center of the world?,"
Phys. Lett. B 345, 203-210 (1995)
[arXiv: hep-th/9411111].
See, for example, J. Garriga,
A. Vilenkin, "A prescription for probabilities in eternal inflation,"
Phys. Rev. D 64, 023507 (2001)
[arXiv: gr-qc/0102090],
and also [53].
M. Tegmark, "What does inflation really
predict?"
arXiv: astro-ph/0410281.
S. Weinberg, "Anthropic bound on the
cosmological constant,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 2607 (1987).
T. Banks, M. Dine, E. Gorbatov, "Is there a
string theory landscape?"
J. High Energy Phys. 0408, 058 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-th/0309170].
For a review, see J. P. Ostriker, P.
Steinhardt, "New light on dark matter,"
Science 300, 1909 (2003)
[arXiv: astro-ph/0306402].
" curve was
normalized for a best fit, and the others were normalized arbitrarily.
P. J. Steinhardt,
"Natural inflation",
in The Very Early Universe, G. W. Gibbons, S. W. Hawking, S. T. C.
Siklos, Eds. (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 1983), p. 251.
A. Vilenkin, "The birth of inflationary
universes,"
Phys. Rev. D 27, 2848 (1983).
A. D. Linde, "Eternally existing
self-reproducing chaotic inflationary universe,"
Phys. Lett. B 175, 395 (1986).
For a review, see A. H. Guth, "Inflation and
eternal inflation,"
Phys. Rep. 333-334, 555 (2000)
[arXiv: astro-ph/0002156].
A. Borde, A. H. Guth,
A. Vilenkin, "Inflationary space-times are incomplete in past
directions,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 151301 (2003)
[arXiv: gr-qc/0110012].
L. A. Kofman, A. D. Linde, A. A. Starobinsky,
"Reheating after inflation,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 3195 (1994)
[arXiv: hep-th/9405187].
Y. Shtanov, J. H. Traschen, R. H. Brandenberger,
"Universe reheating after inflation,"
Phys. Rev. D 51, 5438 (1995)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9407247].
D. Boyanovsky, H. J. de Vega, R. Holman,
D. S. Lee, A. Singh, "Dissipation via particle production in scalar field
theories",
Phys. Rev. D 51, 4419 (1995)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9408214].
D. I. Kaiser, "Post-inflation reheating in an
expanding universe,"
Phys. Rev. D 53, 1776 (1996)
[arXiv: astro-ph/9507108].
For a review, see L. A. Kofman,
"Preheating after inflation", in COSMO-97:
Proceedings, L. Roszkowski, Ed. (World Scientific, Singapore, 1998),
pp. 312-321
[arXiv: astro-ph/9802221].
B. A. Bassett, D. I. Kaiser, R. Maartens,
"General relativistic effects in preheating,"
Phys. Lett. B 455, 84 (1999)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9808404].
Clifford Will,
Theory and Experiment in Gravitational
Physics (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, ed. 2, 1993).
C. D. Hoyle et al., "Sub-millimeter
tests of the gravitational inverse-square law,"
Phys. Rev. D 70, 042004 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-ph/0405262].
See, for example, J. Polchinski, String
Theory (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 1998), vol. 1.
N. Arkani-Hamed, S. Dimopoulos,
G. Dvali, "The hierarchy problem and new dimensions at a millimeter,"
Phys. Lett. B 429, 263 (1998)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9803315].
L. Randall, R. Sundrum, "An alternative to
compactification,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 4690 (1999)
[arXiv: hep-th/9906064].
For a review, see L. Randall, "Extra dimensions
and warped geometries,"
Science 296, 1422 (2002).
J. Garriga, T. Tanaka, "Gravity in the
Randall-Sundrum brane world,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 2778 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/9911055].
S. B. Giddings, E. Katz, L. Randall, "Linearized
gravity in brane backgrounds,"
J. High Energy Phys. 3, 23 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/0002091].
P. Binetruy, C. Deffayet, D. Langlois,
"Non-conventional cosmology from a brane universe,"
Nucl. Phys. B 565, 269 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/9905012].
R. Maartens, D. Wands, B. A.
Bassett, I. P. C. Heard, "Chaotic inflation on the brane,"
Phys. Rev. D 62, 041301 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9912464].
For a review, see D. Langlois,
"Gravitation and cosmology in brane-worlds,"
arXiv: gr-qc/0410129.
F. Quevedo, "Lectures on string/brane cosmology,"
Class. Quant. Grav. 19, 5721 (2002)
[arXiv: hep-th/0210292].
A. D. Linde, "Prospects of inflation,"
arXiv: hep-th/0402051.
C. P. Burgess, "Inflationary string theory?,"
Pramana 63, 1269 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-th/0408037].
G. R. Dvali, S.-H. H. Tye, "Brane inflation,"
Phys. Lett. B 450, 72 (1999)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9812483].
S. Kachru, R. Kallosh, A. Linde, S. P. Trivedi,
"De Sitter vacua in string theory,"
Phys. Rev. D 68, 046005 (2003)
[arXiv: hep-th/0301240].
S. Kachru, R. Kallosh, A. Linde, J. Maldacena, L.
McAllister, and S. P. Trivedi, "Towards inflation in string theory,"
J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 10, 013 (2003)
[arXiv: hep-th/0308055].
N. Iizuka, S. P. Trivedi, "An inflationary model
in string theory,"
Phys. Rev. D 70, 043519 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-th/0403203].
R. Bousso, J. Polchinski, "Quantization of
four-form fluxes and dynamical neutralization of the cosmological constant,"
J. High Energy Phys. 0006, 006 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/0004134].
L. Susskind, "The anthropic landscape of string
theory,"
arXiv: hep-th/0302219.
R. Bousso, J. Polchinski, "The string theory
landscape,"
Sci. Am. 291, 60 (Sept. 2004).
A. D. Linde, D. Linde, A. Mezhlumian, "Do we
live in the center of the world?,"
Phys. Lett. B 345, 203-210 (1995)
[arXiv: hep-th/9411111].
See, for example, J. Garriga,
A. Vilenkin, "A prescription for probabilities in eternal inflation,"
Phys. Rev. D 64, 023507 (2001)
[arXiv: gr-qc/0102090],
and also [53].
M. Tegmark, "What does inflation really
predict?"
arXiv: astro-ph/0410281.
S. Weinberg, "Anthropic bound on the
cosmological constant,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 2607 (1987).
T. Banks, M. Dine, E. Gorbatov, "Is there a
string theory landscape?"
J. High Energy Phys. 0408, 058 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-th/0309170].
For a review, see J. P. Ostriker, P.
Steinhardt, "New light on dark matter,"
Science 300, 1909 (2003)
[arXiv: astro-ph/0306402].




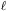 from recent observations, as summarized in
[10].
The cosmic string prediction is taken from
[16]. The
other curves were all calculated for ns = 1,
from recent observations, as summarized in
[10].
The cosmic string prediction is taken from
[16]. The
other curves were all calculated for ns = 1,
 baryon =
0.05, and H = 70 km s-1 Mpc-1, with the
remaining parameters fixed as follows. "Inflation with
baryon =
0.05, and H = 70 km s-1 Mpc-1, with the
remaining parameters fixed as follows. "Inflation with
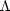 ":
":
 DM(dark
matter) = 0.23,
DM(dark
matter) = 0.23,

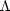 =
0.72, and optical depth parameter
=
0.72, and optical depth parameter
 = 0.17; "Inflation without
= 0.17; "Inflation without
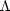 ":
":
 DM = 0.95,
DM = 0.95,

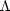 =
0,
=
0,  = 0.06; "Open universe":
= 0.06; "Open universe":
 DM =
0.25,
DM =
0.25,

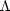 =
0,
=
0,  = 0.06. The
1-SD error bars include both observational uncertainty and
"cosmic variance," the intrinsic quantum uncertainty in the
predictions, as calculated from the "Inflation with
= 0.06. The
1-SD error bars include both observational uncertainty and
"cosmic variance," the intrinsic quantum uncertainty in the
predictions, as calculated from the "Inflation with
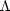 "
model. With our current ignorance of the underlying physics, none
of these theories predicts the overall amplitude of the
fluctuations; the "Inflation with
"
model. With our current ignorance of the underlying physics, none
of these theories predicts the overall amplitude of the
fluctuations; the "Inflation with
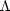 " curve was
normalized for a best fit, and the others were normalized arbitrarily.
P. J. Steinhardt,
"Natural inflation",
in The Very Early Universe, G. W. Gibbons, S. W. Hawking, S. T. C.
Siklos, Eds. (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 1983), p. 251.
A. Vilenkin, "The birth of inflationary
universes,"
Phys. Rev. D 27, 2848 (1983).
A. D. Linde, "Eternally existing
self-reproducing chaotic inflationary universe,"
Phys. Lett. B 175, 395 (1986).
For a review, see A. H. Guth, "Inflation and
eternal inflation,"
Phys. Rep. 333-334, 555 (2000)
[arXiv: astro-ph/0002156].
A. Borde, A. H. Guth,
A. Vilenkin, "Inflationary space-times are incomplete in past
directions,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 151301 (2003)
[arXiv: gr-qc/0110012].
L. A. Kofman, A. D. Linde, A. A. Starobinsky,
"Reheating after inflation,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 3195 (1994)
[arXiv: hep-th/9405187].
Y. Shtanov, J. H. Traschen, R. H. Brandenberger,
"Universe reheating after inflation,"
Phys. Rev. D 51, 5438 (1995)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9407247].
D. Boyanovsky, H. J. de Vega, R. Holman,
D. S. Lee, A. Singh, "Dissipation via particle production in scalar field
theories",
Phys. Rev. D 51, 4419 (1995)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9408214].
D. I. Kaiser, "Post-inflation reheating in an
expanding universe,"
Phys. Rev. D 53, 1776 (1996)
[arXiv: astro-ph/9507108].
For a review, see L. A. Kofman,
"Preheating after inflation", in COSMO-97:
Proceedings, L. Roszkowski, Ed. (World Scientific, Singapore, 1998),
pp. 312-321
[arXiv: astro-ph/9802221].
B. A. Bassett, D. I. Kaiser, R. Maartens,
"General relativistic effects in preheating,"
Phys. Lett. B 455, 84 (1999)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9808404].
Clifford Will,
Theory and Experiment in Gravitational
Physics (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, ed. 2, 1993).
C. D. Hoyle et al., "Sub-millimeter
tests of the gravitational inverse-square law,"
Phys. Rev. D 70, 042004 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-ph/0405262].
See, for example, J. Polchinski, String
Theory (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 1998), vol. 1.
N. Arkani-Hamed, S. Dimopoulos,
G. Dvali, "The hierarchy problem and new dimensions at a millimeter,"
Phys. Lett. B 429, 263 (1998)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9803315].
L. Randall, R. Sundrum, "An alternative to
compactification,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 4690 (1999)
[arXiv: hep-th/9906064].
For a review, see L. Randall, "Extra dimensions
and warped geometries,"
Science 296, 1422 (2002).
J. Garriga, T. Tanaka, "Gravity in the
Randall-Sundrum brane world,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 2778 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/9911055].
S. B. Giddings, E. Katz, L. Randall, "Linearized
gravity in brane backgrounds,"
J. High Energy Phys. 3, 23 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/0002091].
P. Binetruy, C. Deffayet, D. Langlois,
"Non-conventional cosmology from a brane universe,"
Nucl. Phys. B 565, 269 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/9905012].
R. Maartens, D. Wands, B. A.
Bassett, I. P. C. Heard, "Chaotic inflation on the brane,"
Phys. Rev. D 62, 041301 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9912464].
For a review, see D. Langlois,
"Gravitation and cosmology in brane-worlds,"
arXiv: gr-qc/0410129.
F. Quevedo, "Lectures on string/brane cosmology,"
Class. Quant. Grav. 19, 5721 (2002)
[arXiv: hep-th/0210292].
A. D. Linde, "Prospects of inflation,"
arXiv: hep-th/0402051.
C. P. Burgess, "Inflationary string theory?,"
Pramana 63, 1269 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-th/0408037].
G. R. Dvali, S.-H. H. Tye, "Brane inflation,"
Phys. Lett. B 450, 72 (1999)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9812483].
S. Kachru, R. Kallosh, A. Linde, S. P. Trivedi,
"De Sitter vacua in string theory,"
Phys. Rev. D 68, 046005 (2003)
[arXiv: hep-th/0301240].
S. Kachru, R. Kallosh, A. Linde, J. Maldacena, L.
McAllister, and S. P. Trivedi, "Towards inflation in string theory,"
J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 10, 013 (2003)
[arXiv: hep-th/0308055].
N. Iizuka, S. P. Trivedi, "An inflationary model
in string theory,"
Phys. Rev. D 70, 043519 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-th/0403203].
R. Bousso, J. Polchinski, "Quantization of
four-form fluxes and dynamical neutralization of the cosmological constant,"
J. High Energy Phys. 0006, 006 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/0004134].
L. Susskind, "The anthropic landscape of string
theory,"
arXiv: hep-th/0302219.
R. Bousso, J. Polchinski, "The string theory
landscape,"
Sci. Am. 291, 60 (Sept. 2004).
A. D. Linde, D. Linde, A. Mezhlumian, "Do we
live in the center of the world?,"
Phys. Lett. B 345, 203-210 (1995)
[arXiv: hep-th/9411111].
See, for example, J. Garriga,
A. Vilenkin, "A prescription for probabilities in eternal inflation,"
Phys. Rev. D 64, 023507 (2001)
[arXiv: gr-qc/0102090],
and also [53].
M. Tegmark, "What does inflation really
predict?"
arXiv: astro-ph/0410281.
S. Weinberg, "Anthropic bound on the
cosmological constant,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 2607 (1987).
T. Banks, M. Dine, E. Gorbatov, "Is there a
string theory landscape?"
J. High Energy Phys. 0408, 058 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-th/0309170].
For a review, see J. P. Ostriker, P.
Steinhardt, "New light on dark matter,"
Science 300, 1909 (2003)
[arXiv: astro-ph/0306402].
" curve was
normalized for a best fit, and the others were normalized arbitrarily.
P. J. Steinhardt,
"Natural inflation",
in The Very Early Universe, G. W. Gibbons, S. W. Hawking, S. T. C.
Siklos, Eds. (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 1983), p. 251.
A. Vilenkin, "The birth of inflationary
universes,"
Phys. Rev. D 27, 2848 (1983).
A. D. Linde, "Eternally existing
self-reproducing chaotic inflationary universe,"
Phys. Lett. B 175, 395 (1986).
For a review, see A. H. Guth, "Inflation and
eternal inflation,"
Phys. Rep. 333-334, 555 (2000)
[arXiv: astro-ph/0002156].
A. Borde, A. H. Guth,
A. Vilenkin, "Inflationary space-times are incomplete in past
directions,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 151301 (2003)
[arXiv: gr-qc/0110012].
L. A. Kofman, A. D. Linde, A. A. Starobinsky,
"Reheating after inflation,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 3195 (1994)
[arXiv: hep-th/9405187].
Y. Shtanov, J. H. Traschen, R. H. Brandenberger,
"Universe reheating after inflation,"
Phys. Rev. D 51, 5438 (1995)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9407247].
D. Boyanovsky, H. J. de Vega, R. Holman,
D. S. Lee, A. Singh, "Dissipation via particle production in scalar field
theories",
Phys. Rev. D 51, 4419 (1995)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9408214].
D. I. Kaiser, "Post-inflation reheating in an
expanding universe,"
Phys. Rev. D 53, 1776 (1996)
[arXiv: astro-ph/9507108].
For a review, see L. A. Kofman,
"Preheating after inflation", in COSMO-97:
Proceedings, L. Roszkowski, Ed. (World Scientific, Singapore, 1998),
pp. 312-321
[arXiv: astro-ph/9802221].
B. A. Bassett, D. I. Kaiser, R. Maartens,
"General relativistic effects in preheating,"
Phys. Lett. B 455, 84 (1999)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9808404].
Clifford Will,
Theory and Experiment in Gravitational
Physics (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, ed. 2, 1993).
C. D. Hoyle et al., "Sub-millimeter
tests of the gravitational inverse-square law,"
Phys. Rev. D 70, 042004 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-ph/0405262].
See, for example, J. Polchinski, String
Theory (Cambridge Univ. Press, New York, 1998), vol. 1.
N. Arkani-Hamed, S. Dimopoulos,
G. Dvali, "The hierarchy problem and new dimensions at a millimeter,"
Phys. Lett. B 429, 263 (1998)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9803315].
L. Randall, R. Sundrum, "An alternative to
compactification,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 4690 (1999)
[arXiv: hep-th/9906064].
For a review, see L. Randall, "Extra dimensions
and warped geometries,"
Science 296, 1422 (2002).
J. Garriga, T. Tanaka, "Gravity in the
Randall-Sundrum brane world,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 2778 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/9911055].
S. B. Giddings, E. Katz, L. Randall, "Linearized
gravity in brane backgrounds,"
J. High Energy Phys. 3, 23 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/0002091].
P. Binetruy, C. Deffayet, D. Langlois,
"Non-conventional cosmology from a brane universe,"
Nucl. Phys. B 565, 269 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/9905012].
R. Maartens, D. Wands, B. A.
Bassett, I. P. C. Heard, "Chaotic inflation on the brane,"
Phys. Rev. D 62, 041301 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9912464].
For a review, see D. Langlois,
"Gravitation and cosmology in brane-worlds,"
arXiv: gr-qc/0410129.
F. Quevedo, "Lectures on string/brane cosmology,"
Class. Quant. Grav. 19, 5721 (2002)
[arXiv: hep-th/0210292].
A. D. Linde, "Prospects of inflation,"
arXiv: hep-th/0402051.
C. P. Burgess, "Inflationary string theory?,"
Pramana 63, 1269 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-th/0408037].
G. R. Dvali, S.-H. H. Tye, "Brane inflation,"
Phys. Lett. B 450, 72 (1999)
[arXiv: hep-ph/9812483].
S. Kachru, R. Kallosh, A. Linde, S. P. Trivedi,
"De Sitter vacua in string theory,"
Phys. Rev. D 68, 046005 (2003)
[arXiv: hep-th/0301240].
S. Kachru, R. Kallosh, A. Linde, J. Maldacena, L.
McAllister, and S. P. Trivedi, "Towards inflation in string theory,"
J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 10, 013 (2003)
[arXiv: hep-th/0308055].
N. Iizuka, S. P. Trivedi, "An inflationary model
in string theory,"
Phys. Rev. D 70, 043519 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-th/0403203].
R. Bousso, J. Polchinski, "Quantization of
four-form fluxes and dynamical neutralization of the cosmological constant,"
J. High Energy Phys. 0006, 006 (2000)
[arXiv: hep-th/0004134].
L. Susskind, "The anthropic landscape of string
theory,"
arXiv: hep-th/0302219.
R. Bousso, J. Polchinski, "The string theory
landscape,"
Sci. Am. 291, 60 (Sept. 2004).
A. D. Linde, D. Linde, A. Mezhlumian, "Do we
live in the center of the world?,"
Phys. Lett. B 345, 203-210 (1995)
[arXiv: hep-th/9411111].
See, for example, J. Garriga,
A. Vilenkin, "A prescription for probabilities in eternal inflation,"
Phys. Rev. D 64, 023507 (2001)
[arXiv: gr-qc/0102090],
and also [53].
M. Tegmark, "What does inflation really
predict?"
arXiv: astro-ph/0410281.
S. Weinberg, "Anthropic bound on the
cosmological constant,"
Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 2607 (1987).
T. Banks, M. Dine, E. Gorbatov, "Is there a
string theory landscape?"
J. High Energy Phys. 0408, 058 (2004)
[arXiv: hep-th/0309170].
For a review, see J. P. Ostriker, P.
Steinhardt, "New light on dark matter,"
Science 300, 1909 (2003)
[arXiv: astro-ph/0306402].