


The largest dataset for which a thorough comparison with the above picture has been made is the 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey (2dFGRS). This survey was designed around the 2dF multi-fibre spectrograph on the Anglo-Australian Telescope, which is capable of observing up to 400 objects simultaneously over a 2 degree diameter field of view. For details of the instrument and its performance see http://www.aao.gov.au/2df/, and also Lewis et al. (2002). The source catalogue for the survey is a revised and extended version of the APM galaxy catalogue (Maddox et al. 1990a, b, c); this includes over 5 million galaxies down to bJ = 20.5 in both north and south Galactic hemispheres over a region of almost 104 deg2. The bJ magnitude system is related to the Johnson-Cousins system by bJ = B - 0.304(B - V), where the colour term is estimated from comparison with the SDSS Early Data Release (Stoughton et al. 2002).
The 2dFGRS geometry consists of two contiguous
declination strips, plus 100 random 2-degree fields. One strip is in the
southern Galactic hemisphere and covers approximately
75° × 15° centred close to the SGP at
( ,
,
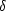 ) =
(01h, -30°); the other strip is in the northern
Galactic hemisphere and covers 75° × 7.5° centred at
(
) =
(01h, -30°); the other strip is in the northern
Galactic hemisphere and covers 75° × 7.5° centred at
( ,
,
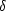 ) =
(12.5h, +0°). The 100 random fields are spread
uniformly over the 7000 deg2 region of the APM catalogue in the
southern Galactic hemisphere.
The sample is limited to be brighter than an extinction-corrected
magnitude of bJ = 19.45 (using the extinction maps of
Schlegel et al. 1998).
This limit gives a good match between the density on the sky of
galaxies and 2dF fibres.
) =
(12.5h, +0°). The 100 random fields are spread
uniformly over the 7000 deg2 region of the APM catalogue in the
southern Galactic hemisphere.
The sample is limited to be brighter than an extinction-corrected
magnitude of bJ = 19.45 (using the extinction maps of
Schlegel et al. 1998).
This limit gives a good match between the density on the sky of
galaxies and 2dF fibres.
After an extensive period of commissioning of the 2dF instrument,
2dFGRS observing began in earnest in May 1997, and terminated
in April 2002. In total, observations were made of 899 fields,
yielding redshifts and identifications for 232,529 galaxies, 13976 stars
and 172 QSOs, at an overall completeness of 93%.
The galaxy redshifts are assigned a quality flag from 1 to 5,
where the probability of error is highest at low Q. Most analyses
are restricted to Q 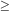 3 galaxies, of which there are currently 221,496.
An interim data release took place in July 2001,
consisting of approximately 100,000 galaxies (see
Colless et al. 2001
for details). A public release of the full photometric and spectroscopic
database is scheduled for July 2003. The completed 2dFGRS yields a striking
view of the galaxy distribution over large cosmological volumes.
This is illustrated in
figure 4, which shows the projection of a subset of
the galaxies in the northern and southern strips onto
(
3 galaxies, of which there are currently 221,496.
An interim data release took place in July 2001,
consisting of approximately 100,000 galaxies (see
Colless et al. 2001
for details). A public release of the full photometric and spectroscopic
database is scheduled for July 2003. The completed 2dFGRS yields a striking
view of the galaxy distribution over large cosmological volumes.
This is illustrated in
figure 4, which shows the projection of a subset of
the galaxies in the northern and southern strips onto
( , z)
slices. This picture is the culmination of decades of effort in
the investigation of large-scale structure, and we are
fortunate to have this detailed view for the first time.
, z)
slices. This picture is the culmination of decades of effort in
the investigation of large-scale structure, and we are
fortunate to have this detailed view for the first time.