


A list of acronyms and terms
- Chimney:
- a
superbubble that extends from the galactic midplane,
where it has been energized by supernovae, into the halo. Chimneys can
be a conduit for hot gas and hydrogen ionizing radiation.
- DIG:
- diffuse
ionized gas characterized
by temperatures ~ 104 K and densities ~ 10-1
cm-3 that
occupies the disk and halo of many spiral galaxies. In our Galaxy the
DIG is often referred to as the warm ionized medium or WIM.
- DM:
- dispersion
measure; the free electron density integrated along
the line of sight to a pulsar;
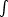 0P
ne ds. Because the free electron density ne
0P
ne ds. Because the free electron density ne
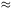 nH+ in the interstellar
medium, DM is essentially the column density of the H+.
nH+ in the interstellar
medium, DM is essentially the column density of the H+.
- EM:
- emission
measure; the product of the proton density
times the electron density integrated along the line of sight. In regions
of nearly fully ionized hydrogen, emission measure is essentially
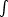 ne2 ds.
ne2 ds.
- EPIC:
- European
Photon Imaging Cameras on the XMM-Newton's X-ray telescopes.
- FIR:
- far infrared
(wavelengths ~ 102 µm).
- Forbidden line:
- an
emission line produced by the decay of an
excited metastable state in an atom or ion, denoted by square brackets
around the ion's symbol. In the low density WIM/DIG, the collisional
de-excitation time scales are much longer than the radiative decay time
scales, and therefore the intensity of a forbidden line measures the
excitation rate of the metastable state due to collisions by the thermal
electrons in the plasma.
- the Galaxy:
- with a
capital `G', our galaxy, the Milky Way.
- Galactic latitude:
-
The angular distance above the Galactic equator,
the midplane of the Milky Way.
- H
 :
: -
the emission at 6563
Å produced by the hydrogen
Balmer-alpha (n = 3
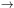 2) transition following the
recombination of ionized hydrogen.
2) transition following the
recombination of ionized hydrogen.
- H I region:
- a
cloud composed primarily of neutral hydrogen atoms.
- H II region:
- a
discrete region of photoionized hydrogen associated
with a hot star; a classical "emission nebula" or "Strömgren
Sphere", as opposed to the more wide-spread, lower density
H+ (the WIM, DIG) not clearly associated with a single,
discrete source of ionization.
- H+:
- ionized hydrogen; in this
paper ionized hydrogen
associated with the wide-spread, low density WIM/DIG.
- HST:
- the Hubble
Space Telescope
- HVC:
- high velocity
cloud; a neutral hydrogen cloud, usually located
far from the Galactic disk and not partaking in the rotation of the disk.
- Ionization parameter:
- the ratio of the ionizing photon density to
the electron density, which along with the spectrum, determines the
population of ionization states in photoionized gas.
- LIC:
- the very
local interstellar cloud within a few parsecs of the sun.
- LyC:
- Lyman
continuum; energies above the Lyman limit, the
ionization potential of hydrogen (13.6 eV).
- Magellanic Stream:
-
an extended complex of neutral atomic hydrogen
gas associated with a pair of satellite galaxies, the Large and
Small Magellanic Clouds, orbiting the Galaxy.
- O and B stars:
- hot
stars that emit Lyman continuum (LyC) photons.
Massive O stars are located in active star forming regions, emit a
large fraction of their luminosity in the LyC, and are believed to be the
primary source of ionization for the WIM/DIG.
- PAH:
- polycyclic
aromatic hydrocarbon; a large interstellar molecule that can inject heat
into the interstellar via its ionization by ultraviolet photons from stars.
- R:
- rayleigh; a
unit of surface brightness for emission lines, equal
to 106 / 4
 photons
s-1 cm-2 sr-1. An ionized region
with an emission measure EM = 2.25 cm-6 pc and a
temperature of 8000 K has an
H
photons
s-1 cm-2 sr-1. An ionized region
with an emission measure EM = 2.25 cm-6 pc and a
temperature of 8000 K has an
H surface brightness of
1 R.
surface brightness of
1 R.
- SFR:
- star
formation rate.
- Spiral galaxy:
- a
galaxy that has a flat, rotating disk of stars, gas, and dust.
- Superbubble:
- a
large cavity of hot (~ 106 K), ionized gas
created by the combined kinetic energy of multiple supernovae occurring
within an active star formation region.
- Te; Ti:
- electron temperature and ion temperature,
respectively. In general, Te = Ti in
the interstellar medium.
- TML:
- turbulent
mixing layer; the transition region between two
adjacent parts of the interstellar medium that have very different
temperatures and are moving with respect to each other.
- VLA:
- The Very
Large Array radio synthesis telescope near Socorro, New Mexico.
- WHAM:
- the
Wisconsin H-Alpha Mapper; a remotely controlled
observatory dedicated to the detection and study of faint emission lines
from the interstellar medium of the Galaxy.
- WIM:
- the
wide-spread, warm, ionized medium in the Galaxy
characterized by temperatures ~ 104 K and densities ~
10-1 cm-3; sometimes also called the "Reynolds Layer".
- WNM:
- wide-spread
neutral atomic hydrogen characterized
by temperatures ~ 103 K and densities ~ 10-1
cm-3.
- XMM-Newton:
- the
Multi-Mirror Mission orbiting X-ray observatory
of the European Space Agency.
- z:
- the
perpendicular distance from the midplane of a spiral galaxy.






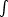 0P
ne ds. Because the free electron density ne
0P
ne ds. Because the free electron density ne
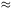 nH+ in the interstellar
medium, DM is essentially the column density of the H+.
nH+ in the interstellar
medium, DM is essentially the column density of the H+.
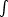 ne2 ds.
ne2 ds.
 :
: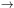 2) transition following the
recombination of ionized hydrogen.
2) transition following the
recombination of ionized hydrogen.
 photons
s-1 cm-2 sr-1. An ionized region
with an emission measure EM = 2.25 cm-6 pc and a
temperature of 8000 K has an
H
photons
s-1 cm-2 sr-1. An ionized region
with an emission measure EM = 2.25 cm-6 pc and a
temperature of 8000 K has an
H surface brightness of
1 R.
surface brightness of
1 R.