


Despite the many caveats of SE mass estimators discussed above, they have been extensively used in recent years to measure BH masses in quasar and AGN samples over wide luminosity and redshift ranges, given their easiness to use. These applications include the Eddington ratio distributions of quasars, the demographics of quasars in terms of the black hole mass function (BHMF), the correlations between BH mass and host properties, and BH mass dependence of quasar properties. It is important to recognize, however, that these BH mass estimates are not true masses, and the uncertainty in these mass estimates has dramatic influences on the interpretation of these measurements.
Below I discuss several major applications of the SE virial mass estimators to statistical quasar samples. Other applications of these SE masses, such as quasar phenomenology, while equally important, will not be covered here.
One of the strong drivers for developing the SE virial mass technique is to estimate BH masses for high redshift quasars to better than a factor of ten accuracy, and to study the growth of SMBHs up to very high redshift (e.g., Vestergaard 2004). Such investigations have been greatly improved in the era of modern, large-scale spectroscopic surveys. The SDSS survey has been influential on this topic by providing more than tens of thousands of optical quasar spectra and SE mass estimates up to z ~ 5 (e.g., McLure & Dunlop 2004, Netzer & Trakhtenbrot 2007, Shen et al. 2008a, Shen et al. 2011, Labita et al. 2009a, Labita et al. 2009b). On the other hand, deeper and dedicated optical and near-IR spectroscopic programs are probing the SMBH growth to even higher redshift (e.g., Jiang et al. 2007, Kurk et al. 2007, Willott et al. 2010, Mortlock et al. 2011).
In Fig. 9 I show a compilation of SE virial mass
estimates
for quasars over a wide redshift range 0 < z
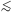 7 from different
studies. The black dots show the SE masses from the SDSS DR7 quasar sample
(Schneider
et al. 2010,
Shen et
al. 2011),
which were estimated based on
H
7 from different
studies. The black dots show the SE masses from the SDSS DR7 quasar sample
(Schneider
et al. 2010,
Shen et
al. 2011),
which were estimated based on
H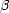 for
z < 0.7, Mg II for 0.7 < z < 1.9 and
C IV for 1.9 < z < 5. As
discussed in Section 3.1.7, the
reliability of C IV-based SE masses for the high-z and
high-luminosity quasars has been questioned, and several
studies have obtained near-IR spectra for z
for
z < 0.7, Mg II for 0.7 < z < 1.9 and
C IV for 1.9 < z < 5. As
discussed in Section 3.1.7, the
reliability of C IV-based SE masses for the high-z and
high-luminosity quasars has been questioned, and several
studies have obtained near-IR spectra for z
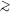 2 quasars to get
H
2 quasars to get
H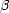 -based
(filled symbols) and Mg II-based (open symbols) SE masses at
high redshift. Albeit with considerable uncertainties and possible biases in
individual SE mass estimates (all on the order of a factor of a few), these
studies show that massive,
-based
(filled symbols) and Mg II-based (open symbols) SE masses at
high redshift. Albeit with considerable uncertainties and possible biases in
individual SE mass estimates (all on the order of a factor of a few), these
studies show that massive,
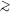 109
M
109
M BHs
are probably already
in place by z ~ 7, when the age of the Universe is only less than 1
Gyr. The abundance of these massive and active BHs then evolves strongly
with redshift, showing the rise and fall of the bright quasar population
with cosmic time.
BHs
are probably already
in place by z ~ 7, when the age of the Universe is only less than 1
Gyr. The abundance of these massive and active BHs then evolves strongly
with redshift, showing the rise and fall of the bright quasar population
with cosmic time.
 |
Figure 9. A compilation of SE virial mass
estimates from different samples of quasars. The black dots are
the SE masses for SDSS quasars from
Shen et
al. (2011),
based on H |
One outstanding question regarding the observed earliest quasars is how they could have grown such massive SMBHs given the limited time they have, which is a non-trivial problem since the discoveries of z > 4 quasars (e.g., Turner 1991, Haiman & Loeb 2001). One concern is if these highest redshift quasars have their luminosities magnified by gravitational lensing or if their luminosities are strongly beamed (e.g., Wyithe & Loeb 2002, Haiman & Cen 2002), which will affect earlier estimates of their BH masses using the Eddington-limit argument. The lensing hypothesis will also lead to overestimated virial BH masses. However later deep, high-resolution imaging of z > 4 quasars with HST did not find any multiple images around these objects (e.g., Richards et al. 2004b, Richards et al. 2006b), rendering the lensing hypothesis highly unlikely (e.g., Keeton et al. 2005). Strong beaming can also be ruled out based on the high values of the observed line/continuum ratio of these high-redshift quasars (e.g., Haiman & Cen 2002).
Given the e-folding time introduced in
Section 1, te = 4.5 ×
108 є /
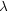 (1 - є) yr, and
a seed BH mass Mseed at
an earlier epoch zi, the final mass at
zf ~ 6 is
(1 - є) yr, and
a seed BH mass Mseed at
an earlier epoch zi, the final mass at
zf ~ 6 is
 |
(20) |
where tf and ti are the cosmic age at zf and zi, respectively.
Assuming continuous accretion with constant radiative efficiency є
and luminosity Eddington ratio
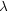 and without
mergers, I showed in Fig. 9 three different
growth histories from a seed BH
at higher redshift. The solid lines are for a seed BH at z = 20 and
and without
mergers, I showed in Fig. 9 three different
growth histories from a seed BH
at higher redshift. The solid lines are for a seed BH at z = 20 and
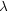 = 1, i.e.,
Eddington-limited accretion; the dashed lines are for a
seed BH at z = 30 and
= 1, i.e.,
Eddington-limited accretion; the dashed lines are for a
seed BH at z = 30 and
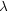 = 1; the dotted lines
are for a seed BH at z = 20 and
= 1; the dotted lines
are for a seed BH at z = 20 and
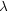 = 1.5, i.e., mildly
super-Eddington accretion. For each model I used three seed BH mass,
Mseed = 10,20,100
M
= 1.5, i.e., mildly
super-Eddington accretion. For each model I used three seed BH mass,
Mseed = 10,20,100
M , which
encloses the reasonable ranges of predicted remnant BH mass from the first
generation of stars (Pop III stars, for a review see, e.g.,
Bromm et
al. 2009).
Then it is clear from Fig. 9
that, if the accretion is Eddington-limited, it is difficult to grow
, which
encloses the reasonable ranges of predicted remnant BH mass from the first
generation of stars (Pop III stars, for a review see, e.g.,
Bromm et
al. 2009).
Then it is clear from Fig. 9
that, if the accretion is Eddington-limited, it is difficult to grow
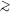 109
M
109
M BHs at
z ~ 6 from a Pop III remnant seed BH at z ~
20-30 (where such first stars were formed out of ~ 106
M
BHs at
z ~ 6 from a Pop III remnant seed BH at z ~
20-30 (where such first stars were formed out of ~ 106
M halos, corresponding to ~ 3-4
halos, corresponding to ~ 3-4
 peaks in the density
perturbation field). On the other hand, if allowing mildly
super-Eddington accretion, then a ~ 109
M
peaks in the density
perturbation field). On the other hand, if allowing mildly
super-Eddington accretion, then a ~ 109
M BH can
be readily formed at z ~ 7 from a large Pop
III star remnant Mseed ~ 100
M
BH can
be readily formed at z ~ 7 from a large Pop
III star remnant Mseed ~ 100
M ,
although more recent
simulations suggest somewhat lower masses of Pop III stars due to possible
effects of clump fragmentation and/or radiative feedback (e.g.,
Turk et
al. 2009,
Hosokawa et
al. 2011,
Stacy et
al. 2012),
and hence
a lower typical value of the remnant mass of less than tens of solar masses.
Mildly super-Eddington accretion (up to
,
although more recent
simulations suggest somewhat lower masses of Pop III stars due to possible
effects of clump fragmentation and/or radiative feedback (e.g.,
Turk et
al. 2009,
Hosokawa et
al. 2011,
Stacy et
al. 2012),
and hence
a lower typical value of the remnant mass of less than tens of solar masses.
Mildly super-Eddington accretion (up to
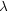 ~ a few) could happen,
for instance, if the radiation and density fields of the accretion flow are
anisotropic and most of the accretion flow is not impeded by the radiation
force. Mergers between BHs at high-z can also help with the
required growth
if the coalesced BH is not ejected from the halo by the gravitational recoil
from the merger. The main challenge here is whether or not such critical
accretion can maintain stable and uninterrupted for the entire time (e.g.,
Pelupessy
et al. 2007).
But in any case, it is quite likely
that the observed z > 6 quasars are all born in rare
environments of the
early Universe, thus extreme conditions (such as large gas density, high
merger rate, etc.) may have facilitated their growth. Indeed, some
theoretical studies can successfully produce such massive BHs at
z ~ 6 growing from a typical Pop III remnant BH seed without
super-Eddington accretion (e.g.,
Yoo &
Miralda-Escude 2004,
Li et al. 2007,
Tanaka &
Haiman 2009).
But the detailed physics (accretion rate, mergers, BH recoils, etc.)
regarding the formation of these earliest SMBHs is still uncertain to
some large extent.
~ a few) could happen,
for instance, if the radiation and density fields of the accretion flow are
anisotropic and most of the accretion flow is not impeded by the radiation
force. Mergers between BHs at high-z can also help with the
required growth
if the coalesced BH is not ejected from the halo by the gravitational recoil
from the merger. The main challenge here is whether or not such critical
accretion can maintain stable and uninterrupted for the entire time (e.g.,
Pelupessy
et al. 2007).
But in any case, it is quite likely
that the observed z > 6 quasars are all born in rare
environments of the
early Universe, thus extreme conditions (such as large gas density, high
merger rate, etc.) may have facilitated their growth. Indeed, some
theoretical studies can successfully produce such massive BHs at
z ~ 6 growing from a typical Pop III remnant BH seed without
super-Eddington accretion (e.g.,
Yoo &
Miralda-Escude 2004,
Li et al. 2007,
Tanaka &
Haiman 2009).
But the detailed physics (accretion rate, mergers, BH recoils, etc.)
regarding the formation of these earliest SMBHs is still uncertain to
some large extent.
While this is not seen as an immediate crisis, there are multiple
pathways to make it much easier to grow
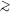 109
M
109
M SMBHs
at z
SMBHs
at z 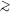 6 by
boosting either the accretion rate or the seed BH mass (for a recent
review, see, e.g.,
Volonteri 2010,
Haiman 2012).
These recipes include:
6 by
boosting either the accretion rate or the seed BH mass (for a recent
review, see, e.g.,
Volonteri 2010,
Haiman 2012).
These recipes include:
1) supercritical accretion (e.g.,
Volonteri
& Rees 2005)
where the accretion rate
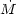 BH greatly
exceeds the Eddington limit with a
canonical radiative efficiency є = 0.1. One possibility is that the
radiation is trapped in the accretion flow (e.g.,
Begelman 1979,
Wyithe &
Loeb 2012),
leading to a very low
є and hence a much shorter e-folding time. Note that in such a
radiatively inefficient accretion flow (RIAF), the luminosity is still
bounded by the Eddington limit;
BH greatly
exceeds the Eddington limit with a
canonical radiative efficiency є = 0.1. One possibility is that the
radiation is trapped in the accretion flow (e.g.,
Begelman 1979,
Wyithe &
Loeb 2012),
leading to a very low
є and hence a much shorter e-folding time. Note that in such a
radiatively inefficient accretion flow (RIAF), the luminosity is still
bounded by the Eddington limit;
2) rapid formation of massive (~ 103-105
M ) BH
seeds from direct collapse of primordial gas clouds (e.g.,
Bromm &
Loeb 2003,
Begelman et
al. 2006,
Agarwal et
al. 2012)
or from a hypothetical supermassive star or "quasi-star" (e.g.,
Shibata
& Shapiro 2002,
Begelman et
al. 2008,
Johnson et
al. 2012)
at high redshift. Supercritical accretion may also be expected in some
of these models to grow to the final seed BH mass, which then continue
to accrete in the normal way. By increasing Mseed it
requires much less e-folds to grow to a >
109
M
) BH
seeds from direct collapse of primordial gas clouds (e.g.,
Bromm &
Loeb 2003,
Begelman et
al. 2006,
Agarwal et
al. 2012)
or from a hypothetical supermassive star or "quasi-star" (e.g.,
Shibata
& Shapiro 2002,
Begelman et
al. 2008,
Johnson et
al. 2012)
at high redshift. Supercritical accretion may also be expected in some
of these models to grow to the final seed BH mass, which then continue
to accrete in the normal way. By increasing Mseed it
requires much less e-folds to grow to a >
109
M BH. Another possible route to produce massive
BH seeds up to ~ 103
M
BH. Another possible route to produce massive
BH seeds up to ~ 103
M is by
the runaway collisional growth in a
dense star cluster formed in a high-redshift halo (e.g.,
Omukai et
al. 2008).
is by
the runaway collisional growth in a
dense star cluster formed in a high-redshift halo (e.g.,
Omukai et
al. 2008).
4.2. Quasar Demographics in the Mass-Luminosity Plane
BH mass estimates provide an additional dimension in the physical properties of quasars. The distribution of quasars in the two-dimensional BH mass-luminosity (M - L) plane conveys important information about the accretion process of these active SMBHs. The first quasar mass-luminosity plane plot was made by Dibai in the 1970s as mentioned in Section 2.2. Over the years, such a 2D plot has been repeatedly generated based on increasingly larger quasar samples and improved BH mass estimates (e.g., Wandel et al. 1999, Woo & Urry 2002, Kollmeier et al. 2006, Shen et al. 2008a, Shen & Kelly 2012), and the much better statistics now allows a more detailed and deeper look into this quasar mass-luminosity plane.
In what follows I will mainly focus on the SDSS quasar sample because this is the largest and most homogeneous quasar samples to date. But as emphasized in Shen & Kelly (2012), the SDSS sample only probes the bright-end of the quasar population, and to probe the mass and accretion rate of the bulk of quasars it is necessary to assemble deeper spectroscopic quasar samples (e.g., Kollmeier et al. 2006, Gavignaud et al. 2008, Trump et al. 2009, Nobuta et al. 2012).
Since I have emphasized the distinction between true BH masses and SE mass
estimates, I shall use the term "observed" or "measured" to refer to
distributions based on SE mass estimates, to distinguish them from "true"
distributions. Fig. 10 shows such an
observed mass-luminosity plane from the same collection of
quasars as shown in Fig. 9. Note that these
samples are flux-limited to different
magnitudes, and several high-redshift samples based on
H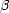 or Mg II
(i.e., large symbols) have a higher flux-limit than the SDSS. I also used
slightly different values of bolometric corrections to convert continuum
luminosity to bolometric luminosity for those non-SDSS samples. From this
plot we see that the observed distributions of quasars are bounded between
constant Eddington ratios 0.01
or Mg II
(i.e., large symbols) have a higher flux-limit than the SDSS. I also used
slightly different values of bolometric corrections to convert continuum
luminosity to bolometric luminosity for those non-SDSS samples. From this
plot we see that the observed distributions of quasars are bounded between
constant Eddington ratios 0.01
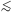
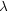
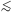 1, with median
values of <
1, with median
values of < 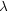 > ~
0.1-0.3 for SDSS quasars, and somewhat higher values for the z
> ~
0.1-0.3 for SDSS quasars, and somewhat higher values for the z
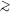 5 samples. The
dispersion in Eddington ratio in these flux-limited samples is typically
~ 0.3 dex. Similar distributions were observed by, e.g.,
Kollmeier
et al. (2006).
However, as demonstrated in, e.g.,
Shen et
al. (2008a),
Kelly et al.
(2009a,
2010),
Shen &
Kelly (2012),
Kelly &
Shen (2013),
the observed distribution suffers from the sample flux limit such that
low-Eddginton ratio objects have a lower probability being selected into the
sample, and from the uncertainties and statistical biases of SE masses
relative to true masses. The selection effect due to the flux limit and
errors in SE masses dramatically modify the intrinsic distribution in the
mass-luminosity plane, and must be taken into account when interpreting the
observations.
5 samples. The
dispersion in Eddington ratio in these flux-limited samples is typically
~ 0.3 dex. Similar distributions were observed by, e.g.,
Kollmeier
et al. (2006).
However, as demonstrated in, e.g.,
Shen et
al. (2008a),
Kelly et al.
(2009a,
2010),
Shen &
Kelly (2012),
Kelly &
Shen (2013),
the observed distribution suffers from the sample flux limit such that
low-Eddginton ratio objects have a lower probability being selected into the
sample, and from the uncertainties and statistical biases of SE masses
relative to true masses. The selection effect due to the flux limit and
errors in SE masses dramatically modify the intrinsic distribution in the
mass-luminosity plane, and must be taken into account when interpreting the
observations.
 |
Figure 10. The observed quasar
mass-luminosity plane based on SE masses for quasars in a wide range of
redshifts (0 < z
|
The best approach to tackle these issues is a forward modeling, in which one specifies an underlying distribution of true masses and luminosities and map to the observed mass-luminosity plane by imposing the flux limit and relations between SE virial masses and true masses (e.g., Shen et al. 2008a, Kelly et al. 2009a, Kelly et al. 2010). Then the comparisons between model and observed distributions constrain the model parameters with standard Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) techniques and Bayesian inference. This is a complicated and model-dependent problem, and the best efforts so far are the studies by Shen & Kelly (2012) and Kelly & Shen (2013), building on earlier work by Shen et al. (2008a), Kelly et al. (2009a) and Kelly et al. (2010). Alternatively, Schulze & Wisotzki (2010) developed a maximum likelihood method (also a forward modeling method), which accounts for the effect of the flux limit, but not the errors in SE masses (although the SE errors can be incorporated in such a framework as well). This maximum likelihood method was subsequently adopted in Nobuta et al. (2012) when modeling a faint quasar sample (again, SE errors not taken into account). Most other quasar mass demographic studies, however, did not explicitly model either of these effects (e.g., Greene & Ho 2007, Vestergaard et al. 2008, Vestergaard & Osmer 2009).
Shen &
Kelly (2012)
used forward modeling with Bayesian inference to
model the observed distribution in the mass-luminosity plane of SDSS
quasars, taking into account a possible luminosity-dependent bias (i.e.,
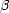 ≠
0, see Section 3.3.2) to be constrained
by the data. The flux limit of the SDSS sample is taken into account
using published selection functions of SDSS quasars
(Richards et
al. 2006a).
Based on this approach,
Shen &
Kelly (2012)
found evidence for a non-zero
≠
0, see Section 3.3.2) to be constrained
by the data. The flux limit of the SDSS sample is taken into account
using published selection functions of SDSS quasars
(Richards et
al. 2006a).
Based on this approach,
Shen &
Kelly (2012)
found evidence for a non-zero
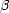 , although the
constraints on
, although the
constraints on
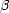 are weak
and cannot rule out a null value.
Kelly &
Shen (2013)
used a more flexible model parametrization to
describe the underlying true distributions (in BH mass and Eddington ratio),
but fixed
are weak
and cannot rule out a null value.
Kelly &
Shen (2013)
used a more flexible model parametrization to
describe the underlying true distributions (in BH mass and Eddington ratio),
but fixed 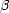 = 0 to test how sensitively the results in
Shen &
Kelly (2012)
depend on different model parameterizations. They
found that the main conclusions are generally consistent, although the
results in the latter work are less constrained than in the former, due to
the more flexible models. Both studies revealed that based on the SDSS
quasar sample alone, it is difficult to constrain the BHMF to better
than a factor of a few at most redshifts. This is both because the SDSS
sample only probes the tip of the active SMBH population at
high-z, and to a larger extent, because the errors of SE masses
are poorly understood. However, there are some solid conclusions from
the two studies:
= 0 to test how sensitively the results in
Shen &
Kelly (2012)
depend on different model parameterizations. They
found that the main conclusions are generally consistent, although the
results in the latter work are less constrained than in the former, due to
the more flexible models. Both studies revealed that based on the SDSS
quasar sample alone, it is difficult to constrain the BHMF to better
than a factor of a few at most redshifts. This is both because the SDSS
sample only probes the tip of the active SMBH population at
high-z, and to a larger extent, because the errors of SE masses
are poorly understood. However, there are some solid conclusions from
the two studies:
The observed
distribution in the mass-luminosity plane is
quite different from the intrinsic distribution, due to the flux
limit and uncertainties in SE masses. This is demonstrated in
Fig. 11, which shows a quasar M -
L plane at z = 0.6 based on the modeling of SDSS quasars by
Shen &
Kelly (2012).
In this plot luminosity L is the restframe 2500 Å monochromatic
luminosity, and the bolometric luminosity is Lbol ~
5L.
The red contours are the true distribution of quasars, while
the black contours are the measured distribution based on
H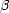 SE
virial masses. The black horizontal line indicates the
flux limit of the sample, hence only objects above this line would be
selected in the SDSS sample, which form the observed
distribution. The flux limit only selects the most luminous objects
into the SDSS sample, missing the bulk of low Eddington ratio
objects; even the highest mass bins are incomplete due to the flux
limit. The distribution based on SE virial BH masses is flatter than
the one based on true masses due to the scatter and
luminosity-dependent bias of these SE masses.
SE
virial masses. The black horizontal line indicates the
flux limit of the sample, hence only objects above this line would be
selected in the SDSS sample, which form the observed
distribution. The flux limit only selects the most luminous objects
into the SDSS sample, missing the bulk of low Eddington ratio
objects; even the highest mass bins are incomplete due to the flux
limit. The distribution based on SE virial BH masses is flatter than
the one based on true masses due to the scatter and
luminosity-dependent bias of these SE masses.
 |
Figure 11. The simulated mass-luminosity
plane at z = 0.6 based on the modeling of SDSS quasars in
Shen &
Kelly (2012),
which extends below the flux limit (the black horizontal line). The
y-axis plots the
restframe 2500Å monochromatic luminosity, and the bolometric
luminosity is Lbol ~ 5L. The red contour
is the distribution based on true BH masses and is determined by the
model BHMF and Eddington ratio distribution in
Shen &
Kelly (2012).
The black contour is the distribution based on
H |
For the observed distribution based on SE masses, there are
fewer objects towards larger SE masses and luminosity. This was
interpreted as the lack of massive black holes accreting at high
Eddington ratios, or the so-called "sub-Eddington boundary" claimed
by
Steinhardt
& Elvis 2010a.
However, such a feature is caused
by the flux limit and errors in SE masses, and there is no evidence
that high-mass quasars on average accrete at lower Eddington ratios,
not for broad-line objects at least
10.
This conclusion seems to be robust against
different model parameterizations of the underlying true
distributions in the forward modeling approach
(Kelly &
Shen 2013).
Of course here I am assuming no systematic biases in these FWHM-based SE
masses measured in
Shen et
al. 2011.
It is possible that
 line-based
SE masses are more reliable, in which case there would be a
"rotation" in the mass-luminosity plane using
line-based
SE masses are more reliable, in which case there would be a
"rotation" in the mass-luminosity plane using
 line-based SE
masses, as discussed in Section 3.1.3. This
also tends to reduce this "sub-Eddington boundary" in the observed
plane (e.g.,
Rafiee &
Hall 2011a,
Rafiee &
Hall 2011b),
but a full modeling taking into account both the flux limit and SE mass
errors is yet to be performed with
line-based SE
masses, as discussed in Section 3.1.3. This
also tends to reduce this "sub-Eddington boundary" in the observed
plane (e.g.,
Rafiee &
Hall 2011a,
Rafiee &
Hall 2011b),
but a full modeling taking into account both the flux limit and SE mass
errors is yet to be performed with
 line-based SE
masses (i.e., the interpretation by Rafiee & Hall is still based on
"observed" rather than true distributions).
line-based SE
masses (i.e., the interpretation by Rafiee & Hall is still based on
"observed" rather than true distributions).
The intrinsic Eddington ratio
distribution at fixed true mass
is broader (~ 0.4 dex) than the observed Eddington ratio
distribution in flux-limited samples
(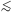 0.3 dex), and the
mean Eddington ratio in the flux-limited samples based on SE masses
is higher
11
than the mean Eddington ratio for all active SMBHs (most of which are
not detected). This is consistent with earlier studies by
Shen et
al. (2008a)
and
Kelly et
al. (2010).
Some deeper spectroscopic surveys indeed start to find these lower Eddington
ratio objects (e.g.,
Babic et
al. 2007,
Gavignaud
et al. 2008,
Nobuta et
al. 2012),
and are consistent with the model-extrapolated distributions from
Shen &
Kelly (2012)
and
Kelly &
Shen (2013);
however, since in general these deep data are noisier and the selection
function is less well quantified than SDSS, care must be paid when
inferring the dispersion in Eddington ratios for these faint
quasars.
0.3 dex), and the
mean Eddington ratio in the flux-limited samples based on SE masses
is higher
11
than the mean Eddington ratio for all active SMBHs (most of which are
not detected). This is consistent with earlier studies by
Shen et
al. (2008a)
and
Kelly et
al. (2010).
Some deeper spectroscopic surveys indeed start to find these lower Eddington
ratio objects (e.g.,
Babic et
al. 2007,
Gavignaud
et al. 2008,
Nobuta et
al. 2012),
and are consistent with the model-extrapolated distributions from
Shen &
Kelly (2012)
and
Kelly &
Shen (2013);
however, since in general these deep data are noisier and the selection
function is less well quantified than SDSS, care must be paid when
inferring the dispersion in Eddington ratios for these faint
quasars.
The next step to utilize this quasar mass-luminosity plane is to measure the abundance of quasars in this plane, and study its redshift evolution. This is a much more powerful way to study the cosmic evolution of quasars than traditional 1D distribution functions such as the luminosity function (LF) and the quasar BHMF.
I demonstrate the power of the mass-luminosity plane in quasar demographic studies in Fig. 12. This is the same simulated, true quasar M - L plane at z = 0.6 as in Fig. 11, using the models in Shen & Kelly (2012) constrained using SDSS quasars. The 2D density (i.e., abundance) of quasars in this plane is shown in the color-coded contours. The traditional LF and BHMF (shown in the right panels) are then just the projection onto each axis. In the right panels I also demonstrate the differences between using true BH masses and SE virial masses, as well as the effect of the sample flux limit. It is clear from this demonstration that the 1D distribution functions lose information by collapsing on one dimension, and a better way to study the demography of quasars is to measure their abundance in 2D, since the mass and luminosity of a quasar are physically connected by the Eddington ratio. The ultimate goal is to study the evolution of the quasar density in the M - L plane as a function of time. Recent studies have started to work in this direction (e.g., Shen & Kelly 2012, Kelly & Shen 2013), although deeper quasar samples and a better understanding of SE mass errors are needed to utilize the full power of the M - L plane.
 |
Figure 12. An example of the forward
modeling of quasar demographics in the mass-luminosity plane by
Shen &
Kelly (2012),
modeled at z = 0.6. Left: The simulated mass-luminosity plane
(with true BH masses), which extends below the SDSS flux limit (the
black horizontal line). Shown here is the comoving
number density map
[ |
To summarize, the quasar mass-luminosity plane has great potential in studying quasar evolution, and efforts have been underway to investigate this plane in detail (e.g., Steinhardt & Elvis 2010a, b, Steinhardt et al.2011, Steinhardt & Elvis 2011, Shen & Kelly 2012, Kelly & Shen 2013). However, it should always be kept in mind that the "observed" distribution in the M - L plane is not the true distribution. I strongly discourage direct interpretations of the observed distributions based on SE masses and flux-limited data, which can easily lead to superficial or even spurious results.
4.3. Evolution of BH-Bulge Scaling Relations
Another important application of SE virial mass estimators is to study the MBH-host scaling relations in broad line AGNs, and to probe the evolution of these relations at high redshift. Measuring the MBH-host relations in low redshift quasars and AGNs has been done using both RM masses and SE masses (e.g., Laor 1998, Greene & Ho 2006, Bentz et al. 2009c, Xiao et al. 2011). Assuming some virial coefficient < f >, these studies were able to add active objects in these scaling relations and extend the dynamic range in BH mass.
In the past a few years, there have been a huge amount of effort to quantify
the evolution of these scaling relations up to z ~ 6, by
measuring host properties in broad-line quasars. Some studies directly
measure the galaxy properties by decomposing the quasar and galaxy light
in either imaging or spectroscopic data (e.g.,
Treu et
al. 2004,
Peng et
al. 2006a,
b,
Woo et al. 2006,
Treu et
al. 2007,
Woo et al. 2008,
Shen et
al. 2008b,
Jahnke et
al. 2009,
McLeod
& Bechtold 2009,
Decarli et
al. 2010,
Merloni et
al. 2010,
Bennert et
al. 2010,
Cisternas
et al. 2011,
Targett et
al. 2012);
other studies use indirect methods to infer galaxy properties, such as using
the narrow emission line width to infer bulge velocity dispersion (e.g.,
Shields et
al. 2003,
2006,
Salviander
et al. 2007,
Salviander
& Shields 2012).
Molecular gas (using CO tracers) has also been detected in the hosts of
z ~ 6 quasars, allowing rough estimates on the host dynamical mass of
these highest redshift quasars (e.g.,
Walter et
al. 2004,
Wang et al. 2010
and references therein). In all cases the BH masses were
estimated using the SE methods based on different broad emission lines. With
a few exceptions, most of these studies claim an excess in BH mass relative
to bulge properties either in the MBH -
 * relation or
in the MBH - Mbulge /
Lbulge relation, and advocate a scenario
where BH growth precedes spheroid assembly.
* relation or
in the MBH - Mbulge /
Lbulge relation, and advocate a scenario
where BH growth precedes spheroid assembly.
It is worth noting that measuring host galaxy properties of Type 1 AGNs could be challenging, and systematic biases may arise when measuring the stellar velocity dispersion from spectra (e.g., Bennert et al. 2011), or host luminosities from image decomposing (e.g., Kim et al. 2008, Simmons & Urry 2008). Conversions from measurables (such as host luminosity) to derived quantities (such as stellar mass) are also likely subject to systematics, especially for low-quality data. Thus careful treatments are required to derive unbiased host measurements.
On the other hand, it is also worrisome that the errors in SE BH mass
estimates may affect the observed offset in the BH scaling relations at
high-redshift. As discussed extensively in
Section 3, there are both
physical and practical concerns that the applications of locally-calibrated
SE estimators to high-redshift quasars may cause systematic biases. Even if
the extrapolations are valid, the luminosity-dependent bias discussed in
Section 3.3.2 may still lead to an
average overestimation of quasar BH masses in flux-limited surveys.
(Shen &
Kelly 2010)
studied the impact of
the luminosity-dependent bias on flux-limited quasar samples, and found an
"observed" BH mass excess of ~ 0.2-0.3 dex for Lbol
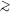 1046 erg s-1 with a reasonable value of
1046 erg s-1 with a reasonable value of
 'l = 0.4
dex (see Section 3.3.2 for details). This
sample bias using SE mass estimates becomes larger (smaller) at higher
(lower) threshold quasar luminosities.
'l = 0.4
dex (see Section 3.3.2 for details). This
sample bias using SE mass estimates becomes larger (smaller) at higher
(lower) threshold quasar luminosities.
Another statistical bias was pointed out by
Lauer et
al. (2007),
which is at work even if there is no error in BH mass estimates. The
basic idea is that since there is an intrinsic scatter between BH mass
and bulge properties
(~ 0.3 dex for the local sample), and since the distribution functions
in BH mass and galaxy properties are expected to be bottom-heavy, a
statistical excess (bias) in the average BH mass relative to bulge
properties arises when the sample is selected based on BH mass (or based
on quasar luminosity, assuming the Eddington ratio is constant). This is
similar to the Malmquist-type bias discussed in
Section 3.3.1. One can work out (e.g.,
Lauer et
al. 2007,
Shen &
Kelly 2010)
that the BH mass offset
introduced by this bias depends on the slope of the galaxy distribution
function, as well as the scatter in the BH-host scaling relations. For
simple power-law models of the galaxy distribution function on property
S with a slope
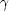 s, and lognormal scatter
s, and lognormal scatter
 µ
at fixed galaxy property S, this bias takes a similar form as the
Malmquist-type bias in Section 3.3.1:
µ
at fixed galaxy property S, this bias takes a similar form as the
Malmquist-type bias in Section 3.3.1:
 |
(21) |
where C is the coefficient of the mean BH-host property (S) scaling relation logMBH = C logS + C'. Thus if the intrinsic scatter in the BH-host scaling relations increases with redshift, then this statistical bias alone can contribute a significant amount to the observed BH mass offset in the high-redshift samples (e.g., Merloni et al. 2010). A larger intrinsic scatter in these scaling relations at high redshift is expected, if the tightness of the local BH-host scaling relations is mainly established via the hierarchical merging of less-correlated BH-host systems at higher redshift (e.g., Peng 2007, Hirschmann et al. 2010, Jahnke & Macció 2011). The real situation is of course more complicated, and one must consider a realistic Eddington ratio distribution at fixed BH mass and the effect of the flux limit. There could also be other factors that may complicate the usage of AGNs to probe the evolution of these BH-host scaling relations, as discussed in detail in Schulze & Wisotzki (2011). But overall a BH mass excess due to the Lauer et al. bias is expected when select on quasar luminosity. An interesting corollary is that a deficit in BH mass is expected if the sample is selected based on galaxy properties. This may explain the findings that high-redshift submillimeter galaxies (SMGs) tend to have on average smaller BHs relative to expectations from local BH-host scaling relations (e.g., Alexander et al. 2008).
The Lauer et al. bias caused by the intrinsic scatter in BH-host scaling
relations works independently with the luminosity-dependent bias caused by
errors in SE masses, so together they can contribute a substantial (or even
full) amount of the observed BH mass excess at high redshift (e.g.,
Shen &
Kelly 2010).
Both biases are generally worse for samples
with a higher luminosity threshold given the curvature in the underlying
distribution function
12,
thus higher-z
samples with higher intrinsic AGN luminosities will have larger BH mass
biases, leading to an apparent evolution. There are several samples that are
probing similar luminosities as the local RM AGN sample (e.g.,
Woo et al. 2006).
Since the SE mass estimators were calibrated
on the local MBH -
 * relation
using the RM AGN sample, one
argument often made is that both biases should be calibrated away for the
high-z sample with similar AGN luminosities. This argument is flawed,
however, because the local RM AGN sample is heterogeneous and is not
sampling uniformly from the underlying BH/galaxy distribution functions,
while the high-z sample usually is sampling uniformly from the
underlying distributions – this is exactly why both biases will
arise for the high-z
samples. The only exception that might work is to compare two quasar samples
at two different redshifts with the same luminosity threshold, where the
predicted BH mass biases should be of the same amount, and see if there is
evolution in the average host properties. But even in this case it requires
that the underlying distributions (slope and scatter) and measurement
systematics are the same for both the low-z and high-z
samples. Proper simulations that take into account the measurement
systematics (in both BH mass and host properties) and underlying
distributions should be performed to verify the interpretations upon the
observations.
* relation
using the RM AGN sample, one
argument often made is that both biases should be calibrated away for the
high-z sample with similar AGN luminosities. This argument is flawed,
however, because the local RM AGN sample is heterogeneous and is not
sampling uniformly from the underlying BH/galaxy distribution functions,
while the high-z sample usually is sampling uniformly from the
underlying distributions – this is exactly why both biases will
arise for the high-z
samples. The only exception that might work is to compare two quasar samples
at two different redshifts with the same luminosity threshold, where the
predicted BH mass biases should be of the same amount, and see if there is
evolution in the average host properties. But even in this case it requires
that the underlying distributions (slope and scatter) and measurement
systematics are the same for both the low-z and high-z
samples. Proper simulations that take into account the measurement
systematics (in both BH mass and host properties) and underlying
distributions should be performed to verify the interpretations upon the
observations.
To summarize, there might be true evolutions in the BH-host scaling relations 13, but the current observations are inconclusive, due to the unknown systematics in the BH mass and host galaxy measurements. Better understandings of these systematics, the selection effects, as well as theoretical priors are all needed to probe the evolution of these scaling relations, and such efforts have been underway (e.g., Croton 2006, Robertson et al. 2006, Lauer et al. 2007, Hopkins et al. 2007, Di Matteo et al. 2008, Booth & Schaye 2009, Shankar et al. 2009, Shen & Kelly 2010, Hirschmann et al. 2010, Schulze & Wisotzki 2011, Jahnke & Macció 2011, Portinari et al. 2012, Salviander & Shields 2012, Zhang et al. 2012).
10 There could be a significant population of high-mass, non-broad-line AGNs accreting at low Eddington ratios, possibly via a different accretion mode than broad line quasars. Back.
11 These SE masses are on average overestimated due to the luminosity-dependent bias discussed in Section 3.3.2, which tends to underestimated the true Eddington ratios. But the mean observed Eddington ratio based on SE masses of the flux-limited sample is still higher than the mean value for all quasars extending below the flux limit (see fig. 19 of Shen & Kelly 2012). Back.
12 This is not always the case. If the
scatter
( µ,
µ,
 'l) increases
at the low-mass end, then both
biases could be worse at the low-mass/luminosity end.
Back.
'l) increases
at the low-mass end, then both
biases could be worse at the low-mass/luminosity end.
Back.
13 If the mass and velocity dispersion
of galaxies bear any
resemblance to the virial mass (Mh, vir) and virial
velocity (Vh,vir) of their host dark matter halos,
then one of the two relations,
MBH -
 * and
MBH - Mbulge, must evolve since the
Mh,vir - Vh,vir relation is
redshift-dependent.
Back.
* and
MBH - Mbulge, must evolve since the
Mh,vir - Vh,vir relation is
redshift-dependent.
Back.