


The ISO LWS sample of galaxies selected from the ISO archive for this paper is presented in Table 1 and lists the galaxy positions, recession velocities, morphologies, optical sizes, and the flux densities of these galaxies in the four IRAS bands along with the IRAS 60 µm / 100 µm ratios. The positions, optical sizes, and velocities were taken from the NASA Extragalactic Database (NED) in mid-2004.
| Galaxy | R.A. | Decl. | cz | Tb | 2ac | 2bc | 12 µm | 25 µm | 60 µm | 100 µm | 60/100 |
| (J2000.0) | (J2000.0) | (km s-1) | ' | ' | (Jy) | (Jy) | (Jy) | (Jy) | |||
| IC 10 a... | 00 20 24.55 | +59 17 30.5 | -344 | 10 | 6.3 | 5.1 | 4.88 | 13.95 | 112.9 | 179.2 | 0.63 |
| ESO 350-IG 38... | 00 36 52.53 | -33 33 18.6 | 6156 | -2 | 0.41 | 2.49 | 6.47 | 5.01 | 1.29 | ||
| Cartwheel... | 00 37 40.80 | -33 42 58.0 | 9050 | 10 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.73 | 1.57 | 0.46 |
| NGC 0185... | 00 38 57.69 | +48 20 12.2 | -202 | -5 | 11.7 | 10.0 | 0.04 | <0.03 | 0.35 | 1.46 | 0.24 |
| NGC 0247 a... | 00 47 08.30 | -20 45 37.6 | 160 | 7 | 21.4 | 6.9 | <0.12 | <0.16 | 7.93 | 27.32 | 0.29 |
| NGC 0253 a... | 00 47 34.37 | -25 17 32.0 | 245 | 5 | 27.5 | 6.8 | 55.84 | 155.7 | 998.7 | 1862 | 0.54 |
| NGC 0278... | 00 52 04.58 | +47 33 02.0 | 640 | 3 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 1.63 | 2.57 | 25.05 | 46.39 | 0.54 |
| UGC 00545... | 00 53 34.90 | +12 41 36.0 | 18330 | -1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.51 | 1.21 | 2.24 | 2.63 | 0.85 |
| MCG +12-02-001... | 00 54 04.01 | +73 05 12.6 | 4706 | 99 | 0.76 | 3.71 | 22.37 | 26.68 | 0.84 | ||
| NGC 0300 a... | 00 54 53.72 | -37 40 56.9 | 144 | 7 | 21.9 | 15.5 | 0.53 | 0.64 | 23.08 | 74.45 | 0.31 |
| IC 1613 a... | 01 05 02.00 | +02 08 03.0 | -234 | 10 | 16.2 | 14.5 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.68 | 1.78 | 0.38 |
| NGC 0449... | 01 16 07.23 | +33 05 22.3 | 4780 | -1 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.34 | 0.89 | 2.53 | 3.05 | 0.83 |
| UGC 00852... | 01 19 38.30 | +17 33 53.0 | 8817 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.77 | 4.02 | 0.19 |
| NGC 0520... | 01 24 34.90 | +03 47 30.0 | 2266 | 99 | 1.9 | 0.7 | 0.76 | 2.84 | 31.1 | 47.12 | 0.66 |
| M33 a... | 01 33 50.90 | +30 39 37.0 | -179 | 6 | 70.8 | 41.7 | 32.69 | 40.26 | 419.7 | 1256 | 0.33 |
| NGC 0625... | 01 35 04.20 | -41 26 15.0 | 405 | 9 | 5.8 | 1.9 | 0.20 | 0.94 | 5.09 | 9.07 | 0.56 |
| NGC 0628 a... | 01 36 41.70 | +15 46 59.0 | 657 | 5 | 10.5 | 9.5 | 2.07 | 1.90 | 20.86 | 65.64 | 0.32 |
| NGC 0660... | 01 43 01.70 | +13 38 34.0 | 850 | 1 | 8.3 | 3.2 | 2.31 | 7.05 | 67.27 | 104.9 | 0.64 |
| Mrk 573... | 01 43 57.80 | +02 21 00.0 | 5174 | -1 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 0.23 | 0.79 | 1.11 | 1.36 | 0.82 |
| III Zw 35... | 01 44 30.50 | +17 06 08.0 | 8225 | 11 | 0.09 | 1.08 | 13.33 | 14.13 | 0.94 | ||
| NGC 0685... | 01 47 43.10 | -52 45 40.0 | 1356 | 5 | 3.7 | 3.3 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 1.60 | 7.14 | 0.22 |
| NGC 0693... | 01 50 31.00 | +06 08 42.0 | 1567 | 90 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 0.29 | 0.55 | 6.73 | 11.81 | 0.57 |
| NGC 0695... | 01 51 14.20 | +22 34 57.0 | 9735 | 10 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.48 | 0.86 | 7.87 | 13.57 | 0.58 |
| UGC 01449... | 01 58 06.70 | +03 05 15.0 | 5589 | 9 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 0.31 | 0.56 | 4.96 | 8.41 | 0.59 |
| NGC 0821... | 02 08 21.20 | +10 59 41.0 | 1735 | -5 | 2.6 | 1.6 | |||||
| NGC 0814... | 02 10 37.70 | -15 46 24.0 | 1616 | -2 | 1.3 | 0.5 | 0.19 | 1.01 | 4.41 | 3.59 | 1.23 |
| Arp 273... | 02 21 32.78 | +39 21 29.9 | 7563 | <0.17 | 0.24 | 1.87 | 3.85 | 0.49 | |||
| NGC 0891 a... | 02 22 33.04 | +42 20 47.7 | 528 | 3 | 13.5 | 2.5 | 5.66 | 7.78 | 61.1 | 198.6 | 0.31 |
| NGC 0925 a... | 02 27 17.00 | +33 34 43.0 | 553 | 7 | 10.5 | 5.9 | 0.26 | 0.66 | 7.65 | 26.68 | 0.29 |
| NGC 0986... | 02 33 34.10 | -39 02 41.0 | 2005 | 2 | 3.9 | 3.0 | 1.41 | 3.65 | 25.14 | 51.31 | 0.49 |
| NGC 1022... | 02 38 32.70 | -06 40 40.0 | 1453 | 1 | 2.4 | 2.0 | 0.75 | 3.29 | 19.83 | 27.16 | 0.73 |
| NGC 1052... | 02 41 04.80 | -08 15 20.8 | 1470 | -5 | 3.0 | 2.1 | 0.20 | 0.49 | 0.93 | 1.5 | 0.62 |
| Maffei 2 a... | 02 41 54.90 | +59 36 14.9 | -17 | 4 | 5.8 | 1.6 | 183.9 | 399.8 | 0.46 | ||
| NGC 1068... | 02 42 40.70 | -00 00 47.9 | 1136 | 3 | 7.1 | 6.0 | 39.7 | 85.04 | 176.2 | 224 | 0.79 |
| UGC 02238... | 02 46 17.40 | +13 05 44.0 | 6436 | 99 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 0.34 | 0.53 | 8.40 | 15.56 | 0.54 |
| NGC 1097 a... | 02 46 18.89 | -30 16 21.0 | 1275 | 3 | 9.3 | 6.3 | 2.88 | 7.70 | 46.73 | 116.3 | 0.40 |
| NGC 1155... | 02 58 12.90 | -10 21 00.0 | 4549 | -2 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.21 | 0.47 | 2.89 | 4.98 | 0.58 |
| NGC 1156... | 02 59 42.60 | +25 14 17.0 | 375 | 10 | 3.3 | 2.5 | 0.17 | 0.55 | 5.24 | 10.48 | 0.50 |
| NGC 1222... | 03 08 56.80 | -02 57 18.0 | 2452 | -3 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.51 | 2.29 | 13.07 | 15.38 | 0.85 |
| UGC 02519... | 03 09 19.70 | +80 07 52.0 | 2377 | 6 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 2.98 | 7.45 | 0.40 |
| NGC 1266... | 03 16 00.80 | -02 25 38.0 | 2194 | -2 | 1.5 | 1.0 | 0.14 | 1.23 | 13.32 | 16.44 | 0.81 |
| NGC 1313 a... | 03 18 15.40 | -66 29 51.0 | 475 | 7 | 9.1 | 6.9 | 1.70 | 3.75 | 45.69 | 97.21 | 0.47 |
| NGC 1275... | 03 19 48.16 | +41 30 42.1 | 5264 | 99 | 2.2 | 1.7 | 1.06 | 3.53 | 7.14 | 6.98 | 1.02 |
| NGC 1316 a... | 03 22 41.51 | -37 12 33.4 | 1760 | -2 | 12.0 | 8.5 | 0.32 | 0.24 | 2.97 | 7.33 | 0.41 |
| NGC 1317... | 03 22 44.40 | -37 06 13.0 | 1941 | 1 | 2.8 | 2.4 | 0.26 | 0.31 | 3.52 | 10.35 | 0.34 |
| NGC 1326... | 03 23 56.40 | -36 27 52.0 | 1360 | -1 | 3.9 | 2.9 | 0.38 | 0.86 | 8.17 | 13.85 | 0.59 |
| NGC 1365 a... | 03 33 35.57 | -36 08 22.9 | 1636 | 3 | 11.2 | 6.2 | 3.37 | 10.82 | 97.79 | 174.6 | 0.56 |
| IC 1953... | 03 33 41.60 | -21 28 41.0 | 1867 | 7 | 2.8 | 2.1 | 0.16 | 0.93 | 8.47 | 11.29 | 0.75 |
| NGC 1377... | 03 36 38.90 | -20 54 06.0 | 1792 | -2 | 1.8 | 0.9 | 0.44 | 1.81 | 7.25 | 5.75 | 1.26 |
| NGC 1385... | 03 37 28.20 | -24 30 04.0 | 1493 | 6 | 3.4 | 2.0 | 1.19 | 2.02 | 17.3 | 37.61 | 0.46 |
| IC 342 a... | 03 46 49.71 | +68 05 44.7 | 31 | 6 | 21.4 | 20.9 | 23.66 | 45.20 | 256.0 | 661.7 | 0.39 |
| UGC 02855... | 03 48 22.60 | +70 07 57.0 | 1202 | 6 | 4.4 | 2.0 | 2.93 | 4.86 | 42.39 | 90.19 | 0.47 |
| NGC 1482... | 03 54 39.50 | -20 30 07.0 | 1916 | -1 | 2.5 | 1.4 | 1.54 | 4.67 | 33.45 | 46.46 | 0.72 |
| IC 356... | 04 07 46.80 | +69 48 45.0 | 895 | 2 | 5.2 | 3.9 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 3.84 | 24.61 | 0.16 |
| NGC 1546... | 04 14 37.20 | -56 03 35.0 | 1276 | 1 | 3.0 | 1.7 | 0.62 | 0.79 | 7.21 | 22.53 | 0.32 |
| NGC 1569... | 04 30 49.00 | +64 50 53.0 | -104 | 10 | 3.6 | 1.8 | 1.23 | 8.98 | 54.25 | 55.36 | 0.98 |
| 3C 120... | 04 33 11.10 | +05 21 15.6 | 9896 | -2 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.28 | 0.63 | 1.28 | 2.78 | 0.46 |
| NGC 1614... | 04 34 00.03 | -08 34 43.7 | 4778 | 5 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 1.44 | 7.28 | 32.31 | 32.69 | 0.99 |
| NGC 1672 a... | 04 45 42.10 | -59 14 57.0 | 1350 | 3 | 6.6 | 5.5 | 1.67 | 4.03 | 32.96 | 69.89 | 0.47 |
| NGC 1741... | 05 01 38.30 | -04 15 25.0 | 4107 | 99 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.10 | 0.57 | 3.91 | 5.83 | 0.67 |
| IRAS 05189-2524... | 05 21 01.42 | -25 21 45.9 | 12760 | 11 | 0.46 | 0.44 | 0.72 | 3.44 | 13.67 | 11.36 | 1.20 |
| UGCA 116... | 05 55 42.60 | +03 23 31.0 | 789 | 11 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.41 | 1.92 | 6.62 | 5.20 | 1.27 |
| UGC 03426... | 06 15 36.74 | +71 02 14.3 | 4050 | -2 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 0.71 | 2.89 | 3.77 | 3.36 | 1.12 |
| NGC 2146... | 06 18 39.70 | +78 21 23.0 | 893 | 2 | 6.0 | 3.4 | 6.22 | 17.58 | 131.0 | 184.2 | 0.71 |
| IC 450... | 06 52 12.32 | +74 25 37.4 | 5537 | -0.5 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.22 | 0.68 | 1.18 | 1.65 | 0.72 |
| NGC 2388... | 07 28 53.50 | +33 49 05.0 | 4134 | 3 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.51 | 2.07 | 17.01 | 25.39 | 0.67 |
| NGC 2415... | 07 36 56.50 | +35 14 32.0 | 3784 | 10 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.42 | 0.91 | 8.56 | 12.89 | 0.66 |
| DDO 50 a... | 08 19 12.66 | +70 43 06.4 | 157 | 10 | 7.9 | 6.3 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 1.51 | 2.62 | 0.58 |
| M81 a... | 09 55 33.20 | +69 03 55.0 | -34 | 2 | 26.9 | 14.1 | 5.86 | 5.42 | 44.73 | 174.0 | 0.26 |
| M82 a... | 09 55 54.03 | +69 40 57.1 | 203 | 90 | 11.2 | 4.3 | 66.61 | 285.0 | 1271 | 1351 | 0.94 |
| IC 2554... | 10 08 50.42 | -67 01 47.5 | 1474 | 4 | 3.1 | 1.3 | 0.98 | 2.71 | 17.25 | 34.13 | 0.51 |
| ESO 317-G023... | 10 24 42.40 | -39 18 21.0 | 2892 | 1 | 1.9 | 0.8 | 0.34 | 0.88 | 13.5 | 23.68 | 0.57 |
| NGC 3256... | 10 27 51.41 | -43 54 20.6 | 2738 | 99 | 3.8 | 2.1 | 3.23 | 16.03 | 88.3 | 115.3 | 0.77 |
| NGC 3344 a... | 10 43 31.10 | +24 55 20.0 | 586 | 4 | 7.1 | 6.5 | 0.34 | 0.48 | 5.51 | 22.54 | 0.24 |
| NGC 3359 a... | 10 46 37.65 | +63 13 22.2 | 1014 | 5 | 7.2 | 4.4 | 0.16 | 0.28 | 4.06 | 14.66 | 0.28 |
| NGC 3368 a... | 10 46 45.70 | +11 49 12.0 | 897 | 2 | 7.6 | 5.2 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 8.26 | 25.93 | 0.32 |
| IRAS F10565+2448... | 10 59 18.10 | +24 32 34.0 | 12921 | 99 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.21 | 1.13 | 12.08 | 15.29 | 0.79 |
| NGC 3557... | 11 09 57.40 | -37 32 17.0 | 3067 | -5 | 4.1 | 3.0 | 0.35 | 0.24 | 0.71 | 0.34 | |
| NGC 3556 a... | 11 11 31.79 | +55 40 14.7 | 699 | 6 | 8.7 | 2.2 | 2.25 | 4.09 | 32.19 | 80.77 | 0.40 |
| NGC 3583... | 11 14 10.80 | +48 19 03.0 | 2136 | 3 | 2.8 | 1.8 | 0.63 | 0.78 | 7.08 | 18.63 | 0.38 |
| NGC 3620... | 11 16 04.30 | -76 12 54.0 | 1680 | 2 | 2.8 | 1.1 | 1.29 | 4.71 | 46.8 | 66.86 | 0.70 |
| NGC 3623 a... | 11 18 55.20 | +13 05 35.0 | 807 | 1 | 9.8 | 2.9 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 2.42 | 14.35 | 0.17 |
| NGC 3683... | 11 27 32.00 | +56 52 43.0 | 1716 | 6 | 1.9 | 0.7 | 1.06 | 1.53 | 13.61 | 29.59 | 0.46 |
| NGC 3690... | 11 28 32.20 | +58 33 51.0 | 3121 | 9 | 3.8 | 23.19 | 103.7 | 107.4 | 0.97 | ||
| NGC 3705... | 11 30 06.70 | +09 16 36.0 | 1018 | 2 | 4.9 | 2.0 | 0.38 | 0.44 | 3.72 | 11.27 | 0.33 |
| NGC 3885... | 11 46 46.50 | -27 55 22.0 | 1802 | 0 | 2.4 | 1.0 | 0.46 | 1.41 | 11.66 | 16.42 | 0.71 |
| NGC 3949... | 11 53 41.40 | +47 51 32.0 | 807 | 4 | 2.9 | 1.7 | 0.82 | 1.37 | 11.28 | 25.64 | 0.44 |
| NGC 4027... | 11 59 30.58 | -19 15 48.3 | 1671 | 8 | 3.2 | 2.4 | 0.65 | 1.04 | 11.61 | 27.64 | 0.42 |
| NGC 4038 a... | 12 01 52.82 | -18 51 54.3 | 1642 | 9 | 5.2 | 3.1 | |||||
| NGC 4039 a... | 12 01 53.82 | -18 53 06.3 | 1641 | 9 | 3.1 | 1.6 | |||||
| NGC 4041... | 12 02 12.20 | +62 08 14.0 | 1234 | 4 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 0.87 | 1.42 | 13.34 | 32.88 | 0.41 |
| NGC 4051 a... | 12 03 09.50 | +44 31 54.2 | 725 | 4 | 5.2 | 3.9 | 0.85 | 1.59 | 7.13 | 23.92 | 0.30 |
| NGC 4102... | 12 06 23.10 | +52 42 39.0 | 837 | 3 | 3.0 | 1.7 | 1.72 | 7.05 | 48.1 | 70.74 | 0.68 |
| NGC 4125... | 12 08 05.60 | +65 10 29.0 | 1356 | -5 | 5.8 | 3.2 | 0.08 | <0.09 | 0.70 | 1.46 | 0.48 |
| IRAS 12071-0444... | 12 09 45.10 | -05 01 14.0 | 38480 | -2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.08 | 0.64 | 2.48 | 2.64 | 0.94 |
| NGC 4151... | 12 10 32.60 | +39 24 21.0 | 995 | 2 | 6.3 | 4.5 | 2.02 | 4.95 | 6.18 | 7.90 | 0.78 |
| VCC 66... | 12 12 46.20 | +10 51 49.1 | 378 | 8 | 5.1 | 1.8 | 0.14 | 0.29 | 2.0 | 8.09 | 0.25 |
| NGC 4189... | 12 13 47.30 | +13 25 29.0 | 2115 | 6 | 2.4 | 1.7 | 0.26 | 0.40 | 3.04 | 8.92 | 0.34 |
| VCC 92 a... | 12 13 48.17 | +14 53 42.4 | -142 | 2 | 9.8 | 2.8 | 0.65 | 0.36 | 7.19 | 23.18 | 0.31 |
| NGC 4194... | 12 14 09.60 | +54 31 35.0 | 2506 | 10 | 1.8 | 1.1 | 0.83 | 4.53 | 23.81 | 25.06 | 0.95 |
| PG 1211+143... | 12 14 17.60 | +14 03 12.0 | 24253 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.34 | 0.61 | 0.56 | |
| NGC 4222... | 12 16 22.80 | +13 18 28.0 | 230 | 7 | 3.3 | 0.5 | <0.12 | <0.13 | 0.98 | 3.19 | 0.31 |
| NGC 4236a... | 12 16 43.37 | +69 27 56.4 | 0 | 8 | 21.9 | 7.2 | 0.11 | 0.57 | 3.98 | 10.02 | 0.40 |
| NGC 4278... | 12 20 06.82 | +29 16 50.7 | 649 | -5 | 4.1 | 3.8 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.62 | 1.74 | 0.36 |
| VCC 460... | 12 21 12.91 | +18 22 57.7 | 893 | 0 | 5.6 | 2.6 | 0.18 | 0.50 | 4.58 | 10.44 | 0.44 |
| NGC 4294... | 12 21 17.80 | +11 30 32.0 | 359 | 6 | 3.2 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 0.19 | 2.72 | 9.40 | 0.29 |
| NGC 4299... | 12 21 40.20 | +11 30 10.0 | 232 | 8 | 1.7 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 0.24 | 2.63 | 8.08 | 0.33 |
| NGC 4314... | 12 22 31.97 | +29 53 44.3 | 963 | 1 | 4.2 | 3.7 | 0.16 | 0.36 | 3.78 | 7.14 | 0.53 |
| NGC 4374... | 12 25 03.65 | +12 53 14.2 | 1000 | -5 | 6.5 | 5.6 | 0.23 | 0.26 | 0.52 | 0.98 | 0.53 |
| VCC 857... | 12 25 56.07 | +18 12 53.7 | 922 | 3 | 3.6 | 3.2 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.95 | 4.01 | 0.24 |
| VCC 873... | 12 26 07.85 | +13 06 45.7 | 232 | 3 | 3.9 | 1.1 | 0.53 | 0.56 | 5.31 | 17.39 | 0.31 |
| I Zw 36... | 12 26 16.02 | +48 29 36.6 | 281 | 8 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.08 | 0.58 | 0.91 | 0.64 | |
| NGC 4414... | 12 26 26.69 | +31 13 24.0 | 716 | 5 | 3.6 | 2.0 | 1.91 | 2.30 | 26.81 | 66.07 | 0.41 |
| NGC 4418... | 12 26 54.60 | -00 52 40.0 | 2179 | 1 | 1.4 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 9.69 | 43.89 | 32.04 | 1.37 |
| VCC 1003... | 12 27 26.34 | +11 06 29.4 | 1106 | -1 | 5.6 | 2.6 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 1.65 | 4.27 | 0.39 |
| VCC 1043... | 12 27 45.46 | +13 00 35.5 | 71 | 0 | 8.5 | 3.2 | 0.2 | 0.17 | 3.76 | 11.27 | 0.33 |
| NGC 4449 a... | 12 28 12.00 | +44 05 41.0 | 207 | 10 | 6.2 | 4.4 | 1.37 | 35.49 | 67.97 | 0.52 | |
| VCC 1110... | 12 28 29.30 | +17 05 05.0 | 1954 | 2 | 5.2 | 3.9 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 1.23 | 7.43 | 0.17 |
| VCC 1158... | 12 29 02.94 | +13 11 08.2 | 1931 | -1 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.34 | 0.38 |
| VCC 1253... | 12 30 02.41 | +13 38 10.7 | 1353 | -1 | 3.8 | 3.5 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.58 | 1.08 | 0.54 |
| NGC 4490... | 12 30 36.90 | +41 38 23.0 | 565 | 7 | 6.3 | 3.1 | 1.86 | 4.20 | 45.9 | 76.5 | 0.60 |
| NGC 4486... | 12 30 49.42 | +12 23 28.0 | 1282 | -4 | 8.3 | 6.6 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.50 | 0.58 | 0.86 |
| VCC 1326... | 12 30 57.20 | +11 28 59.0 | 497 | 1 | 1.7 | 0.9 | 0.11 | 0.35 | 2.68 | 3.42 | 0.78 |
| VCC 1412... | 12 32 06.36 | +11 10 41.9 | 1342 | -3 | 3.5 | 1.7 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.79 | 0.30 | |
| NGC 4519... | 12 33 30.30 | +08 39 17.0 | 1220 | 7 | 3.2 | 2.5 | 0.36 | 0.55 | 3.74 | 7.06 | 0.53 |
| NGC 4522... | 12 33 39.80 | +09 10 31.0 | 2337 | 6 | 3.7 | 1.0 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 1.29 | 4.19 | 0.31 |
| NGC 4559 a... | 12 35 58.17 | +27 57 33.4 | 816 | 6 | 10.7 | 4.4 | 0.49 | 0.73 | 9.69 | 27.05 | 0.36 |
| NGC 4569 a... | 12 36 50.02 | +13 09 47.9 | -235 | 2 | 9.5 | 4.4 | 0.75 | 1.28 | 9.19 | 27.33 | 0.34 |
| NGC 4589... | 12 37 25.00 | +74 11 31.0 | 1980 | -5 | 3.2 | 2.6 | <0.11 | <0.09 | 0.20 | 0.82 | 0.24 |
| VCC 1727... | 12 37 44.12 | +11 49 10.5 | 1519 | 3 | 5.9 | 4.7 | 0.34 | 0.37 | 4.74 | 18.09 | 0.26 |
| VCC 1813... | 12 39 56.02 | +10 10 33.0 | 1874 | -1 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.49 | 1.39 | 0.35 |
| VCC 1869... | 12 41 13.42 | +10 09 20.4 | 1864 | -2 | 3.2 | 2.7 | 0.09 | 0.06 | |||
| VCC 1972... | 12 43 32.32 | +11 34 55.8 | 1422 | 5 | 2.9 | 2.3 | 0.49 | 0.61 | 5.32 | 15.42 | 0.35 |
| NGC 4651... | 12 43 42.60 | +16 23 36.0 | 805 | 5 | 4.0 | 2.6 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 5.44 | 15.57 | 0.35 |
| VCC 1987... | 12 43 56.54 | +13 07 33.2 | 1037 | 6 | 4.9 | 2.8 | 0.90 | 1.34 | 13.08 | 34.91 | 0.37 |
| NGC 4656 a... | 12 43 57.70 | +32 10 05.0 | 646 | 9 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 5.90 | 11.46 | 0.51 | ||
| NGC 4670... | 12 45 16.90 | +27 07 30.0 | 1069 | 0 | 1.4 | 1.1 | <0.16 | 0.28 | 2.63 | 4.47 | 0.59 |
| NGC 4691... | 12 48 13.54 | -03 19 58.2 | 1110 | 0 | 2.8 | 2.3 | 0.71 | 2.43 | 14.73 | 20.59 | 0.72 |
| VCC 2070... | 12 48 23.49 | +08 29 15.9 | 1002 | 2 | 4.0 | 2.5 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 2.03 | 0.15 |
| NGC 4713... | 12 49 57.80 | +05 18 39.0 | 652 | 7 | 2.7 | 1.7 | 0.24 | 0.17 | 4.60 | 10.95 | 0.42 |
| Mrk 231... | 12 56 14.23 | +56 52 25.2 | 12642 | 5 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 1.87 | 8.66 | 31.99 | 30.29 | 1.06 |
| IC 3908... | 12 56 40.40 | -07 33 40.0 | 1296 | 7 | 1.8 | 0.7 | 0.44 | 0.87 | 8.09 | 17.08 | 0.47 |
| NGC 4818... | 12 56 48.80 | -08 31 31.0 | 1065 | 1.7 | 4.3 | 1.5 | 0.83 | 3.85 | 20.01 | 25.18 | 0.79 |
| NGC 4861... | 12 59 01.80 | +34 51 40.0 | 847 | 9 | 4.0 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 0.41 | 1.92 | 2.60 | 0.74 |
| NGC 4945 a... | 13 05 22.90 | -49 28 06.0 | 560 | 6 | 20.0 | 3.8 | 23.65 | 43.28 | 588.1 | 1416 | 0.42 |
| NGC 5005 a... | 13 10 56.23 | +37 03 33.1 | 946 | 4 | 5.8 | 2.8 | 0.95 | 1.20 | 19.65 | 54.26 | 0.36 |
| UGCA 332... | 13 11 58.90 | -12 03 49.0 | 2107 | 7 | 1.7 | 1.1 | 0.23 | ||||
| IC 860... | 13 15 03.50 | +24 37 08.0 | 3347 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 1.31 | 17.93 | 18.6 | 0.96 |
| IC 883... | 13 20 35.30 | +34 08 22.0 | 7000 | 99 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 0.25 | 1.41 | 17.01 | 24.41 | 0.70 |
| Cen A a... | 13 25 27.62 | -43 01 08.8 | 547 | -2 | 25.7 | 20.0 | 23.03 | 30.74 | 217.6 | 501.2 | 0.43 |
| IC 4249... | 13 27 06.50 | -27 57 22.0 | 2023 | 1.3 | 0.4 | <0.06 | <0.15 | 0.55 | 0.74 | 0.74 | |
| ESO 173-G015... | 13 27 23.70 | -57 29 21.0 | 3006 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 1.19 | 7.59 | 81.58 | 99.87 | 0.82 | |
| M51 a... | 13 29 52.30 | +47 11 54.0 | 463 | 4 | 11.2 | 6.9 | 11.02 | 17.47 | 108.7 | 292.1 | 0.37 |
| M83 a... | 13 37 00.23 | -29 52 04.5 | 516 | 5 | 12.9 | 11.5 | 26.28 | 47.72 | 266.0 | 638.6 | 0.42 |
| NGC 5248 a... | 13 37 32.00 | +08 53 07.0 | 1153 | 4 | 6.2 | 4.5 | 1.15 | 1.73 | 18.38 | 44.54 | 0.41 |
| Mrk 273... | 13 44 42.03 | +55 53 13.2 | 11326 | 99 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 0.23 | 2.28 | 21.74 | 21.38 | 1.02 |
| NGC 5322... | 13 49 15.50 | +60 11 28.0 | 1781 | -5 | 5.9 | 3.9 | <0.09 | <0.08 | 0.40 | 0.81 | 0.49 |
| IC 4329A... | 13 49 19.39 | -30 18 35.3 | 4813 | -0.7 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 1.08 | 2.21 | 2.03 | 1.66 | 1.22 |
| Mrk 463... | 13 56 02.90 | +18 22 19.0 | 14895 | 10 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.51 | 1.57 | 2.18 | 1.92 | 1.14 |
| NGC 5430... | 14 00 45.69 | +59 19 48.2 | 2961 | 3 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 0.56 | 1.62 | 10.41 | 19.47 | 0.53 |
| NGC 5433... | 14 02 36.00 | +32 30 38.0 | 4354 | 5 | 1.6 | 0.4 | 0.27 | 0.70 | 6.62 | 11.57 | 0.57 |
| NGC 5457 a... | 14 03 12.50 | +54 20 55.0 | 241 | 6 | 28.8 | 26.9 | 6.2 | 11.78 | 92.7 | 237.7 | 0.39 |
| Circinus... | 14 13 09.30 | -65 20 21.0 | 436 | 3 | 6.9 | 3.0 | 19.59 | 67.93 | 245.6 | 409 | 0.60 |
| NGC 5643... | 14 32 40.70 | -44 10 28.0 | 1199 | 5 | 4.6 | 4.0 | 1.09 | 3.64 | 19.49 | 38.16 | 0.51 |
| NGC 5713... | 14 40 11.30 | -00 17 27.0 | 1883 | 4 | 2.8 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 2.84 | 21.89 | 38.09 | 0.57 |
| I Zw 92... | 14 40 38.10 | +53 30 16.0 | 11332 | -2 | 0.12 | 0.50 | 1.31 | 1.85 | 0.71 | ||
| NGC 5772... | 14 51 38.90 | +40 35 57.0 | 4900 | 3 | 2.1 | 1.3 | <0.10 | <0.08 | 0.34 | 1.66 | 0.20 |
| NGC 5786... | 14 58 56.70 | -42 00 45.0 | 2998 | 4 | 2.3 | 1.1 | 0.36 | 0.76 | 5.26 | 14.98 | 0.35 |
| NGC 5866... | 15 06 29.49 | +55 45 43.9 | 672 | -1 | 4.7 | 1.9 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 5.21 | 17.11 | 0.30 |
| CGCG 1510.8+0725... | 15 13 13.30 | +07 13 27.0 | 3897 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 0.83 | 20.84 | 31.52 | 0.66 |
| IRAS 15206+3342... | 15 22 38.00 | +33 31 36.0 | 37297 | 0.2 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.34 | 1.76 | 1.88 | 0.94 | |
| IRAS 15250+3609... | 15 26 59.40 | +35 58 38.0 | 16535 | 10 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.13 | 1.31 | 7.39 | 5.94 | 1.24 |
| NGC 5937... | 15 30 46.02 | -02 49 44.9 | 2807 | 3 | 1.9 | 1.1 | 0.64 | 1.13 | 9.76 | 20.35 | 0.48 |
| NGC 5953... | 15 34 32.33 | +15 11 41.8 | 1965 | 1 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 0.53 | 1.16 | 10.04 | 18.97 | 0.53 |
| Arp 220... | 15 34 57.34 | +23 30 11.9 | 5434 | 90 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 0.48 | 7.90 | 103.8 | 112.4 | 0.92 |
| NGC 5962... | 15 36 31.70 | +16 36 32.0 | 1958 | 5 | 3.0 | 2.1 | 0.74 | 1.03 | 8.89 | 22.11 | 0.40 |
| IC 4545... | 15 41 27.80 | -81 37 33.0 | 2696 | 5 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 1.18 | 5.38 | 0.22 |
| Mrk 297... | 16 05 12.90 | +20 32 32.0 | 4716 | 5 | 0.27 | 0.82 | 6.15 | 10.19 | 0.60 | ||
| IC 4595... | 16 20 44.20 | -70 08 35.0 | 3410 | 5 | 2.7 | 0.5 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 7.05 | 18.04 | 0.39 |
| NGC 6217... | 16 32 39.83 | +78 11 54.4 | 1362 | 4 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 0.50 | 1.61 | 10.83 | 19.33 | 0.56 |
| NGC 6156... | 16 34 52.71 | -60 37 00.8 | 3300 | 4.8 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.00 | 2.47 | 16.11 | 33.35 | 0.48 |
| CGCG 025-007... | 16 51 25.10 | -02 48 18.0 | -1 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.71 | 2.77 | 0.26 | |
| NGC 6221... | 16 52 46.67 | -59 12 59.0 | 1482 | 5 | 3.5 | 2.5 | 1.89 | 5.95 | 40.68 | 81.6 | 0.50 |
| NGC 6240... | 16 52 58.85 | +02 24 08.8 | 7339 | 90 | 2.1 | 1.1 | 0.55 | 3.41 | 22.68 | 27.78 | 0.82 |
| NGC 6286... | 16 58 31.40 | +58 56 13.0 | 5501 | -1 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 0.42 | 0.56 | 8.22 | 22.13 | 0.37 |
| IRAS 17208-0014... | 17 23 21.90 | -00 17 01.0 | 12834 | -2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.19 | 1.65 | 31.14 | 34.9 | 0.89 |
| IC 4662... | 17 47 06.40 | -64 38 25.0 | 308 | 10 | 2.8 | 1.6 | 0.30 | 1.27 | 8.81 | 11.9 | 0.74 |
| NGC 6503 a... | 17 49 27.10 | +70 08 43.0 | 62 | 6 | 7.1 | 2.4 | 0.44 | 0.50 | 7.57 | 25.94 | 0.29 |
| Ark 535... | 17 58 07.10 | +21 16 19.0 | 6000 | -3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.67 | 2.47 | 0.27 |
| 3C 368... | 18 05 06.30 | +11 01 35.2 | z = 1.13 | 1.4 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 1.14 | 0.12 | ||
| NGC 6574... | 18 11 51.30 | +14 58 52.0 | 2282 | 4 | 1.4 | 1.1 | 0.80 | 1.60 | 13.22 | 27.96 | 0.47 |
| [HB89] 1821+643... | 18 21 57.31 | +64 20 36.4 | 89038 | 0.23 | 0.59 | 1.21 | 2.06 | 0.59 | |||
| NGC 6764... | 19 08 16.43 | +50 56 00.1 | 2416 | 3.5 | 2.3 | 1.3 | 0.36 | 1.29 | 6.32 | 11.56 | 0.55 |
| NGC 6744 a... | 19 09 45.31 | -63 51 21.5 | 841 | 4 | 20.0 | 12.9 | 0.17 | 0.22 | 28.84 | 96.13 | 0.30 |
| NGC 6753... | 19 11 23.30 | -57 02 56.0 | 3124 | 3 | 2.5 | 2.1 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 9.77 | 28.26 | 0.35 |
| IRAS 19254-7245... | 19 31 21.40 | -72 39 18.0 | 18500 | -2 | 0.22 | 1.24 | 5.48 | 5.78 | 0.95 | ||
| IRAS 19297-0406... | 19 32 21.20 | -03 59 56.0 | 25701 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.11 | 0.68 | 7.14 | 8.55 | 0.84 | |
| NGC 6810... | 19 43 34.16 | -58 39 20.6 | 2031 | 2 | 3.2 | 0.9 | 1.10 | 3.49 | 17.79 | 34.5 | 0.52 |
| NGC 6824... | 19 43 41.03 | +56 06 38.9 | 3386 | 3 | 1.7 | 1.2 | 0.50 | 0.63 | 5.48 | 15.53 | 0.35 |
| NGC 6821... | 19 44 24.10 | -06 50 02.0 | 1525 | 7 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 0.14 | 0.31 | 3.63 | 5.71 | 0.64 |
| NGC 6822 a... | 19 44 56.14 | -14 48 05.5 | -57 | 10 | 15.5 | 13.5 | 0.84 | 6.63 | 58.86 | 130.3 | 0.45 |
| Cygnus A... | 19 59 28.30 | +40 44 02.0 | 16811 | -2 | 0.20 | 1.06 | 2.32 | <8.3 | 0.28 | ||
| IRAS 20100-4156... | 20 13 29.50 | -41 47 35.0 | 38848 | -2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.10 | 0.46 | 5.26 | 5.11 | 1.03 |
| IC 5020... | 20 30 38.10 | -33 29 05.0 | 3071 | 4 | 3.0 | 2.1 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 1.07 | 4.36 | 0.25 |
| NGC 6946 a... | 20 34 52.30 | +60 09 14.0 | 48 | 6 | 11.5 | 9.8 | 15.17 | 23.34 | 167.7 | 362.7 | 0.46 |
| Mrk 509... | 20 44 09.08 | -10 43 22.0 | 10312 | -6 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.31 | 0.70 | 1.36 | 1.52 | 0.89 |
| NGC 6958... | 20 48 42.20 | -37 59 42.0 | 2713 | -4 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.97 | 1.91 | 0.51 |
| IC 5063... | 20 52 02.00 | -57 04 09.0 | 3402 | -0.8 | 2.1 | 1.4 | 1.06 | 3.91 | 5.33 | 4.16 | 1.28 |
| IRAS 20551-4250... | 20 58 26.89 | -42 39 06.2 | 12840 | -2 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.28 | 1.90 | 12.78 | 9.94 | 1.29 |
| NGC 7217... | 22 07 52.30 | +31 21 32.0 | 952 | 2 | 3.9 | 3.2 | 0.37 | 0.30 | 4.96 | 18.45 | 0.27 |
| NGC 7218... | 22 10 11.70 | -16 39 36.0 | 1662 | 6 | 2.5 | 1.1 | 0.28 | 0.56 | 4.67 | 11.18 | 0.42 |
| NGC 7314... | 22 35 45.76 | -26 03 02.7 | 1422 | 4 | 4.6 | 2.1 | 0.26 | 0.57 | 3.73 | 14.15 | 0.26 |
| NGC 7331 a... | 22 37 04.99 | +34 25 07.6 | 816 | 3 | 10.5 | 3.7 | 3.36 | 4.20 | 35.29 | 115.1 | 0.31 |
| IRAS 22491-1808... | 22 51 49.20 | -17 52 23.0 | 23312 | 3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.09 | 0.54 | 5.25 | 4.73 | 1.11 |
| NGC 7418... | 22 56 36.00 | -37 01 47.0 | 1446 | 6 | 3.5 | 2.6 | 0.63 | 0.69 | 5.38 | 16.13 | 0.33 |
| IC 1459... | 22 57 10.61 | -36 27 44.0 | 1691 | -5 | 5.2 | 3.8 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.49 | 0.94 | 0.52 |
| NGC 7469... | 23 03 15.59 | +08 52 29.3 | 4892 | 1 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 1.34 | 5.78 | 25.87 | 34.9 | 0.74 |
| IRAS 23128-5919... | 23 15 47.01 | -59 03 16.9 | 13371 | -2 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.24 | 1.59 | 10.8 | 10.99 | 0.98 |
| NGC 7552... | 23 16 11.00 | -42 34 59.0 | 1585 | 2 | 3.4 | 2.7 | 2.94 | 12.16 | 72.03 | 101.5 | 0.71 |
| NGC 7582... | 23 18 23.19 | -42 22 11.1 | 1575 | 2 | 5.0 | 2.1 | 1.62 | 6.43 | 49.1 | 72.92 | 0.67 |
| IC 5325... | 23 28 43.10 | -41 19 58.0 | 1503 | 4 | 2.8 | 2.5 | 0.48 | 0.70 | 5.15 | 14.35 | 0.36 |
| III Zw 107... | 23 30 09.90 | +25 31 58.0 | 5734 | -2 | 0.08 | 0.36 | 1.59 | 1.81 | 0.88 | ||
| NGC 7714... | 23 36 14.01 | +02 09 22.3 | 2798 | 3 | 1.9 | 1.4 | 0.46 | 2.85 | 10.36 | 11.51 | 0.90 |
| IRAS F23365+3604... | 23 39 01.30 | +36 21 10.0 | 19331 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.13 | 0.88 | 7.44 | 8.83 | 0.84 |
| NGC 7771... | 23 51 24.80 | +20 06 42.0 | 4277 | 1 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 0.77 | 1.77 | 19.67 | 40.12 | 0.49 |
| Mrk 331... | 23 51 26.80 | +20 35 10.0 | 5541 | 1 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.55 | 2.39 | 18.04 | 23.61 | 0.76 |
| NGC 7793 a... | 23 57 49.41 | -32 35 23.6 | 227 | 7 | 9.3 | 6.3 | 1.54 | 2.09 | 19.62 | 56.34 | 0.35 |
| Notes.- Units of right ascension are hours, minutes, and seconds, and units of declination are degrees, arcminutes, and arcseconds. IRAS fluxes of the unresolved sample are taken from the IRAS Point Source Catalog. IRAS fluxes of the resolved sample are integrated flux densities from high-resolution processed maps. | |||||||||||
| a alaxy is considered an extended source in this paper. | |||||||||||
| b Optical morphology classified by Harold Corwin using the RC3 numerology. | |||||||||||
| c The major and minor diameters at the B-band 25 mag arcsec-2 level. | |||||||||||
The sample includes both normal and Seyfert galaxies that were initially selected by identifying galaxies in the IRAS Cataloged Galaxies and Quasars Observed in the IRAS Survey (CGQ; Fullmer & Lonsdale 1989). The galaxies identified from the CGQ range in 60 µm and 100 µm flux density from 1 to 1300 Jy. The ISO Data Archive was queried using this list, from which 198 galaxies were observed in the LWS L01 "spectral range" or L02 "line" observing modes. Later, galaxies with IRAS fluxes less than 1 Jy or those with no cataloged IRAS flux were added to the sample in order to enlarge the sample. With these considerations, another 29 galaxies were identified within the ISO Archive. Photometric mode L02 observations in which the grating remained in a fixed position are excluded from this sample. The large, nearby galaxies M 31 and the Small and Large Magellanic Clouds are excluded from this sample because the size of these three galaxies is over 100 times larger than the LWS beam.
Among these 227 galaxies there are two distinct subsets, distinguished by the far-infrared size of the galaxy. The 181 galaxies in the first subset are unresolved in the far-infrared with respect to the ~ 75" LWS beam. This unresolved subset of galaxies is an extension of the combined sets of smaller samples observed with the LWS (Malhotra et al. 2001; Pierini et al. 1999; Luhman et al. 2003; Negishi et al. 2001) with additional sources added from the ISO Data Archive. The second subset consists of 46 galaxies resolved by the LWS beam in the far-infrared. The data from this resolved subset of galaxies can be used to complement past studies (Stacey et al. 1991; Madden et al. 1993, 1997) of large galaxies with data taken from the Kuiper Airborne Observatory and ISO. The resolved galaxies are denoted as such in Table 1. The IRAS flux densities presented in Table 1 are selected from either Rice et al. (1988) or Dale et al. (2000) for the large, nearby galaxies in the resolved subset. For the unresolved subset of galaxies, the IRAS fluxes in Table 1 are taken from SCANPI co-additions of the IRAS survey scans.
The galaxies in this sample are distributed across the entire sky. Figure 1 displays the galaxy distribution in Galactic coordinates. The clump of galaxies at (l, b) ~ (280°, 74°) is the Virgo Cluster. Approximately 40 galaxies lie within the Zone of Avoidance, where |b| < 20°. Although there may be some serendipitous Galactic line and continuum emission in all directions of the sky, this serendipitous contamination is more likely toward galaxies within the Zone of Avoidance in either the galaxy spectra or the spectra of an off-source position taken during these observations. This contamination of the observed line measurements by Milky Way emission is a concern, and a discussion of detected Galactic emission lines is found in Section 5.
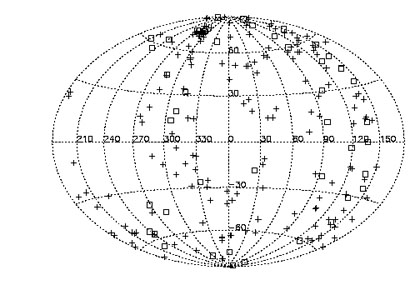 |
Figure 1. Aitoff projection of the galaxies selected for this sample. The galaxies in this sample are distributed across the sky. Galaxies unresolved by the LWS in the far-infrared are displayed with crosses. Resolved galaxies by the LWS in the far-infrared are shown with open squares. The clump of galaxies at RA, Dec (70°, 280°) are members of the Virgo Cluster. |
The Palomar Observatory Sky Survey plates and other observations found within NED were used to reexamine the optical morphology for each galaxy (Harold Corwin, private communication). In Figure 2, the distribution of the optical morphological types for the two subsets is shown. Both the resolved and unresolved subsets span the range of early- to late-type galaxies. The unresolved subset contains a relatively large number of S0 galaxies while the resolved subset contains no elliptical, S0/a, or peculiar galaxies.
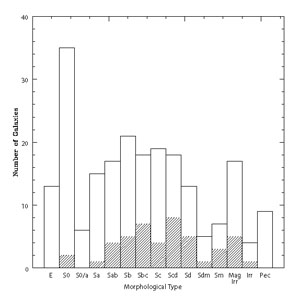 |
Figure 2. The distributions of the optical morphologies of the resolved and unresolved subsets of galaxies. The resolved subset is cross-shaded. |
Most of the galaxies in both the unresolved and resolved subsets are relatively nearby, and Figure 3 shows the redshift distribution for both subsets. All galaxies in the resolved subset have an absolute redshift less than 2000 km s-1. With the exception of a large bin (22/181) of galaxies with redshifts greater than 10000 km s-1, most galaxies in the unresolved subset have redshifts less than 6000 km s-1.
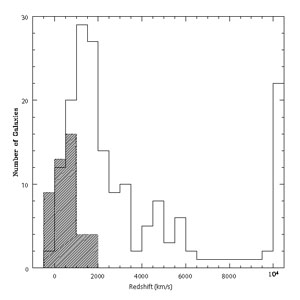 |
Figure 3. The distributions of redshifts for the resolved and unresolved subsets. The resolved galaxy redshifts are cross-shaded. |
Figure 4 shows the distribution of measured flux densities at 60 µm and 100 µm for the resolved and unresolved galaxies in this contribution, with IRAS detections taken from Table 1. At 60 µm, the resolved galaxies span a more elevated flux density range (~ 1-1300 Jy) than the unresolved galaxies (~ 0.2-150 Jy), with the median flux density for unresolved galaxies smaller by a factor of roughly 4.5. At 100 µm, the unresolved and resolved galaxy subsets have similar distributions over flux density, covering the range ~ 0.5 to 1000 Jy with the median flux density of unresolved galaxies smaller by only a factor of 1.6.
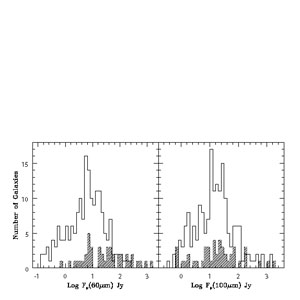 |
Figure 4. The distributions of IRAS 60 µm and 100 µm flux densities. The resolved galaxy subset is cross-shaded. |
The distributions of the 60 µm / 100 µm ratio and
far-infrared flux are displayed in Figure 5. The
60 µm / 100 µm
ratio is an indicator of the typical heating intensity of dust in
galaxies and may also suggest the relative star formation activity level
of a galaxy. Lower 60 µm / 100 µm ratios typically
correspond to quiescent galaxies, whereas higher 60 µm / 100
µm ratios indicate either a higher rate of star formation or
perhaps the presence of an AGN
(Helou 1986).
The far-infrared flux is
defined as FIR = 1.26 × 10-14 [2.58
f (60) + f
(60) + f (100)] W m-2, where
f
(100)] W m-2, where
f (60 µm)
and f
(60 µm)
and f (100 µm) are the 60
µm and 100 µm IRAS flux densities in Jy
(Helou et al. 1988).
The unresolved and resolved galaxy subsets peak
near 60 µm / 100 µm ratios of 0.5 and 0.4,
respectively, and the resolved subset does not contain many warm
galaxies with 60 µm / 100 µm ratios greater than
0.7. It is not surprising that resolved galaxies are on average closer
and more quiescent than unresolved galaxies. The larger subset of
unresolved (~ distant) systems should include more galaxies exhibiting
extreme luminosities and activity levels. The distribution of FIR
values for the two subsets spans five orders of magnitude with a peak
between 10-12 and 10-13 W m-2. The
resolved galaxies reach FIR values as large as
10-10 W m-2, an order of magnitude
larger than the brightest unresolved galaxies. In
Figure 6, the IRAS 12 µm / 25
µm ratio is plotted against the 60 µm/100
µm ratio for the resolved and unresolved subsets. The
sequence of infrared colors in Figure 6 is
associated with a sequence of star formation activity in galaxies
(Helou 1986)
and dust-heating intensity
(Boulanger et al. 1988),
with the upper left populated by quiescent galaxies and the lower right
by warmer, more actively star-forming galaxies.
(100 µm) are the 60
µm and 100 µm IRAS flux densities in Jy
(Helou et al. 1988).
The unresolved and resolved galaxy subsets peak
near 60 µm / 100 µm ratios of 0.5 and 0.4,
respectively, and the resolved subset does not contain many warm
galaxies with 60 µm / 100 µm ratios greater than
0.7. It is not surprising that resolved galaxies are on average closer
and more quiescent than unresolved galaxies. The larger subset of
unresolved (~ distant) systems should include more galaxies exhibiting
extreme luminosities and activity levels. The distribution of FIR
values for the two subsets spans five orders of magnitude with a peak
between 10-12 and 10-13 W m-2. The
resolved galaxies reach FIR values as large as
10-10 W m-2, an order of magnitude
larger than the brightest unresolved galaxies. In
Figure 6, the IRAS 12 µm / 25
µm ratio is plotted against the 60 µm/100
µm ratio for the resolved and unresolved subsets. The
sequence of infrared colors in Figure 6 is
associated with a sequence of star formation activity in galaxies
(Helou 1986)
and dust-heating intensity
(Boulanger et al. 1988),
with the upper left populated by quiescent galaxies and the lower right
by warmer, more actively star-forming galaxies.
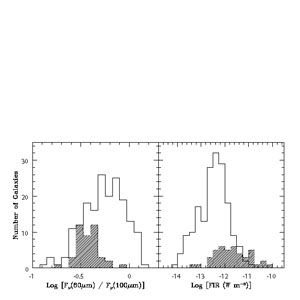 |
Figure 5. The distributions of IRAS 60 µm / 100 µm ratio and FIR. The resolved galaxy subset is cross-shaded. |