


This paper presents the complete list of objects in the IRAS
Revised Bright Galaxy Sample, a sample of extragalactic objects selected at
60µm from the IRAS all-sky survey. The observed slope of
-1.49 ± 0.10 in the logN -
logS relation at 60 µm confirms that the RBGS
is statistically complete down to the limit of
S60 = 5.24 Jy.
The properties of the RBGS objects were computed using the final release
of the IRAS Level 1 Archive and thus the RBGS replaces the
earlier BGS
samples which were determined using older versions of the IRAS
data products. The RBGS contains 39 objects which were not present in
the BGS1 + BGS2, and 28 objects
from the BGS1 + BGS2 have been dropped from the
RBGS because their revised 60 µm flux
densities are not greater than 5.24 Jy. Improved methods were used to
measure the total IRAS flux densities of individual sources,
resulting in typical
changes of 5-25% when compared to previous values reported for the
BGS1 + BGS2,
with changes of up to a factor of 2 for the faintest sources at 12
µm and
25 µm. Better procedures for resolving position
uncertainties and resolving
cross-identifications with other galaxy catalogs resulted in name
changes for ~ 7% of the previous BGS1 + BGS2
compilations. This work presents the
most accurate estimates to date of the total IRAS flux densities
and derived infrared luminosities of galaxies in the local Universe.
Basic properties of the RBGS galaxies are summarized below.
relation at 60 µm confirms that the RBGS
is statistically complete down to the limit of
S60 = 5.24 Jy.
The properties of the RBGS objects were computed using the final release
of the IRAS Level 1 Archive and thus the RBGS replaces the
earlier BGS
samples which were determined using older versions of the IRAS
data products. The RBGS contains 39 objects which were not present in
the BGS1 + BGS2, and 28 objects
from the BGS1 + BGS2 have been dropped from the
RBGS because their revised 60 µm flux
densities are not greater than 5.24 Jy. Improved methods were used to
measure the total IRAS flux densities of individual sources,
resulting in typical
changes of 5-25% when compared to previous values reported for the
BGS1 + BGS2,
with changes of up to a factor of 2 for the faintest sources at 12
µm and
25 µm. Better procedures for resolving position
uncertainties and resolving
cross-identifications with other galaxy catalogs resulted in name
changes for ~ 7% of the previous BGS1 + BGS2
compilations. This work presents the
most accurate estimates to date of the total IRAS flux densities
and derived infrared luminosities of galaxies in the local Universe.
Basic properties of the RBGS galaxies are summarized below.
 ).
).
 (Lir), for infrared
bright galaxies in the Local Universe remains best fit by a double power
law,
(Lir), for infrared
bright galaxies in the Local Universe remains best fit by a double power
law, 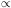 L
L , with
, with
 = - 0.6 ± 0.1, and
= - 0.6 ± 0.1, and
 = - 2.2 ± 0.1
below and above Lir ~ 1010.5
L
= - 2.2 ± 0.1
below and above Lir ~ 1010.5
L ,
respectively.
,
respectively.
We thank George Helou for helpful discussions, and the anonymous referee for comments that improved the presentation of this material. This research made extensive use of the NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED), which is operated by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under contract with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Queries of the IRAS catalogs and scan coadd processing using SCANPI were supported by the NASA/IPAC Infrared Science Archive (IRSA), which is operated by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under contract with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. DBS acknowledges support from a Senior Award from the Alexander von Humboldt-Foundation and from the Max-Planck-Institut fur extraterrestrische Physik as well as support from NASA grant NAG90-1217. JMM, DCK, and JS were supported by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, under contract with NASA. JS and BTS are supported by the SIRTF Science Center at the California Institute of Technology; SIRTF is carried out at JPL, under contract with NASA.