To be published in Astronomy & Astrophysics
astro-ph/0405465
For a PDF version of the article, click
here.
THE DISTANCE OF M 33 AND THE STELLAR POPULATION IN ITS
OUTSKIRTS
S. Galleti 1, 2, M. Bellazzini
1, F.R. Ferraro
2
1 INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna, Via Ranzani 1,
40127 Bologna, Italy
2 Dipartimento di Astronomia, Università di Bologna,
Via Ranzani 1, 40127 Bologna, Italy
e-mail:
silvia.galleti2@unibo.it,
michele.bellazzini@bo.astro.it,
francesco.ferraro3@unibo.it
Abstract.
We present deep V,I photometry of two
9.4' × 9.4' field in the outer regions of the M 33 galaxy. We
obtain a robust detection of the luminosity of the Red Giant Branch Tip
(ITRGB = 20.72 ± 0.08) from which we derived a new
estimate of the distance modulus of M 33,
(m - M)0 = 24.64 ± 0.15, corresponding to a
distance D = 847 ± 60 Kpc. By comparison of the color and
magnitude of the
observed Red Giant Branch stars with ridge lines of template globular
clusters we obtained the photometric metallicity distribution of the
considered fields in three different metallicity scales. The derived
metallicity distributions are very similar over a range of distances from
the galactic center
10' 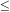 R
R
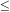 33', and are characterized by
a well defined peak at
[M / H]
33', and are characterized by
a well defined peak at
[M / H] 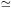 -
0.7 ([Fe / H]
-
0.7 ([Fe / H] 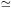 - 1.0, in the Zinn & West scale) and a weak metal-poor tail reaching
[M / H]
- 1.0, in the Zinn & West scale) and a weak metal-poor tail reaching
[M / H]
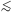 - 2.0.
Our observations demonstrate that Red Giant Branch and Asymptotic Giant
Branch stars have a radial distribution that is much more extended than
the young MS stars associated with the star-forming disc.
- 2.0.
Our observations demonstrate that Red Giant Branch and Asymptotic Giant
Branch stars have a radial distribution that is much more extended than
the young MS stars associated with the star-forming disc.
Keywords: Galaxies: individual: M 33 - Galaxies: distances and
redshifts
Table of Contents

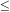 R
R
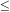 33', and are characterized by
a well defined peak at
[M / H]
33', and are characterized by
a well defined peak at
[M / H] 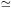 -
0.7 ([Fe / H]
-
0.7 ([Fe / H] 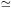 - 1.0, in the Zinn & West scale) and a weak metal-poor tail reaching
[M / H]
- 1.0, in the Zinn & West scale) and a weak metal-poor tail reaching
[M / H]
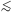 - 2.0.
Our observations demonstrate that Red Giant Branch and Asymptotic Giant
Branch stars have a radial distribution that is much more extended than
the young MS stars associated with the star-forming disc.
- 2.0.
Our observations demonstrate that Red Giant Branch and Asymptotic Giant
Branch stars have a radial distribution that is much more extended than
the young MS stars associated with the star-forming disc.
