





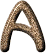
| A | Spectral type for white stars, such as Sirius, Vega, Altair, Deneb, and Fomalhaut. [C95] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AAT | Anglo-Australian Telescope | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A band | One of about a dozen of the strongest Fraunhofer lines seen in the Solar spectrum, the A band at 7600 angstoms is due to telluric lines of molecular oxygen in the Earth's atmosphere. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A-coefficient | Einstein coefficient, where Aji is the coefficient of spontaneous emission from upper level j to lower level i. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A-number | Atomic Mass Number: The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus. For example, Oxygen-16 has a mass number of sixteen, because it has eight protons and eight neutrons. [C95] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A Shell Stars | A-type stars in which two different types of line profiles co-exist. [JJ95] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A Star | A star of spectral type A with a surface temperature of about 10,000 K, in whose spectrum the Balmer lines of hydrogen attain their greatest strength. Helium lines can no longer be seen. Some metallic lines are present; in late A stars the H and K lines of ionized calcium appear. A0 stars have a color index of zero. Examples of A stars are Vega and Sirius. [H76] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ab Variables | A sub-class of Bailey type RR Lyrae variables, having asymmetric lioght curves of large amplitude. [H76] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AB Magnitude System | The AB magnitude system is defined such that for any bandpass or filter being considered, the magnitude zero-point corresponds to a flux density of 3631 Jy (1 Jy = 1 Jansky = 10-26 W Hz-1 m-2 = 10-23 erg s-1 Hz-1 cm-2) [BFM03]. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ABT | Abbreviation employed in this book to mean After the Beginning of Time, which is here defined as the beginning of the expansion of the Universe. [F88] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ae or A Emission Stars | A-type stars with emission in one or several Balmer lines. [JJ95] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Am Stars | (a) Peculiar stars whose metallic lines are as strong
as those of the
F stars but whose hydrogen lines are so strong as to require that they
be classed with the A stars. They are generally short-period
(<300d) spectroscopic binaries with high atmospheric
turbulence and variable spectra, and are slower rotators than normal A
stars. [H76]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ap Stars | Peculiar A-type stars ("magnetic" A stars) that show abnormally strong lines, sometimes of varying intensity, of certain ionized metals. Recent evidence indicates that all Ap stars are slow rotators compared with normal A stars. [H76] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abelian Group | A mathematical group of transformations with the property that the end result of a series of transformations does not depend on the order in which they are performed. [CD99] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aberration | (a) Defect in the image formed by a lens, mirror
or optical
system. Spherical aberration results when different rays of light are
brought to more than one focus, producing a blurred image or
coma; chromatic aberration when different wavelengths within a
ray of light are brought to more than one focus, producing an image
distorted by colored fringes. Aberration in lenses can be overcome
by the use of an achromatic lens or a combination of lenses
made of glasses of different refractive indices.
[A84]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aberration | A defect in an optical system such that the image is
not a true picture of the object. For instance, colored fringes may
appear, the image may not be focused, or the shape may show
distortion. Techniques of aberration correction exist; these can,
however, be complex and costly.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aberration, Annual | The component of stellar aberration (see Aberration, Stellar) resulting from the motion of the Earth about the Sun. [S92] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aberration, Diurnal | The component of stellar aberration resulting from the observer's diurnal motion about the center of the Earth. [S92] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aberration, E-terms of | Terms of annual aberration depending on the eccentricity and longitude of perihelion of the Earth (abbreviation for Ecliptic Aberration). [S92] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aberration, Planetary | The apparent angular displacement of the observed position of a celestial body produced by the motion of the observer and the actual motion of the observed object. [S92] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aberration, Secular | The component of stellar aberration resulting from the essentially uniform and rectilinear motion of the entire Solar System in space. Secular aberration is usually disregarded. [S92] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aberration, Spherical | Always occurs with rays that are distant from the axis and incident on a spherical mirror or lens. It is the cause of the caustic curve. Spherical aberration is corrected by using parabolic reflecting and refracting surfaces. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aberration, Stellar | (a) Difference in a star's apparent
position in the sky from the apparent position it would have if the
Earth were stationary. Such displacement caused by the Earth's
sidereal motion results in an optical positioning difference
of up to about 20.5 seconds of arc, much greater than any displacement
observed by parallax.
[A84]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aberrations | Effects associated with the performance of optical components which give rise to imperfect optical images. [McL97] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ablation | Erosion of an object (generally a meteorite) by the friction generated when it passes through the Earth's atmosphere. [H76] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absolute Brightness | The total luminosity radiated by an object. [Silk90] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absolute Luminosity | see Luminosity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absolute Magnitude | (a) A measure of the intrinsic brightness of a star or
galaxy. Absolute magnitude is defined as the apparent magnitude the
star or galaxy would have if it were 32.6 light-years (10 parsecs)
from Earth. The lower an object's absolute magnitude, the
greater its intrinsic brightness. For example, the Sun has an
absolute magnitude of +4.83, while Sirius, whose intrinsic brightness
is greater, has an absolute magnitude of +1.43. A star that is one
absolute magnitude brighter than another (e.g., +4 versus +5) is 2.5
times intrinsically brighter; a star that is 5 absolute magnitudes
brighter is 100 times intrinsically brighter; and a star that is 10
absolute magnitudes brighter is 10,000 times intrinsically
brighter. [C95]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absolute Space | Newtonian space, hypothesized to define a cosmic reference frame independent of its content of matter or energy. The existence of absolute space, enshrined in aether theory, was denied in relativity. [F88] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absolute Temperature | (a) Temperature measured on the Kelvin scale: 0
Kelvin = -273.15° Celsius.
Absolute temperature is directly related to (kinetic) energy via the
equation E = kBT, where
kB is Boltzmann's constant. So, a temperature
of 0 K corresponds to zero energy, and room temperature, 300 K = 27°C,
corresponds to an energy of 0.025 eV.
[CD99]
T = | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absolute Unit | A unit defined in terms of fundamental quantities (such as length, mass, time, and electric charge). [DC99] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absolute Zero | (a) The zero value of thermodynamic temperature; 0
kelvin or -273.15°C.
[DC99]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absorptance | Symbol: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absorption | (a) A process in which a gas is taken up by a
liquid or
solid, or in which a liquid is taken up by a solid. In absorption, the
substance absorbed goes into the bulk of the material. Solids that
absorb gases or liquids often have a porous structure. The absorption
of gases in solids is sometimes called sorption. Compare
adsorption. [DC99]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absorption Band | see Band Spectrum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absorption Coefficient | Fraction of the incident radiation absorbed at a
certain wavelength per unit thickness of the absorber. The absorption
coefficient is in general a function of temperature, density, and
chemical composition. ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absorption Edges | Sudden rises superposed on the smooth decrease of the curve of the attenuation coefficient, which cause the curve to have a typical sawtooth aspect. They generally occur at the limit of spectral lines. [H76] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absorption Lines | Dark lines in a spectrum, produced when light or other electromagnetic radiation coming from a distant source passes through a gas cloud or similar object closer to the observer. Like emission lines, absorption lines betray the chemical composition and velocity of the material that produces them. [F88] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absorption of Radiation | No medium transmits radiation without some energy loss. This loss of energy is called absorption. The energy is converted to some other form within the medium. see also Lambert's Law. [DC99] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absorption Spectrum | Dark lines superposed on a continuous spectrum, caused by the absorption of light passing through a gas of lower temperature than the continuum light source. [H76] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absorption Trough | Range of wavelengths (around 21 cm) at which atomic hydrogen absorbs (or emits) radiation; this is a concept used in the attempt to detect intergalactic matter. [A84] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Absorptivity | Symbol: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abundance | (a) The relative amount of a given element among
others; for example, the abundance of oxygen in the Earth's crust is
approximately 50% by weight.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abundance Ratio | The ratio of the number of atoms of an isotope to the number of atoms of another isotope of the same element in a sample. [DC99] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acausal Initial Conditions | Initial conditions that could not have been caused by any prior physical process. [LB90] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acceleration | (a) The SI unit is the meter per
second per second (m s-2). 1. When considering
motion in one dimension, and in unscientific usage, acceleration means
rate of increase of speed. This is a scalar quantity, which can be
positive or negative. Negative values mean that the speed is
decreasing and may be called deceleration or retardation. 2.
In scientific study of motion in two or three dimensions acceleration
means rate of change of velocity; a = dv / dt. This is a vector
quantity having magnitude (which is always positive) and
direction. Whenever speed changes (increasing or decreasing), or
direction changes, or both speed and direction change, this is an
acceleration.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accelerator | (a) A machine for speeding subatomic particles to
high velocity, then
colliding them with a stationary target or with another beam of
particles moving in the opposite direction. (In the latter instance,
the machine may be called a
collider.) At velocities approaching
that of light the mass of the particles increases dramatically, adding
greatly to the energy released on impact. The resulting explosion
promotes the production of exotic particles, which are analyzed
according to their behavior as they fly away through a particle
detector. [F88]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accretion | (a) Collection of material together, generally to
form a single
body. [A84]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accretion Disk | A disk of gas that accumulates around a center of gravitational attraction, such as a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole. As the gas spirals in, it becomes hot and emits light or even X-radiation. [HH98] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accumulation Theory | The theory by which planetesimals are assumed to collide with one another and coalesce, eventually sweeping up enough material to form the planets. [Silk90] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Achernar | A subgiant of spectral type B5, about 35 pc
distant. ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Achilles | Asteroid No. 588, a Trojan 60° ahead of Jupiter (P = 11.98 yr, a = 5.2 AU, e = 0.15, i = 10°.3). It was the first Trojan to be discovered (in 1906). [H76] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Achromat | An achromatic lens. [DC99] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Achromatic Color | A color that has no hue; i.e. black, white, or gray. [DC99] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Achromatic Lens | (a) Lens (or combination of lenses) that brings
different
wavelenghts within a ray of light to a single focus, thus overcoming
chromatic aberration. It was first successfully made by Joseph von
Fraunhofer. [A84]
where | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Achromatic Objective | A lens of two or more components with different refraction indices (e.g., crown glass and flint glass), used to correct for chromatic aberration. [H76] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actinic Radiation | Radiation that can cause a chemical reaction; for example, ultraviolet radiation is actinic. [DC99] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actinium | A soft silvery-white radioactive metallic element that
is the first member of the actinoid series. It occurs in minute
quantities in uranium ores. It can be produced by neutron bombardment
of radium and is used as a source of alpha particles. The metal glows
in the dark.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Action | A quantity related to the momentum and position of a body or system of particles. The Principle of Least Action asserts that the integral, or sum of this action, taken over a particular path must be a minimum. This Principle of Least Action can be used instead of Newton's Laws to determine the motion of a system. [P88] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Action-at-a-Distance | A description of a force, such as Newton's law of gravity, in which two separated bodies are said to directly exert forces on each other. In the modern description, the bodies produce a gravitational field, which in turn exerts forces on the two bodies. see Gravitational Field [G97] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Active Galactic Nucleus | AGN -- An unusually bright galactic nucleus whose light is not due to starlight. [HH98] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Active Galaxy


| Any galaxy which is emitting large quantities of
non-thermal radiation. [C97]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Active Optics | Controlling the shape of a telescope mirror at a relatively slow rate. [McL97] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Active Sun | The Sun during its 11-year cycle of activity when spots, flares, prominences, and variations in radiofrequency radiation are at a maximum. [H76] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Activity | Symbol: A For a radioactive substance, the average number of atoms disintegrating per unit time. [DC99] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acuity, Visual | The ability of the eye to see separately two points close to each other. It is a measure of the resolving power of the eye's optical system and depends on the density of cells in the retina. The maximum acuity of the normal human eye is around 0.5 minutes of arc - points separated by this angle at the eye should be seen as separate. see Resolution [DC99] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adaptive Optics | Compensating for atmospheric distortions in a wavefront by high-speed changes in the shape of a small, thin mirror. [McL97] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADC | Analog-to-Digital Converter -- An electronic circuit which takes an input voltage in a given range (typically 0-10 volts) and provides a corresponding digital output by setting output lines (bits) high or low. A 16-bit ADC has 16 output lines. [McL97] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADF | Astrophysical Data Facility, located at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC), is responsible for designing, developing, and operating data systems that support the processing, management, archiving and distribution of NASA mission data. The ADF serves three broadly-defined astrophysics disciplines: high-energy astrophysics, UV/optical astrophysics, and infrared/submillimeter/radio astrophysics. The ADF collaborates with the GSFC Laboratory for High Energy Astrophysics (LHEA) and the Laboratory for Astronomy and Solar Physics (LASP) in managing data for specific missions. The ADF staff also support the astrophysics community's access to multi-mission and multi-spectral data archives in the National Space Science Data Center (NSSDC). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adhesion | A force of attraction between atoms or molecules of different substances. For example, adhesion between water molecules and glass creates a meniscus. [DC99] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adiabatic Change | A change taking place in a system that has
perfect thermal insulation, so that heat cannot enter or leave the
system and energy can only be transferred by work. In practice, a
close approximation to an adiabatic change can be achieved by the
process being too rapid for significant heat transfer, or by the large
scale of the system (e.g. a large volume of air in the atmosphere).
pV
where K1, K2, and
K3 are constants and
A method of producing temperatures
close to absolute zero. A sample of a paramagnetic salt is cooled in
liquid helium in a strong magnetizing field. The sample is then
thermally isolated by pumping away the helium, and the magnetic field
is removed. The sample demagnetizes itself at the expense of its
internal energy so that the temperature falls. Temperatures of the
order of a millikelvin can be obtained. [DC99]
The ratio of the fractional change in pressure to
the fractional
change in density as an element of fluid expands (or contracts)
without exchange of heat with its surroundings. [H76]
Fluctuations in both the matter and radiation
density, as though a volume of the Universe were slightly squeezed but
allowing no radiation to escape. Prior to the Decoupling Era,
adiabatic fluctuations behaved like waves, on scales smaller than the
horizon size. After decoupling, gravitational instability sets in on
scales above about 1013 M A process in which a layer of atoms or molecules of
one substance forms on the surface of a solid or liquid. All solid
surfaces take up layers of gas from the surrounding atmosphere. The
adsorbed layer may be held by chemical bonds (chemisorption) or
by weaker van der Waals' forces (physisorption). Compare
absorption. [DC99]
Analog-to-Digital Units see DN [McL97]
The slow rotation of the major axis of a planet's
orbit in the
same direction as the revolution of the planet itself, due to
gravitational interactions with other planets and/or other effects
(such as those due to general relativity). [H76]
The transfer of matter such as water vapor or heat
through the atmosphere as a result of horizontal movement of an air
mass. [DC99]
In astronomical terms, 1,000 million years. [A84]
A stony meteorite, composed primarily of
silicates. About 93
percent of all known falls are aerolites. They include the
carbonaceous chondrites, other chondrites, and achondrites. (lit. "air
stone.") [H76]
An image seen after the eye's retina has been
exposed for a time to an intense or stationary light source. It may be
negative or positive, or appear in complementary colors. [DC99]
(1) In Aristotelian physics, the fifth
element, of which the stars and planets are made. (2) In
Classical physics, an invisible
medium that was thought to suffuse all space. [F88]
The time elapsed since the singularity predicted
by the Big Bang theory, estimated to be around 13 billion years.
[BFM02]
Astronomical Image Processing System --
National Radio Astronomy Observatory
Light in the nighttime sky caused by the
collision of atoms and
molecules (primarily oxygen, OH, and Ne) in Earth's geocorona with
charged particles and X-rays from the Sun or outer space. The airglow
varies with time of night, latitude, and season. It is a minimum at
zenith and maximum about 10° above the horizon. (also called
nightglow)[H76]
The central spot in the diffraction pattern of
the image of a star at the focus of a telescope. Named for Sir George
Airy (1801-1892), seventh Astronomer Royal.
[McL97]
(a) The ratio of the amount of light reflected from a
surface to the amount of incident light.
[DC99]
Art of bringing parts of the Universe to the
perfect state toward
which they were thought to aspire - e.g., gold for metals, immortality
for human beings.
[F88]
( ( Explanation of the big-bang theory in terms of
nuclear physics, proposed by Ralph Alpher, Hans Bethe and George
Gamow in 1948; it was later slightly corrected by Chushiro
Hayashi. [A84]
A dimensionless number characterizing steady fluid
flow past an obstacle in
a uniform magnetic field parallel to the direction of flow. It has a
partial analogy to the Mach number. The Alfven number is given by
vl( A cosmological model in which the early
Universe is depicted as a giant collapsing spherical cloud of matter
and antimatter. When a critical density is reached, the matter and
antimatter begin to annihilate, the resulting release of radiation and
energy causing the Universe to expand. There are many difficulties with
this model of the expanding Universe, which is largely discredited on
observational grounds. [Silk90]
The speed at which hydromagnetic waves are
propagated along a
magnetic field: (VA) = B / (4 Waves moving perpendicularly through a magnetic
field. They are
caused by the oscillation of magnetic lines of force by the motions of
the fluid element around its equilibrium position, which in turn is
caused by the interactions between density fluctuations and magnetic
variations. [H76]
( In a discrete Fourier transform, the overlapping
of replicas of
the basic transform, usually due to undersampling. [H76]
The existence of a solid substance in different
physical forms. Tin, for example, has metallic and non-metallic
crystalline forms. Carbon has two crystalline allotropes: diamond and
graphite. [DC99]
Arabic title for Ptolemy of Alexandria's
Syntaxis, the
writings in which he combined his own astronomical researches with
those of others. Although much of the work is inaccurate even in
premise, until Nicolaus Copernicus published his results fourteen
centuries later the Almagest remained the standard reference
source in Europe. [A84]
The nucleus of a 4He atom, consisting
of two protons and
two neutrons. Mass of Nuclei formed by the A hypothetical process of nucleosynthesis (now
considered
obsolete terminology), which consisted of redistributing (a) Bright binary star in which both components
contribute
to a magnitude of -0.27: it is also the nearest of the bright stars
(at a distance of 4.3 light years). [A84]
(a) A type of radioactive decay in which the unstable
nucleus emits a helium nucleus. The resulting nuclide has a mass
number decreased by 4 and a proton number decreased by 2. An example
is:
88226 Ra
The particles emitted in alpha decay are alpha
particles. Streams of alpha particles are alpha rays or
alpha radiation. They penetrate a few centimeters of air at STP
or a metal foil of mass/area a few milligram/cm2. see
also Beta Decay [DC99]
Particles first discovered in radioactive
( (a) Comprising a means of measuring or precisely
locating in
coordinates the position of objects at any altitude or azimuth. The
term is now used mainly to describe a type of mounting for a
telescope. (also Alt-Az)[A84]
(a) Angular distance above the horizon. [A84]
A soft moderately reactive metal. Aluminum has the
electronic structure of neon plus three additional outer
electrons. There are numerous minerals of aluminum; it is the most
common metallic element in the Earth's crust (8.1% by weight) and the
third in order of abundance.
A unit of molar volume at 0° C and a
pressure of 1.0 atmosphere.
This unit varies slightly from one gas to another, but in general it
corresponds to 2.24 × 104 cm3. Also, a unit
of density
equal to 0.0446 gram mole per liter at 1 atm pressure. [H76]
Jupiter V, the innermost satellite of
Jupiter. Diameter about 140
km; i = 0°.4, e = 0.0028, period 0.498
days. Discovered by Barnard in 1892. (also called Barnard's
satellite)[H76]
A highly toxic radioactive silvery element of the
actinoid series of metals. A transuranic element, it is not found
naturally on Earth but is synthesized from plutonium. 241Am
has been used in gamma-ray radiography.
Denoting a solid that has no crystalline structure;
i.e. there is no long-range ordering of atoms. Many substances that
appear to be amorphous are in fact composed of many tiny
crystals. Soot and glass are examples of truly amorphous materials. [DC99]
The SI unit of electric current. "The ampere is
that constant
current which, if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of
infinite length, of negligible circular cross-section, and placed 1
meter apart in vacuum, would produce between these conductors a force
equal to 2 × 10-7 newton per meter of length" (CIPM
[1946], Resolution 2, approved by the 9th CGPM 1948). A current of 1 A
is equivalent to the passage along the filament of a light bulb of
about 6 × 1018 electronic charges per second. [H76]
A device that increases an electrical signal applied
to it as an input. If the input is an alternating voltage, the output
voltage has a similar waveform with an increased amplitude.
(a) The maximum value of a varying quantity from
its mean
or base value. In the case of a simple harmonic motion - a wave or
vibration - it is half the maximum peak-to-peak value. [DC99]
(AM) A type of modulation in which the
amplitude of a carrier wave is modulated by an imposed signal, usually
at audio frequency.
A device for determining the plane of
polarization of plane-polarized radiation. Maximum intensity is
transmitted if the plane is parallel with the analyzer's direction of
polarization; the intensity is a minimum (theoretically zero) if the
two are perpendicular. For visible radiation, analyzers are usually
Polaroid sheets or Nicol prisms. [DC99]
The difference in magnification along the
spectrum and perpendicular to the spectrum in a spectrograph. [McL97]
A lens designed so as to minimize its
astigmatic aberration. Anastigmatic lenses have different curvatures
in different directions; the surface of an anastigmatic lens is part
of a toroid. [DC99]
A constellation near Perseus and
Pegasus.
(a) Major spiral galaxy, 2.2 million
light-years from
Earth. Gravitationally bound to the
Milky Way galaxy with which it
shares membership in the Local Group,
it is currently approaching us, rather than receding as is the case
for most galaxies. [F88]
Three dwarf spheroidal galaxies, in the Andromeda
subgroup of the
Local Group, discovered by van den Bergh in 1972. They are among the
intrinsically faintest members of the Local Group. [H76]
A supernova seen in 1885 in the Andromeda
Galaxy. [H76]
(a) A unit that measures the wavelength of light and
equals 0.00000001 of a
centimeter. Blue light has a wavelength of about 4400 angstroms,
yellow light 5500 angstroms, and red light 6500 angstroms. [C95]
The unit was introduced by the International Union for Solar Research in
1907[19]. It was named after A. J. Ångström (1814-1874), the
Scandinavian
scientist who used units of 10-10 m to describe wavelengths
in his classical
map of the Solar spectrum made in 1868. The ångström was not
confirmed as
a unit of length by the International Congress of Weights and Measures
until 1927. For over half a century the ångström was equal to
1.0000002 × 10-10 m
but when the metre was defined in terms of the wavelength of krypton in
1960[20] the ångström became equal to 10-10 m
exactly. The ångström is sometimes called a tenth metre.
X-ray wavelengths are often given ångström stars
(Å*). This unit was
devised by J. A. Bearden[21] in 1965 and is based on the wavelength
of the K Symbol:
Here Symbol: The rate of change of angle (due to refraction or
diffraction) with wavelength of the emergent beam in a
spectrograph. [McL97]
(Pulsatance) Symbol:
(a) The angular momentum of a system about a
specified origin is the
sum over all the particles in the system (or an integral over the
different elements of the system if it is continuous) of the vector
products of the radius vector joining each particle to the origin and
the momentum of the particle. For a closed system it is conserved by
virtue of the isotropy of space. [H76]
The angle subtended by an object on the sky. For
example, the angular size of the moon is 30 arcminutes. [HH98]
A system whose vibration, while still
periodic, cannot be described in terms of simple harmonic motions
(i.e. sinusoidal motions). In such cases, the period of oscillation is
not independent of the amplitude. [DC99]
see Mixmaster Model
A system of fermions in
which Cooper pairs form in a state of finite relative orbital motion
and possibly finite total spin. [D89]
(a) A medium is anisotropic if a certain physical
quantity differs in value in. different directions. Most crystals are
anisotropic electrically; important polarization properties result
from differences in transmission of electromagnetic radiation in
different directions. [DC99]
A reaction between a particle and its
antiparticle; for example, between an electron and a positron. The
energy released is equal to the sum of the rest energies of the
particles and their kinetic energies. In order that momentum be
conserved two photons are formed, moving away in opposite
directions. This radiation (annihilation radiation) is in the
gamma-ray region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The quantum energy
is about 0.51 MeV.
The direction and strength of the Earth's
magnetic field at any point changes with time. This must be allowed
for by navigators. One such change is a variation with a period of a
year, but there are others. The amplitude of the annual variation is
greatest during maximum sun-spot activity. [DC99]
An eclipse of the Sun in which the Moon is too
far from Earth to
block out the Sun completely, so that a ring of sunlight appears
around the Moon. [H76]
The interval (27.555 days) between two successive
perigee passages
of the Moon.[H76]
The interval (365.2596 ephemeris days) between
two successive
perihelion passages of Earth. [H76]
The refractive index of a transparent
medium normally increases as the wavelength is reduced. There is then
a range of wavelengths (usually in the ultraviolet) in which the
radiation is absorbed fairly strongly. Such little radiation as is
transmitted in this region shows anomalous dispersion, that is the
refractive index decreases as the wavelength is
reduced. see Dispersion [DC99]
An increase in volume resulting from a
decreased temperature. Most liquids increase in volume as their
temperature rises. The density of the liquid falls with increased
temperature. Water, however, shows anomalous behavior. Between 0 and
4°C the density increases with increasing temperature. [DC99]
Splitting of spectral lines into several
components, in contrast
to the normal Zeeman effect which results in only two distinct
components. The anomalous Zeeman effect is due to the fact that the
electrons in the magnetic field have opposite directions of
spin. [H76]
An angular value used to describe the position of
one member of a
binary system with respect to the other. The true anomaly of a star is
the angular distance (as measured from the central body and in the
direction of the star's motion) between periastron and the observed
position of the star. The mean anomaly is the angular distance
(measured in the same manner) between periastron and a fictitious body
in the direction of the star, which is moving in a circular orbit with
a period equal to that of the star. [H76]
(a) The "handles", or extremities, of Saturn's
rings as viewed from
Earth
An old name for an RR Lyrae star. [H76]
The direction in the sky (in Columba) away from
which the Sun
seems to be moving (at a speed of 19.4 km s-1) relative to
general field stars in the Galaxy. [H76]
( The part of a radio telescope responsible for
detecting an electromagnetic wave. (or Aerial) [McL97]
A measure of the directivity of a radio
telescope. It is the ratio
of the amount of power received in the direction the dish is pointing
to the smaller amount of power from other directions in the
sidelobes. [H76]
A term used to describe the strength of a signal
received from a
radio source. It is the convolution of the true brightness
distribution and the effective area of the antenna. [H76]
A famous pair of interacting galaxies in the
constellation
Corvus. Each galaxy's tidal force has drawn out a long tail of stars
from the other. The Antennae are also known as NGC 4038 and NGC
4039. [C95]
(a) The doctrine that the value of certain
fundamental constants of
nature can be explained by demonstrating that, were they otherwise,
the Universe could not support life and therefore would contain nobody
capable of worrying about why they are as they are. Were the
strong nuclear force slightly
different in strength, for instance, the stars
could not shine and life as we know it would be impossible. [F88]
The belief that humans are central to the
Universe. [HH98]
The projection of human attributes onto nonhuman
entities such as animals, the planets, or the Universe as a
whole. [HH98]
The antiparticle of a baryon. [G97]
The direction of the sky (in Auriga) opposite to
that toward the
center of the Milky Way. [H76]
A particle counter in which the circuit has been
designed so as
not to register the passage of an ionizing particle through more than
one counting tube. [H76]
a solid in which the spins of neighboring atoms are
oppositely aligned. The lattice is composed of two equivalent
sublattices, and on each sublattice the spins are magnetized, as in a
ferromagnet, but the directions of the magnetisations are opposed so
that there is no net magnetisation. [D89]
A kind of magnetism found in many solids at
low temperatures. The molecular magnets form two arrays, aligned
antiparallel. At the lowest temperatures there are equal numbers with
equal magnetic moments in opposite directions, giving zero resultant
magnetization. As the temperature is raised, the susceptibility
increases up to the Néel temperature above which the
substance is paramagnetic. [DC99]
(a) For every variety of particle there exists an
antiparticle with opposite properties such as sign of electrical
charge. When a particle and its antiparticle meet they can mutually
annihilate and produce energy. Thus, antiquark, antiproton, etc. [D89]
A metalloid element existing in three allotropic
forms; the most stable is a brittle silvery metal. It is used in
alloys - small amounts of antimony can harden other metals. It is also
used in semiconductor devices.
The antiparticle of a neutrino. [Silk90]
The antiparticle of a neutron. A neutron and
antineutron
both have the same mass and zero electric charge, but can be
differentiated by their interactions: a neutron and an antineutron can
annihilate into gamma rays, while two neutrons cannot. [G97]
(a) An elementary particle of opposite charge but
otherwise
identical to its partner. Most of the observable Universe consists of
particles and matter, as opposed to antiparticles and
antimatter. [Silk90]
The antiparticle of a proton, identical in
mass and spin
but of opposite (negative) charge. [Silk90]
The antiparticle of the quark. [G97]
Also AR coating. A layer of material of lower
refractive index of just the right thickness (1/4 wave) is deposited on
the optical surface to be coated. More complex coatings are possible
which cover a large wavelength range. [McL97]
The point in the orbit of one component of a
binary system where
it is farthest from the other. [H76]
(a) The effective diameter of the primary mirror or
lens of a telescope. [H76]
aperture = d/f
Thus a 50-mm camera lens may be used with an aperture diameter of 12.5
mm. Then, aperture = 12.5/50. This is usually described with the
f-number. In this case the aperture diameter is f/4,
often written as f4.
The ratio of the effective aperture of the
antenna, A, to
its geometric aperture, Ag = In radio astronomy, a distribution of direction
assignments
applying to a uniform background. [H76]
Usually refers to magnitude measurements made from
digital images by deriving the flux that would have been recorded within
a circular aperture large enough to enclose the star's seeing disk. [McL97]
The ratio of the aperture of a telescope to the focal
length. [H76]
The method of combining the signals received by
several smaller telescopes distributed over a very large area or
baseline to provide the angular resolution of a much large telescope.
Used extensively in radio astronomy, e.g. the VLA. [McL97]
see Solar Apex
The point in a planetary
orbit that is at the greatest
distance from the Sun. [S92]
A lens designed so as to minimize both its
astigmatic and coma aberration. [DC99]
A system of three lenses which, taken together,
correct for
spherical aberration, chromatic aberration, and coma. [H76]
The point in the orbit of one component of a
binary system which
is farthest from the center of mass of the system. [H76]
A lens designed to correct for chromatic
aberration at three different wavelengths. Apochromatic lenses are
constructed of three or more kinds of glass. They thus have better
correction than achromatic lenses, which correct at two different
wavelengths (usually in the red and blue regions of the
spectrum). see Achromatic Lens [DC99]
A mathematical process performed on the data
received from an
interferometer before carrying out the calculations of the Fourier
transformation to obtain the spectrum, in order to modify the
instrumental response function. [H76]
The point at which a body in
orbit around the Earth reaches its
farthest distance from the Earth. [S92]
One of a small group of asteroids whose orbits
intersect that of
Earth. They are named for the prototype, Apollo (P =
622d, a = 1.486 AU, e = 0.57, i =
6°.4). [H76]
Successful US lunar exploration program in
which the Apollo spacecraft 1 to 6 were unmanned;
7 to 10 were manned but did not land; and 11,
12 and 14 to 17 landed and returned safely. (Apollo 13 was an
aborted
mission.) The first men to land on the Moon were Neil Armstrong and
Edwin Aldrin, from Apollo 11, on 20 July 1969. The final
Apollo flight (17) lasted from 7 to 19 December 1972, and left
a considerable quantity of exploratory devices on the lunar surface. [A84]
The point in a star's orbit farthest from the Galactic
center. [C95]
Because radiation travels at different speeds in
different media, the apparent depth or thickness of a transparent
sample is not the same as its real depth or thickness. The effect is
very obvious when one looks down into a glass of water or a clear
pool. It is associated with the fact that a long object partly
submerged in water seems bent at the water surface.
refractive index = real depth / apparent depth
The relation is used in a number of methods for finding the refractive
constant of a transparent medium. It applies to all wave radiations,
not just to visible radiation. [DC99]
(a) A measure of how bright a star looks in the
sky. The brighter the
star, the smaller the apparent magnitude. A star that is one magnitude
brighter than another (e.g., +1 versus +2) looks 2.5
times brighter. The brightest star of all, of course, is the Sun,
whose apparent magnitude is -26.74, followed by Sirius, whose apparent
magnitude is -1.46, Canopus (-0.72), Alpha Centauri (-0.27), Arcturus
(-0.04), and Vega (+0.03). Stars of the Big Dipper are fainter, most
of them around magnitude +2. On a clear, dark night, the unaided eye
can see stars as faint as apparent magnitude +6, and the largest
telescopes penetrate to apparent magnitude +30. [C95]
The position on a
celestial sphere, centered at
the Earth, determined by removing from the directly observed position of a
celestial body the effects that depend on the
topocentric location of
the observer; i.e., refraction,
diurnal aberration. see
Aberration, Diurnal), and geocentric (diurnal)
parallax. Thus the position
at which the object would actually be seen
from the center of the Earth, displaced by planetary aberration
(except the diurnal part - see
Aberration, Planetary; Aberration, Diurnal) and referred to the
true equator and equinox. [S92]
Interval between two successive culminations of
the Sun - i.e.,
the period from apparent noon to apparent noon. The apparent Solar day
is longest in late December. [H76]
The measure of time based on the diurnal motion
of the true
Sun. The rate of diurnal motion undergoes seasonal variation because
of the obliquity of the
ecliptic and because of the
eccentricity of
the Earth's orbit. Additional
small variations result from
irregularities in the rotation of the Earth on its axis. [S92]
The period during which a celestial body is
visible. [H76]
(F-layer) The upper of the two main layers in
the ionosphere, at a height above about 150 km. It reflects radio
waves. see Ionosphere [DC99]
A penumbral eclipse of the Moon. [H76]
Rotation of the line of apsides in the
plane of the orbit;
(in a binary) precession of the line of apsides due to mutual tidal
distortion. [H76]
The major axis of an elliptical orbit. [H76]
One sixtieth of a degree of angular measure. The
Moon is 31
arcminutes across. [C95]
Making a permanent record which can be accessed
later at any time. [McL97]
One sixtieth of an arcminute, or 1/3600 of a
degree. Jupiter is
40 arcseconds across. [C95]
The spectra of neutral atoms produced in a
laboratory arc
(cf. spark spectra). [H76]
( see Kepler's Second Law
a diagram in which the length and phase-angle of a
complex quantity is displayed. {D89]
A method of classifying stars according to image
size. If the
sequence stars are labeled a, b, etc., in order of image
size and if the image size of a variable appears to be, say, 0.7 of
the way from sequence star a to sequence star b, its
brightness is listed as a7b. (also called the step method
)[H76]
An inert colorless odorless monatomic element of the
rare-gas group. It forms 0.93% by volume of air. Argon is used to
provide an inert atmosphere in electric and fluorescent lights, in
welding, and in extracting titanium and silicon. The element forms no
known compounds.
Angular distance (measured in the plane of the
object's orbit and
in the direction of its motion) from the ascending node to the
perihelion point. [H76]
Second satellite of Uranus about 1600 km in
diameter, discovered
by Lassell in 1851. Period 2.52 days. [H76]
Physics as promulgated by Aristotle; includes
the hypothesis that
our world is comprised of four elements, and that the Universe beyond
the moon is made of a fifth element and so is fundamentally different
from the mundane realm. [F88]
Young stars typical of those found in spiral arms
(Population I
stars). [H76]
Ancient Greek, Arabic and medieval alt-azimuth
device, comprising a calibrated ring fixed in the meridian plane,
within which a second concentric ring, also calibrated, was mobile
around a vertical axis. [A84]
In organic chemistry, carbon which has bonds that
are between single
and double bonds (e.g., the molecule has a bond with a delocalized
electron.) [SEF01]
In radio astronomy, an arrangement of antenna
elements designed to
produce a particular antenna pattern. [H76]
see Dispersion
The direction, apparently inviolable, of the
"flow" of time that distinguishes the past from the future.The
direction, apparently inviolable, of the "flow" of
time that distinguishes the past from the future. [HH98]
A toxic metalloid element existing in several
allotropic forms; the most stable is a brittle gray metal. It is used
in semiconductor devices, alloys, and gun shot.
In the orbit of a Solar-System body, the point
where the body
crosses the ecliptic from south to north: for a star, out of the plane
of the sky toward the observer. [H76]
A faint glow from the unlit side of Venus when it
is in the
crescent phase. Its cause is unknown; it may be the Venusian analog to
terrestrial airglow. [H76]
Magnitudes
expressed as the inverse hyperbolic sine (or ``asinh''), sometimes
referred to informally as luptitudes. The transformation from
linear flux measurements to asinh magnitudes is designed to be virtually
identical to the standard astronomical magnitude at high
signal-to-noise ratio, but switches over to linear behavior at low S/N
thereby accommodating even negative values of flux, where the
logarithm, as used in the Pogson magnitude, fails. [sinh-1(x) =
asinh(x)*ln(x+SQRT(x2+1))]
Application Specific Integrated Circuit
The apparent position of any of the planets or
the Moon relative
to the Sun, as seen from Earth. [S92]
Ratio of the major axis (e.g., of a rocket) to
the minor axis. (Of
a fusion device) ratio of the plasma diameter to the major diameter of
the torus. [H76]
An optical surface with departures in shape from a
perfect
sphere in order to cancel optical imperfections or aberrations. [McL97]
A sparsely populated grouping (mass range
102-103 M A radioactive element belonging to the halogen
group. It occurs in minute quantities in uranium ores. Many
short-lived radioisotopes are known, all alpha-particle emitters.
(a) A small rocky body that orbits a star. In the
Solar System,
most asteroids lie between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. The largest
asteroid is Ceres, about 900 kilometers in diameter. [C95]
A region of space lying between Mars (1.5 AU) and
Jupiter (5.2
AU), where the great majority of the asteroids are found. None of the
belt asteroids have retrograde motion. [H76]
(a) A common eye defect in which the
observer cannot
focus clearly on objects at any distance. The cause is usually a
non-spherical cornea. Visual astigmatism may be corrected with a lens
with a suitable degree of cylindrical curvature. [DC99]
The processing of matter through stars. [H76]
(a) Ancient Arabic and medieval alt-azimuth device
comprising two or more
flat, metal, calibrated discs, attached so both or all could rotate
independently. For early navigators and astronomers it acted as
star-chart, compass, clock and calendar. [A84]
(a) The belief that human affairs and people's
personalities and
characters are influenced by (or encoded in) the positions of the
planets. [F88]
see Binary System
An ephemeris of a
Solar-System body in which the tabulated
positions are essentially comparable to catalog
mean places of stars
at a standard epoch. An
astrometric position is obtained by adding to
the geometric position, computed
from gravitational theory, the
correction for light-time. Prior
to 1984, the E-terms of annual
aberration (see Aberration, Annual;
Aberration, E-terms of) were also added to the
geometric position. [S92]
The branch of astronomy that deals with
measuring the
positions of celestial objects, especially stars. Astrometrists
measure parallaxes and proper motions, which allow astronomers to
determine the distances and velocities of the stars. [C95]
Difference in a star's brightness when
measured on two selected wavelengths, in order to determine the star's
temperature. Cooler stars emit more light at longer wavelengths (and
so appear redder than hot stars). Modern methods involve photoelectric
filtering and the UBV system. [A84]
The longitude and latitude of a point on the
Earth relative to the
geoid. These coordinates are
influenced by local gravity
anomalies. see Zenith;
Longitude, Terrestrial;
Latitude, Terrestrial) [S92]
The period from sunset to the time that the Sun
is 18° below
the horizon; or the corresponding period before sunrise. [H76]
(a) Mean distance between the Earth and the Sun:
149,598,500km. [A84]
The science that studies the natural world beyond
the earth. [F88]
(a) The science that studies the physics and
chemistry of
extraterrestrial objects. The alliance of physics and astronomy, which
began with the advent of
spectroscopy, made it possible
to investigate what celestial objects are and not just
where they are. [F88]
The negative of the mean V velocity of a stellar
population. In general, the older the stellar population, the more
negative the V velocity and therefore the greater the asymmetric
drift. The young thin disk has an asymmetric drift of 0 kilometers per
second, whereas the halo has an asymmetric drift of 200 kilometers per
second. [C95]
A violation of symmetry. [F88]
Globular cluster stars, which are found in that
part of the HR diagram that connects the top pf the giant tip with the
horizontal branch. [JJ95]
(a) A term used to describe the observed
decrease in the intrinsic
strength of the color force between quarks as they are brought closer
together. At asymptotically small separations, the quarks are
virtually free. This is in contrast to the electromagnetic force whose
intrinsic strength increases as two charged particles approach each
other. [CD99]
Acronym for After The Bang; usually used in
reference to time elapsed since the big bang. [G99]
(a) Mantle of gases round a star planet or moon,
sometimes even
forming the apparent surface of the body. For a body to retain an
atmosphere depends on the body's gravity, and the temperature and
composition of the gases. The atmosphere of the Earth is, by volume,
78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen (with 1% of other gases); mean
atmospheric pressure at the surface is 10,330 kg/m2, and is also
referred to as atmosphere. [A84]
The gaseous outer layers of the Sun, including,
from the deeper
layers outward, the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the corona. The
atmosphere constitutes those layers of the Sun that can be observed
directly. [H76]
An optical device usually comprising
two thin prisms which can rotate to compensate for the elongation of a
star image caused by the wavelength dependence of the refractive index
of air. [McL97]
Decrease in the intensity of light from a
celestial body due to
absorption and scattering by the Earth's atmosphere. The extinction
increases from the zenith to the horizon and affects short wavelengths
more than long wavelengths, so that objects near the horizon appear
redder than they are at the zenith. [H76]
(a) The smallest component of matter that retains its
chemical
properties. An atom consists of a nucleus and at least one electron. [HH98]
Individual hydrogen atoms that do not belong
to molecules.
In its neutral form (HI), atomic hydrogen consists of a proton and
an electron and generates radio waves that are 21 centimeters
long. In its ionized form (HII), atomic hydrogen is simply a
proton. HII regions look red because a few of the protons capture
electrons, which can radiate red light as they settle into position
around the protons. [C95]
The total number of protons and neutrons in
an atom's
nucleus. For example, oxygen-16 has a mass number of sixteen,
because it has eight protons and eight neutrons. [C95]
(a) A unit of mass used for atoms
and molecules, equal to 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon-12. It
is equal to 1.660 33 × 10-27 kg. [DC99]
In 1960[29] the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics followed
the proposal made a year earlier by the International Union of Pure and
Applied Chemistry that all atomic weights should be based on the
126C scale.
This enabled more isotopes to have integral mass numbers than would have
been possible on the oxygen scale. This reduced the values given on the
previous chemical scale by a factor of 1.000043 and changed the values
of the
Faraday and Avogadro's constant by a similar amount. Values on the physical
scale can be converted to the new scale by multiplying by 0.999685. [JM92]
(a) The number of protons in an atom's nucleus.
This determines
the type of element. For example, hydrogen has an atomic number of
one, so all hydrogen atoms have one proton; helium has an atomic
number of two, so all helium atoms have two protons; and oxygen has an
atomic number of eight, so all oxygen atoms have eight protons. [C95]
Representation of the electron cloud surrounding
an atom. Named by
primary quantum number and shape (i.e., 1s, 2s, 2p). [SEF01]
see Second; Systeme
International [S92]
The theory that matter is made up of atoms that
combine to form molecules. Each chemical element has a particular type
of atom, which may join with like atoms to form molecules of the
element, or with atoms of other elements to form molecules of a
compound. The atom consists of a dense positively charged nucleus
containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons. The number
of protons in the nucleus determines the number and distribution of
the electrons, which are held by the positive charge of the
nucleus. Because the outer electrons form the chemical bonds between
atoms, the chemical properties of an element depend on the electronic
structure of the atom, and therefore also on the number of
protons. The number of neutrons in the nucleus may vary, forming
different isotopes of an element. These cannot usually be separated by
chemical means. [DC99]
Time based on the atomic second (see
Second). Atomic time was
officially adopted 1972 January 1. From 1972 January to 1974 January
1, 3 leap seconds had to be introduced to keep atomic time within 0.7
seconds of Universal Time. [H76]
The mean atomic mass of a particular element in
atomic mass
units. [H76]
The fundamental units of a chemical element. An
atom consists of a nucleus, which may contain
protons and neutrons, and electrons, which occupy shells that
surround the nucleus and are centered on it. [F88]
(a) The reduction of intensity of a
radiation as it
passes through a medium. It includes reductions due to both absorption
and scattering.
In a rocket-borne or satellite-borne telescope,
the ratio of the
expected counting rate to the observed counting rate. [H76]
Position of a rocket with respect to the horizon
or some other
fixed reference plane. [H76]
(a) A mechanical system may be such that its dynamical
evolution causes it to approach a stable end-state. In the phase space
representing the system, the representative point tends to a fixed set
of points called an attractor. The attractor may be a point, a line,
or a fractal. [D89]
A prefix meaning 10-18. [H76]
Having a stellar spectral type of A, that is, hot and
white, like
Sirius and Vega. [C95]
Astronomical Unit
(a) The ejection of an electron from an atom or ion
without the emission of radiation (x-rays or gamma rays). It results
from the de-excitation of an excited electron within the atom. It can
be regarded as the internal conversion of the photon that would
otherwise have been emitted. [DC99]
The amount by which the apparent
semidiameter of a celestial
body, as observed from the surface of the Earth, is greater than the
semidiameter that would be observed from the center of the Earth. [S92]
An O9.5 V runaway star. [H76]
see Capella
An eclipsing binary with an invisible supergiant
companion. The
primary is an extremely luminous A8 Ia supergiant of 30 M A dG5e T Tauri star with a strong ultraviolet
excess. [H76]
In general, binaries with a K supergiant primary and a
main-sequence secondary. [H76]
(a) Spectacular array of light in the night sky,
caused by charged
particles from the Sun hitting the Earth's upper atmosphere. The
aurora borealis is seen in the north of the Northern hemisphere; the
aurora australis in the south of the Southern. [A84]
the ability of certain chemicals to enhance by their
presence the rate of their own production in a sequence of chemical
reactions. Part of the more general class of feedback processes. [D89]
(a) The spontaneous ionization of excited atoms,
ions, or molecules, as in the Auger effect. see Auger Effect;
Ionization [DC99]
see Equinoxes [A84]
A process such as that in which a single ionization
leads to a large number of ions. The electrons and ions produced
ionize more atoms, so that the number of ions multiplies quickly. [DC99]
see Mean Life [H76]
(a) Symbol: NA number of
particles in one mole of a substance. Its value is 6.002 52 ×
1023. [DC99]
Equal volumes of all gases at the same
temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules. It is
often called Avogadro's hypothesis. It is strictly true only
for ideal gases. [DC99]
(6.02 × 1023): The number of
atoms in 12 grams of 12C; by extension,
the number of atoms in a gram-atom (or the number of molecules in a
mole) of any substance. [H76]
The fact that galaxies appear to
"avoid" the Milky Way, and are most numerous in other parts of the
sky. When galaxies were known as spiral
nebulae and their nature
was not yet understood, avoidance was thought by some researchers to
indicate a connection between them and the Milky Way. Now the effect
is understood to be due to dark clouds of dust and gas in our galaxy,
which obscure our view of the Universe beyond in those quarters of the
sky. [F88]
Advanced X-ray Astronomical Facility
A hypothetical spin-0 particle with a very small
mass of 10-5-10-3 eV.
It was postulated in order to provide a natural solution to the
"strong CP problem".
Theoretical straight line through a celestial
body, around which
it rotates. [A84]
Collapse of mass in such
a way that the mass maintains the symmetry of a cylinder. [LB90]
Aseotrope: A mixture of two liquids that
boils without any change in composition. The proportions of components
in the vapor are the same as in the liquid. Azeotropic mixtures cannot
be separated by distillation. [DC99]
(a) Directional bearing around the horizon, measured
in degrees from north (0°). [A84]
A measure of the minor axis of an elliptic
orbital of an electron
according to the Bohr-Sommerfeld theory. [H76]
|