





| N-Magnitude | A magnitude derived from observations made at a wavelength of 10 microns. [H76] |
N Galaxy

| A galaxy with a small, bright, blue nucleus superposed on a considerably fainter red background. (In the Yerkes 1974 system, a galaxy with a small nucleus containing a considerable fraction of the luminosity; N-, less pronounced N galaxies; N+, extreme examples of N galaxies.) Also, a type of radio galaxy having a brilliant, starlike nucleus containing most of the luminosity of the system. N galaxies are compact galaxies, and as a class are intermediate between Seyfert galaxies and quasars in properties of form, color, spectra, redshift, and optical and radio variability. [H76] |
| N Lines | Two green forbidden lines of doubly ionized oxygen [O III]. N1 is at 5007 Å; N2 at 4959 Å. [H76] |
| N Star | (a) Stars of spectral type N are very red stars
similar to M stars
except that bands of C2, CN, and CH are present instead of
those of TiO. N stars are strongly concentrated toward the Galactic
plane. [H76]
|
| Nadir | The point on the celestial sphere diametrically opposite to the zenith. [S92] |
| Naked Singularity | A singularity that will be visible and communicable to the outside world. [H76] |
| nano- | A prefix meaning 10-9. [H76] |
| Nanosecond | A billionth of a second. [LB90] |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration US government body set up in 1958, under which the Space Center at Houston, Texas, and the Space Center at Cape Canaveral, Florida, are responsible for manned and unmanned space flights. [A84] |
| NASDA | National Air and Space Development Agency (Japan). [LLM96] |
| Native Oxide | The silicon dioxide layer which grows in air on the exposed backside surface of a thinned CCD. [McL97] |
| Natural Line Broadening | The broadening of spectral lines resulting from the fact that excited levels have certain mean lives, and these mean lives, by virtue of the uncertainty principle, imply a spread in the energy values. [H76] |
| Natural Philosophy | A term widely employed in the seventeenth century to mean what today is encompassed in the word science. [F88] |
| Natural Selection | Tendency of individuals better suited to their environment to survive and perpetuate their species, leading to changes in the genetic makeup of the species and, eventually, to the origin of new species. see Evolution [F88] |
| Natural Units | Units of length, time, mass, etc. in which the
fundamental constants c
(the speed of light), |
| Nautical Mile | Equals 1.15 statute miles. [F88] |
| N-body Simulations | Computer simulations of the behavior of a large number of bodies under their mutual interactions. In cosmological N-body simulations, the bodies are usually galaxies and the interactions are gravitational. Thus, the computer simulates how a group of galaxies should behave under their mutual gravitational attraction. The law of gravity and the initial positions and velocities of the hypothetical galaxies and other masses are fed into the computer. The computer then calculates the evolution of the system. [LB90] |
| NBS | National Bureau of Standards (USA). [LLM96] |
| Near Zone | The zone of a pulsar within the velocity-of-light radius. [H76] |
| Nebula | (a) The term
"nebula" was previously applied to all kinds of hazy patches in
the sky, many of which are now recognized to be clusters or
galaxies. (The plural is nebulae) [H76]
|
| Nebular Hypothesis | Hypothesis, maintained in the nineteenth and early twentieth century, that the spiral nebulae are not galaxies but are instead whirlpools of gas from which new systems of stars and planets are condensing. Compare Island Universe Theory [F88] |
| Nebular Lines | Lines that originate from forbidden transitions. [H76] |
| Nebular Variable Stars | Also called T Tauri variables, a type of variable star of spectral classification F, G or K (giants above the main sequence on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram) that loses an appreciable proportion of its mass in its (irregular) more luminous periods, and is thus surrounded by volumes of gas and dust. [A84] |
| NEC | Noise Equivalent Charge [LLM96] |
| NEF | Noise Equivalent Flux [LLM96] |
| Negative Hydrogen Ion | H- ion. [H76] |
| Negatron | A negatively charged electron, as opposed to a positron. [H76] |
| NELG | Narrow Emission Line Galaxy |
Neodymium

| A toxic silvery element belonging to the lanthanoid
series of metals. It occurs in association with other
lanthanoids. Neodymium is used in various alloys, as a catalyst, in
compound form in carbon-arc searchlights, etc., and in the glass
industry.
|
Neon

| Element with atomic number 10, and the third most common metal in the Universe. Neon is produced by carbon burning in high-mass stars and released into the Galaxy when they explode. [C95] |
| Neon Burning | The stage in which a star burns neon into oxygen and magnesium. [C95] |
| NEP | Noise Equivalent Power [LLM96] |
| Neptune | (a) Eighth major planet out from the Sun, discovered
in 1846 by
Johann Galle and Louis d'Arrest following predictions calculated by
Urbain Le Verrier. Similar predictions had been made a year earlier by
John Couch Adams but were not followed up. [A84]
|
| Neptunium | A toxic radioactive silvery element of the actinoid
series of metals that was the first transuranic element to be
synthesized (1940). Found on Earth only in minute quantities in
uranium ores, it is obtained as a by-product from uranium fuel
elements.
|
| Nereid | The outer satellite of Neptune (radius 150-250 km). Period about 360 days direct. It has the most eccentric orbit (e = 0.76) of any natural satellite. Discovered by Kuiper in 1950. [H76] |
| Nernst Theorem | All substances have zero entropy at 0 K. (Third law of thermodynamics)[H76] |
| Neumann Lines | In iron meteorites, groups of very fine parallel lines that cross each other at various angles. Irons containing Neumann lines can easily be cleaved in three mutually perpendicular directions. [H76] |
| Neutral Current | A type of reaction between particles subject to the weak nuclear force. In this reaction, all intermediary particles that transmit the forces are electrically neutral, which is the origin of the word "neutral". [LB90] |
| Neutral Current | weak interaction where no change takes place in the charges of the participants. [D89] |
| Neutral Current Reactions | Weak-interaction reactions in which no electric charge is exchanged between the colliding particles. Observation of such reactions in 1973 provided important support for the then-developing gauge theory of the weak interactions. We now know that these reactions are mediated by the exchange of a massive, neutral gauge boson - the Z0. [CD99] |
| Neutral Hydrogen | A hydrogen atom that has a proton and an electron and so is electrically neutral. Neutral hydrogen produces radio waves that are 21 centimeters long. [C95] |
| Neutral Region (solar) | A region where the magnetic field strength approaches zero. Generally, neutral regions occur between regions of opposite polarity. [H76] |
| Neutrino | (a) An electrically neutral, very weakly interacting
particle,
with a rest energy which is either zero or very small. The particle
was predicted in 1931 as a means of reconciling the measurements of
beta decays with the conservation of energy, but it was not directly
detected until 1956. [G97]
|
| Neutrino Bremsstrahlung | The reaction in which an electron scatters from a nucleus, emitting a neutrino-antineutrino pair. [H76] |
| Neutrino Process | Nucleosynthesis induced by neutrinos. It may create fluorine and boron. [C95] |
| Neutron | (a) Uncharged particle in the nucleus of all atoms
except
hydrogen. Through beta decay, a neutron may become a proton and an
electron; the process occurs in reverse during the formation of a
neutron star. [A84]
|
| Neutron Drip | The rapid increase in the abundance of free neutrons that occurs when physical conditions are such that the neutron becomes the stable nucleon with respect to electron capture (as will happen in a degenerate assembly of electrons with sufficiently high Fermi threshold energy). [H76] |
Neutron Excess (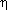 ) )
| The excess of neutrons over protons in an atomic
nucleus. |
| Neutron Lifetime | The time it takes an isolated neutron at rest to disintegrate into other elementary particles, about equal to 15 minutes. [LB90] |
| Neutron Matter | Degenerate matter in which the electron:proton:neutron ratio is about 1:1:8 (or perhaps 1:1:10 or 1:1:12). [H76] |
| Neutron Star | (a) A dead, collapsed star that consists mostly of
neutrons
and is only about 20 kilometers across. Neutron stars are much denser
than white dwarfs. [C95]
|
| New Inflation | (a) The first fully successful version
of the inflationary theory, discovered independently by Andrei Linde
in the Soviet Union, and by Andy Albrecht and Paul Steinhardt in the
U.S. see Inflation; False Vacuum; Decay of the False Vacuum [G97]
|
| New Inflationary Universe | a revised form of the Inflationary Universe model that provides a mechanism to avoid the gross inhomogeneities which result from the theory as originally proposed. [D89] |
| Newton (N) | The SI derived unit of force, equal to the force necessary to give an acceleration of 1 meter per second2 to a mass of 1 kg. N = 105 dynes. [H76] |
| Newton's Constant G | Newton's law of gravitation says that the gravitational for ce between any two bodies is proportional to the product of their masses and decreases as the square of the distance between them. This statement is turned into an equation by inserting the constant G, so the force F = Gmm'/r2. Because all of the particles feel the gravitational force, G is universal, so G can be used to form quantities with dimensions, giving the Planck scale. G is measured by finding the force between two objects of known masses separated by a known distance. [K2000] |
| Newton's Laws | (1) A body remains in a state of rest or uniform motion when left to itself. (2) The net force on a body is equal to the product of its mass and its acceleration. (3) When two bodies interact, the force on the first due to the second is equal and opposite to the force on the second due to the first. [H76] |
| Newton's Laws of Motion | Laws describing the motion of bodies based on the conception of an absolute and immutable space and time; these laws held sway until Einstein's discovery of special relativity. [G99] |
| Newton's Universal Gravitational Constant | the constant that sets the scale of gravitational forces. Its value is independent of the actual constitution of the matter producing the gravitational field.[D89] |
| Newton's Universal Theory of Gravity | Theory of gravity declaring that the force of attraction between two bodies is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Subsequently supplanted by Einstein's general relativity. [G99] |
| Newtonian | A class of reflecting telescope developed by Sir Issac Newton with a paraboloidal primary mirror and a small, plane secondary mirror at 45° to deflect the focus of the primary to a position outside the tube near the top of the telescope. [McL97] |
| Newtonian Cosmology | The simplest cosmological models, including the standard Big Bang models, can be derived in the framework of Newtons classical theory of gravitation, although Birkhoff's theorem from the theory of general relativity is needed to justify the use of Newtonian theory in an infinite medium. [Silk90] |
| Ney-Allen Nebula | An extended infrared source in the Trapezium region of Orion, which shows a strong 10-µ emission feature assumed to result from circumstellar shells of silicate dust. [H76] |
| NGC | New General Catalogue -- A catalogue of 7,840 nebulae, star clusters, and galaxies that was published in 1888 by John Dreyer. [C95] |
Nickel

| A transition metal that occurs naturally as the
sulfide and silicate. It is used as a protective coating (on other
metals) and in the manufacture of various alloys, such as Nichrome and
stainless steel.
|
| NICMOS | Near Infrared Camera for Multi-Object Spectrography [HST] [LLM96] |
| Nicol Prism | A device for producing plane polarized light, consisting of a crystal of calcite cut with a 68° angle, cleaved along the optic axis, and stuck together with a thin layer of Canada balsam. The Canada balsam, which is not birefringent, has the same refractive constant for both ordinary and extraordinary rays (n = 1.66). The latter ray passes through the prism (in calcite n = 1.66). However, the ordinary ray in calcite has a lower refractive constant (n = 1.48) than in the Canada balsam, and suffers total internal reflection at the interface. Nicol prisms are more transparent than Polaroid. [DC99] |
| Nicol Prism | A device made from a split crystal of Iceland spar with which plane-polarized light can be detected. [H76] |
| Nightglow | see Airglow [H76] |
| Night-Sky Light | The faint, diffuse glow of the night sky. It comes from four main sources : airglow, diffuse Galactic light, Zodiacal light, and the light from these sources scattered by the troposphere. [H76] |
Niobium

| |
| NIR | Near InfraRed |
Nitrogen

| (a) Element with atomic number seven and the fourth
most common
metal in the Universe. It formed during hydrogen burning in
main-sequence stars and red giants, via the CNO cycle. [C95]
|
| NLR | Narrow Line Region |
| NLRG | Narrow-Line Radio Galaxy |
| NLS1 | The class of Narrow-Line Seyfert 1 galaxies was first proposed by Osterbrock and Pogge (1985, Ap.J., 297, 166). These objects have permitted linewidths (on the order of 1,000 km/sec) which are much smaller than normal Seyfert 1 galaxies (which have linewidtths on the order of 10,000 km/s). However, they differ from Seyfert 2 galaxies in that their optical spectra show several characteristics normally associated with Seyfert 1 galaxies, such as [OIII]/H_beta < 3, permitted lines somewhat broader than forbidden lines, and either blends of Fe II or very high excitation lines of [Fe VII] or [Fe X], etc. About 10% of Seyfert 1 galaxies may be Narrow-Line Seyfert galaxies. [BFM06] |
NLXG

| Narrow Emission Line X-ray Galaxy |
| NOAO | National Optical Astronomy Observatory (USA). [LLM96] |
| Nobelium | A radioactive transuranic element of the actinoid
series, not found naturally on Earth. Several very short-lived
isotopes have been synthesized.
|
| No-Boundary Proposal | An initial (boundary) condition for the Universe proposed by James Hartle and Stephen Hawking. In this proposal, the mathematics of general relativity is reformulated so that time is replaced by a space-like coordinate, in effect representing the Universe as having 4 space dimensions instead of 3 space dimensions and a time dimension. (In such a formulation, "time" does not have its usual meaning.) Hawking and Hartle suggest that the geometry of this representation of the Universe should be analogous to the geometry of the surface of a sphere, that is, a shape with no edges-hence the name no-boundary proposal. When translated back into ordinary time and space, this suggested boundary condition takes the form of a specific initial condition for the Universe. The no-boundary proposal is formulated within a quantum mechanical calculation of the behavior of the early Universe. [LB90] |
| Node | (a) The point at which a standing wave pattern
intersects the
horizontal axis and at which the wave consequently has zero
amplitude. [H76]
|
| Nodes, Line of | The intersection between the orbital plane of the Moon or a planet and the plane of the ecliptic. [H76] |
| Nodical Month | The interval of time (27.2122 days) between two successive transits of the Moon through its ascending node. (also called Draconic month)[H76] |
| Noether's Theorem | A mathematical theorem that states that for every symmetry of the Lagrangian of a physical system (i.e. for every set of transformations under which the Lagrangian is invariant), there will be some quantity which is conserved by the dynamics of the system. [CD99] |
| No Hair Theorem | (a) Proposed by John Wheeler, it states that the only
properties of matter conserved after entering a black hole are its
mass, its angular momentum and its electrical charge; it thus becomes
neither matter nor antimatter. [A84]
|
| Noise | (a) Sound composed of a random mix of different
frequencies. White noise is a completely random mix over a wide
frequency range; it has a confusing effect on the listener. Pink
noise - random frequencies in a selected range - is often used as
a background to mask other sounds.
|
| Noise Source | An electronic device designed to generate known amounts of radio noise in order to test and calibrate the receivers of radio telescopes. [H76] |
| Non-Baryonic Matter | Material that consists of exotic subatomic
particles. These subatomic particles can move slowly (cold dark
matter) or fast (hot dark matter). Cosmologists who believe in
inflation - or anyone else who thinks the mass density of the Universe
( |
| Non-Coherent Scattering | Absorption of a photon and reemission at a different frequency (as seen by an observer) by scattering atoms. The natural width of the lines, Doppler broadening, and pressure broadening are the main processes that give rise to noncoherent scattering. [H76] |
| Non-Conservative Scattering | Scattering that occurs in the presence of absorption. [H76] |
| Non-Destructive Readout | A means of reading out an infrared array or a CCD with a skipper output in which the output voltage is sampled without resetting the detector. The output voltage can be sampled a large number of times to improve noise performance. [McL97] |
| Non-Euclidean Geometry | Geometry that does not follow the postulates and results of Euclidean geometry. For example, in a non-Euclidean geometry, the sum of the interior angles of a triangle differs from 180 degrees. According to Einstein's general relativity theory, gravity distorts space into a non-Euclidean geometry. [LB90] |
| Non-Gray Atmosphere | A model atmosphere constructed by letting the absorption coefficient vary with frequency. [H76] |
| Non-Linear Optics | This is concerned with the optical properties of matter in intense radiation fields. The induced electromagnetic polarization does not depend linearly on the radiation strength but is severely distorted by the strong field. Optical harmonics, frequency mixing and intensity dependent refractive indices are all produced by this nonlinear response. [D89] |
| Non-Perturbative | Feature of a theory whose validity is not dependent on approximate, perturbative calculations; an exact feature of a theory. [G99] |
| Non-Relativistic Zone | The region far from a pulsar where r 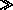 M. [H76] M. [H76]
|
| Non-Thermal Radiation | Radiation emitted by energetic particles for reasons other than high temperature of the source. The spectrum of nonthermal radiation is different from that predicted by Planck's law for a blackbody. [H76] |
| Nordtvedt Effect | A theoretical violation of the principle of equivalence for massive, self-gravitating bodies. [H76] |
| Normal | The perpendicular to a reflecting or refracting surface at the point of incidence of the ray concerned. Angles of incidence, reflection, and refraction are measured between the normal and the incident ray, reflected ray, and refracted ray respectively. A normal ray is one incident perpendicularly on a surface - the angle of incidence is zero. [DC99] |
| Normal Modes | (a) All the characteristic frequencies of an
oscillating body. [H76]
|
| Normalization | A mathematical technique for eliminating divergent terms or for making them converge. [H76] |
| North Point | The point at which the meridian intersects the horizon below the North Celestial Pole. [H76] |
| North America Nebula | An emission nebula (NGC 7000) in Cygnus. [H76] |
| North Galactic Pole | A point in the constellation Coma Berenices where we look perpendicular to and above the Galactic Plane. The nearest bright star to the North Galactic Pole is Arcturus, in the neighboring constellation Bootes. [C95] |
| North Polar Sequence | (a) Or circumpolar stars, comprises those stars which
never set, from the viewpoint of an observer on Earth. [A84]
|
| North Polar Spur | A radio continuum feature extending from the galactic plane to the vicinity of the North Galactic Pole. It is probably about 50-200 pc distant, and is believed to be a supernova remnant. It is also an X-ray source. [H76] |
| North Star | Polaris. [C95] |
| Northern Cross | A group of bright stars in the constellation Cygnus. [H76] |
| Nova | (a) A star that brightens suddenly and to an
unprecedented degree,
creating the impression that a new star has appeared where none was
before. Hence the name, from nova for "new". see Supernova [F88]
|
| NRAO | National Radioastronomy Observatory (USA). [LLM96] |
| NSF | National Science Foundation (USA). [LLM96] |
| NTT | New Technology Telescope [LLM96] |
| Nuclear Chronology | A method of dating an object by measuring how many atomic nuclei have disintegrated and changed into other nuclei. Uranium dating of the earth is an example of nuclear chronology. [LB90] |
| Nuclear Density | The density of an atomic nucleus (about 1014 g cm-3). [H76] |
| Nuclear Disk | A rotating disk of about 106
M |
| Nuclear Forces | (a) There are two kinds of nuclear forces: the strong
nuclear force and the weak nuclear force. These two forces, plus the
gravitational and electromagnetic forces, comprise the four
fundamental forces of nature. The strong nuclear force, which is the
strongest of all four forces, is the force that holds protons and
neutrons together in the atomic nucleus. The weak nuclear force is
responsible for certain kinds of radioactivity; for example, the
disintegration of a neutron into a proton, electron, and
antineutrino. [LB90]
|
| Nuclear Fusion | Process by which the Sun (and other stars) radiates energy. The nucleus of an atom fuses with the nuclei of other atoms to form new, heavier atoms at the same time releasing large amounts of energy. In the Sun, hydrogen atoms are converted into helium by this process, with carbon and nitrogen as intermediates. Cooler stars undergo the proton-proton cycle with a similar result. [A84] |
| Nuclear Matter | Matter in which the numbers of protons and neutrons are roughly equal, as in atomic nuclei. Nuclear matter is probably in a liquid or a solid state. [H76] |
| Nuclear Statistical Equilibrium | Equilibrium with respect to strong and electromagnetic interactions. [H76] |
| Nuclear Time Scale | Time required for a star to evolve a significant distance off the main sequence; the time it takes a star to convert all its available hydrogen into helium. For the Sun, it is 1010 years. (Cf. Kelvin time scale.) [H76] |
| Nucleon | (a) The generic name for the proton and the
neutron. [CD99]
|
Nucleosynthesis

| (a) The transformation of one element or isotope into
another. Nucleosynthesis occurred just after the big bang, but today
most nucleosynthesis takes place in stars - for example, the Sun
presently converts hydrogen into helium. [C95]
|
| Nucleosynthetic Era | The era following the Leptonic Era, between 1 second and 1,000 seconds after the Big Bang, when neutrons were produced and helium and deuterium were synthesized. [Silk90] |
| Nucleus | (a) The central part of an atom, composed of
protons and
neutrons (which are made of quarks) and containing nearly all of each
atom's mass. [F88]
|
| Nucleus (of a comet) | The stellar-appearing frozen core, containing almost the entire cometary mass, in the head of a comet. [H76] |
| Nuclide | A species of atomic nucleus, analogous to the word "isotope" for a species of atom. The word is also used to distinguish between atomic nuclei that are in different energy states. [H76] |
| Null Geodesic | The path of a light ray in curved spacetime. It is characterized by the fact that its tangent U at any point is of zero length: Uµ Uµ = 0. (same as null line) [H76] |
| Null Line | The path, in space-time, of a light ray or other massless object. Space-time distances measured along a null line are zero. (same as null geodesic) [P88] |
| Number-Count Test | A cosmological test that involves counting all galaxies down to a certain limiting magnitude and repeating this procedure for fainter and fainter limiting magnitudes. Deviations from the relation expected in Euclidean space can help ascertain whether the Universe is open or closed. In practice, this test provides a strong constraint on models of galactic evolution and luminosity at past eras. [Silk90] |
| Number Density | Number of particles per cm3 (cf. column density). [H76] |
| Numbers (Dirac): | Big Number Hypothesis: In 1937 Dirac pointed out that the ratio of the largest to the smallest natural units of length, of force and of time, each came to about 1040; a number which he called a cosmological constant; they have subsequently been often referred to as big numbers. Thus
radius of the Universe / radius of an electron
where T is the time taken for light to reach the edge of the Universe and t that required for light to cover a distance equal to the radius of an electron. Furthermore, the ratio of the mass of the Universe to the mass of an average particle of matter comes to about 1079, which is approximately (1040)2; the figure 1079 is also called the Eddington number after the British astronomer Sir Arthur Eddington (1882-1944) who predicted the number of particles in the Universe in the late 1920s. The big number hypothesis indicates that if the fundamental constants are all expressed as dimensionless ratios to rid them of man-made dimensions (e.g. by using units of length, mass and time from the hydrogen atom) the constants will tend to lie within a few orders of magnitude of unity with the notable exception of the gravitational constant G. [JM92] |
| Nutation | (a) Slight but recurrent oscillation of the axis
of the Earth, caused by the Moon's minutely greater gravitational effect on
the Earth's equatorial "bulge". [A84]
|
| Nyquist Sampling | The minimum number of resolution elements required to properly describe or sample a signal, such as a star image, without causing erroneous effects known as aliasing. For electronic imaging, this number is generally taken as 2 pixels across the seeing disk diameter at the half intensity points (FWHM). [McL97] |